当前位置:网站首页>Interprocess communication - shared memory shmat
Interprocess communication - shared memory shmat
2022-07-21 08:20:00 【Kobayashi meow】
Interprocess communication - Shared memory shmat
Three methods of interprocess communication
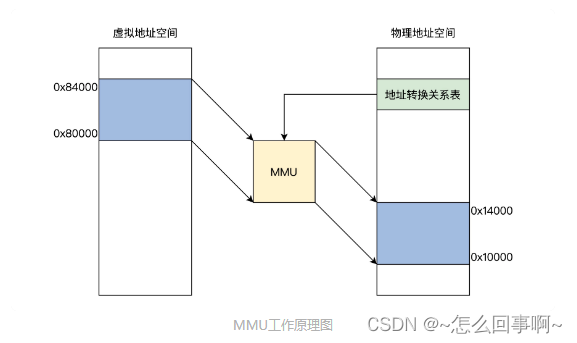
stay linux In the system , Each process has its own virtual space address , adopt MMU Address translation maps virtual addresses to physical addresses , The same virtual address space of each process is mapped to different physical addresses , Each process is independent and isolated from each other in the physical memory space .
If different processes need to communicate with each other , What should I do ? Because different processes are isolated from each other in physical memory , So we need to use third-party tools to complete interprocess communication . In fact, the essence of interprocess communication is to exchange data , There are three ways to exchange data between processes : Through documents 、 Through the kernel 、 Shared memory .
- Through documents :AB The process accesses the same disk file (I/O visit ) Data exchange
- Through the kernel : The user space between processes is independent of each other , But the kernel space is the same , Therefore, the kernel can be used as an intermediary for data exchange
- Shared memory : Virtual addresses between processes are mapped to different physical addresses , If mapping to the same physical address is allowed, data exchange can be carried out

Shared memory features
- Shared memory VS Through documents : Shared memory reads and writes faster
- Shared memory VS Through the kernel : Abandoned the kernel “ The agent ” role , Let two processes communicate directly through a piece of memory . Reduced memory copy ( Copy from user to kernel 、 Copy from kernel to user space ), Less 2 Secondary system call , Improve system performance
- Shared memory disadvantages : Shared memory does not provide a synchronization mechanism , So we need to use other mechanisms to synchronize the orientation of shared memory , This will be done by the programmer . In general, you can use semaphores 、 The mutex 、 File lock, etc , Prevent data from trampling .
Shared memory principle
Shared memory is made up of IPC A special address range created for the process , Appears in the address space of the process , Other processes can connect the same piece of shared memory to their own address space . All processes have access to addresses in shared memory , It's as if they were made up of malloc The distribution is the same . If a process writes data to shared memory , Then other processes will immediately be able to see .
Shared memory usage

establish / Get shared memory shmget
This function is used to create / Get shared memory
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int shmget(key_t key, size_t size, int shmflg);
- key:IPC The key value of the object , It's usually IPC_PRIVATE or ftok Back to key value
- size: Shared memory University , Generally, it is an integer multiple of the physical page
- shmflg:IPC_CREAT: If there is no such thing as key The corresponding segment , Then create a new segment ;IPC_EXCL: if key The specified memory exists and is specified IPC_CREAT, return EEXIST error ;
- Return value : Identifier of shared memory ID
Map shared memory shmat
This function will shmid The identified shared memory is introduced into the virtual address space of the current process
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
void *shmat(int shmid, const void *shmaddr, int shmflg);
- shmid: Shared memory IPC object ID
- shmaddr: if NULL: Shared memory will be attach To a suitable virtual address space , It is recommended to use NULL; Not for NULL: The system will assign an appropriate address according to parameters and address boundary alignment
- shmflg:IPC_RDONLY: Additional read-only permissions , If not specified, the default is read-write permission ;IPC_REMAP: Replace at shmaddr Any existing mapping at : Shared memory segment or memory mapping ;
- Return value : The address of the shared memory segment
Shared memory read / write
When reading and writing shared memory, you should pay attention to the synchronization of shared memory multi process access , In general, you can use semaphores 、 The mutex 、 File lock, etc , Prevent data from trampling .
Unmapping memory shmdt
This function unmaps the memory , Separate the shared memory from the address space of the current process
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int shmdt(const void *shmaddr);
- shmaddr: Shared memory address
Be careful , function shmdt Just decouple the process from shared memory , Decrements the reference count of shared memory by 1, And delete shared memory for . adopt #ipc -m You can view a IPC Object state , among “ The number of connections ” Is the count of references to the shared memory object .
Delete shared memory
See above ,shmdt Just decouple the process from shared memory , Shared memory was not deleted . When the number of shared memory references is not 0, You can call shmctl Of IPC_RMID Command to delete shared memory . Or after the process ends , It will also be deleted .
shmctl obtain / Set shared memory object properties
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int shmctl(int shmid, int cmd, struct shmid_ds *buf);
- shmid: Shared memory objects ID
- cmd:IPC_RMID: Delete the shared memory segment and its associated shmid_ds data structure
- buf: Point to the structure that contains the sharing mode and access rights
- Return value : Successfully returns 0, Failure to return -1
added cmd Can pass man shmct To view the .
producer - Consumer code example
Here is a simple producer - Consumer model , producer producer The process is responsible for writing the data entered by the user to the shared memory , consumer customer The process is responsible for reading out and printing out the shared memory . The following program example uses shared memory variables written_by_you Mark for a read-write synchronization , Ensure that read and write operations are mutually exclusive .
//share.h
#define TEXT_SZ 2048
struct shared_use_st
{
int written_by_you;
char some_text[TEXT_SZ];
};
//customer.c
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include "share.h"
int main()
{
int running = 1;
void *shared_memory = (void *)0;
struct shared_use_st *shared_stuff;
int shmid;
srand((unsigned int)getpid());
shmid = shmget((key_t)1234, sizeof(struct shared_use_st), 0666 | IPC_CREAT);
if (shmid == -1)
{
fprintf(stderr, "shmget failed\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
shared_memory = shmat(shmid, (void *)0, 0);
if (shared_memory == (void *)-1) {
fprintf(stderr, "shmat failed\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("Memory attached at %X\n", (int)shared_memory);
shared_stuff = (struct shared_use_st *)shared_memory;
shared_stuff->written_by_you = 0;
while(running)
{
if (shared_stuff->written_by_you)
{
printf("You wrote: %s", shared_stuff->some_text);
sleep( rand() % 4 );
shared_stuff->written_by_you = 0;
if (strncmp(shared_stuff->some_text, "end", 3) == 0)
{
running = 0;
}
}
}
if (shmdt(shared_memory) == -1)
{
fprintf(stderr, "shmdt failed\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, 0) == -1)
{
fprintf(stderr, "shmctl(IPC_RMID) failed\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("customer exit.\n");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
//producer.c
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include "share.h"
int main()
{
int running = 1;
void *shared_memory = (void *)0;
struct shared_use_st *shared_stuff;
char buffer[BUFSIZ];
int shmid;
shmid = shmget((key_t)1234, sizeof(struct shared_use_st), 0666 | IPC_CREAT);
if (shmid == -1)
{
fprintf(stderr, "shmget failed\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
shared_memory = shmat(shmid, (void *)0, 0);
if (shared_memory == (void *)-1)
{
fprintf(stderr, "shmat failed\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("Memory attached at %X\n", (int)shared_memory);
shared_stuff = (struct shared_use_st *)shared_memory;
while(running)
{
while(shared_stuff->written_by_you == 1)
{
sleep(1);
printf("waiting for client...\n");
}
printf("Enter some text: ");
fgets(buffer, BUFSIZ, stdin);
strncpy(shared_stuff->some_text, buffer, TEXT_SZ);
shared_stuff->written_by_you = 1;
if (strncmp(buffer, "end", 3) == 0)
{
running = 0;
}
}
if (shmdt(shared_memory) == -1)
{
fprintf(stderr, "shmdt failed\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("producer exit.\n");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
Reference material
[1] The embedded C Phonetic self-cultivation , Wang Litao
[2] Dalian University of Technology 《 Embedded software design 》 MOOC
边栏推荐
- 你必须知道的4种 Redis 集群方案及优缺点对比
- shell判断文件是否存在,判断文件大小是否为0
- 海思多媒体芯片选型
- 你还觉得难吗?那就给盘活数据支个招
- thinkphp 实现 MongoDB CURD
- AD活动目录和域网络
- ProSci 14-3-3(磷酸 Ser58)抗体说明书
- Director of Shanghai Bureau of culture and Tourism: safety is the lifeline of culture and tourism, and we are seizing the new track of yuancosmos
- 【29. DFS深度优先】
- POI导入导出小案例
猜你喜欢

ProSci 14-3-3(磷酸 Ser58)抗体说明书
V853开发板硬件资料——RISC-V核E907用户手册

华为摄像机布局

双快门技术
执行程序的三种模式,内存与缓存
![From giving up to mastering, these 13 recommended system papers must be read! [attached data]](/img/79/7a8dafbcdecba2327a7e46a073aaa5.png)
From giving up to mastering, these 13 recommended system papers must be read! [attached data]
Module learning (III) - laser ranging module (tof10120)

Rose pass is being issued!

Go语言中的数据竞争模式

Solve the problem of function name conflict (dlopen, dlsym, dlclose)
随机推荐
5 个骚气满满的项目,诞生了!
stap命令行小技巧(笔记,持续更新)
Overview | comprehensive comparative research on image denoising
多省份用电负荷创历史新高 力保迎峰度夏能源供应安全
鸿蒙3.0发布,多屏融合稳步推进,谷歌却再受重挫
C语言数组详解
5G网络用户4.5亿,5G套餐用户超9亿,为何用户还不愿接受5G?
为什么<keep-alive>组件的exclude或include属性设置无效
Spatial noise reduction and time domain noise reduction
Data competition mode in go language
From giving up to mastering, these 13 recommended system papers must be read! [attached data]
Jay Chou's new album is stolen immediately after its release. How to protect intellectual property rights Those things on the cloud
Apache bench (AB) stress test Overview - from 0 to 1, covering all major use scenarios
海思多媒体芯片选型
从0到1 拿下C语言—程序结构及使用示例
Highly recommended | overview of convolutional neural networks: from basic technology to research prospects
AD活动目录和域网络
【27. 表达式求值(中缀表达式)】
codevs——2750 心系南方灾区
commonJS导出导入