当前位置:网站首页>Multithreading et haute concurrence day09
Multithreading et haute concurrence day09
2022-07-22 11:43:00 【Dream qisun】
Conseils:Après avoir écrit l'article,Le répertoire peut être généré automatiquement,Comment générer un document d'aide à droite
Catalogue des articles
Préface
Notes d'étude personnelles,Pour information seulement!Bienvenue.!
Un.、Extension de plusieurs classes communes de pool de Threads
1.Excutor
public interface Executor {
/** * Executes the given command at some time in the future. The command * may execute in a new thread, in a pooled thread, or in the calling * thread, at the discretion of the {@code Executor} implementation. */
void execute(Runnable command);
}
ExcutorServiceDeExcutor, En outre, le cycle de vie complet de l'exécuteur de tâches a été amélioré . L'implémentation du pool de Threads est ExcutorServiceBasé sur.
public interface ExecutorService extends Executor {
/** * Initiates an orderly shutdown in which previously submitted * tasks are executed, but no new tasks will be accepted. * Invocation has no additional effect if already shut down. * * <p>This method does not wait for previously submitted tasks to * complete execution. Use {@link #awaitTermination awaitTermination} * to do that. * */
void shutdown();
/** * Attempts to stop all actively executing tasks, halts the * processing of waiting tasks, and returns a list of the tasks * that were awaiting execution. * <p>This method does not wait for actively executing tasks to * terminate. Use {@link #awaitTermination awaitTermination} to * do that. * @return list of tasks that never commenced execution */
List<Runnable> shutdownNow();
boolean isShutdown();
boolean isTerminated();
boolean awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException;
/** * Submits a value-returning task for execution and returns a * Future representing the pending results of the task. The * Future's {@code get} method will return the task's result upon * successful completion. */
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
<T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result);
Future<?> submit(Runnable task);
......
......
}
2.CallableInterface
Cette interface est compatible avec RunnableSimilaire, Il peut être fileté , Mais il y a des résultats .
/** * A task that returns a result and may throw an exception. * Implementors define a single method with no arguments called * {@code call}. * * <p>The {@code Callable} interface is similar to {@link * java.lang.Runnable}, in that both are designed for classes whose * instances are potentially executed by another thread. A * {@code Runnable}, however, does not return a result and cannot * throw a checked exception. * * <p>The {@link Executors} class contains utility methods to * convert from other common forms to {@code Callable} classes. * * @see Executor * @since 1.5 * @author Doug Lea * @param <V> the result type of method {@code call} */
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Callable<V> {
/** * Computes a result, or throws an exception if unable to do so. * * @return computed result * @throws Exception if unable to compute a result */
V call() throws Exception;
}
- Oui.Callable,C'est exact.RunnableA été étendu, C'est exact.CallableAppel de,Peut avoir une valeur de retour:
public class Day08 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
Callable<String> c = new Callable() {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
return "Hello Callable";
}
};
ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Future<String> future = service.submit(c); //Asynchrone
System.out.println(future.get());//Blocage
service.shutdown();
}
}
3.Future
Stocker les résultats futurs de l'exécution :
FutureTask -> Future+Runnable
CompletableFuture:Plusieurs peuvent être gérésFutureLes résultats de, Les tâches peuvent être combinées de diverses façons , Quels sont les résultats de toutes les tâches à accomplir après ? Et ce qu'il faut faire une fois la tâche terminée ?Attendez un peu!:
public class Day08 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
long start, end;
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
CompletableFuture<Double> futureTM = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->priceOfTM());
CompletableFuture<Double> futureTB = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->priceOfTB());
CompletableFuture<Double> futureJD = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->priceOfJD());
CompletableFuture.allOf(futureTM, futureTB, futureJD).join();
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->priceOfTM())
.thenApply(String::valueOf)
.thenApply(str-> "price " + str)
.thenAccept(System.out::println);
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("use completable future! " + (end - start));
try {
System.in.read();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static double priceOfTM() {
delay();
return 1.00;
}
private static double priceOfTB() {
delay();
return 2.00;
}
private static double priceOfJD() {
delay();
return 3.00;
}
private static void delay() {
int time = new Random().nextInt(500);
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(time);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.printf("After %s sleep!\n", time);
}
}
2.、Pool de Threads
1.ThreadPoolExecutor
ThreadPoolExcutorDeAbstractExcutorService. Le manuel d'Ali stipule que les pools de Threads doivent être personnalisés :


Définir manuellement un pool de Threads ,Voici un exemple de code::
public class T05_00_HelloThreadPool {
static class Task implements Runnable {
private int i;
public Task(int i) {
this.i = i;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Task " + i);
try {
System.in.read();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Task{" +
"i=" + i +
'}';
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutor tpe = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 4,
60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(4),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
tpe.execute(new Task(i));
}
System.out.println(tpe.getQueue());
tpe.execute(new Task(100));
System.out.println(tpe.getQueue());
tpe.shutdown();
}
}
Thread Pool Internal mainteneur two collections , Un fil de stockage, une autre tâche de stockage : Logiquement, cela peut être compris comme suit ( En fait, l'entretien interne est une référence )
Thread Pool7Paramètres:
int corePoolSize Nombre de fils de base, Le thread Core ne participe généralement pas au retour du système d'exploitation ( Temps libre supérieur à la durée de vie )
int maximumPoolSize Nombre maximum de fils, Le nombre maximum de Threads qui peuvent être activés lorsque des Threads supplémentaires sont nécessaires, y compris les Threads Core
long keepAliveTime Durée de vie, Le thread est inactif depuis longtemps( Sous réserve de la durée de vie ), Retour au système
TimeUnit unit L'unité de temps de survie , Ça peut être une seconde 、Milliseconde, etc.
BlockingQueue workQueue File d'attente des tâches
ThreadFactory threadFactory Thread Factory:

Il n'y a qu'une seule façon.,Est de créer un thread, Le paramètre doit être .
Par exemple:Executors.defaultThreadFactory() Par défautdefaultThreadFactoryEst une réalisationThreadFactoryClasse d'usine pour:
Par défautdefaultThreadFactoryEst une réalisationThreadFactoryClasse d'usine pour:
/** * The default thread factory */
static class DefaultThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
private static final AtomicInteger poolNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final ThreadGroup group;
private final AtomicInteger threadNumber = new AtomicInteger(1);
private final String namePrefix;
DefaultThreadFactory() {
SecurityManager s = System.getSecurityManager();
group = (s != null) ? s.getThreadGroup() :
Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
namePrefix = "pool-" +
poolNumber.getAndIncrement() +
"-thread-";
}
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread t = new Thread(group, r,
namePrefix + threadNumber.getAndIncrement(),//Spécifier le nom du fil
0);
if (t.isDaemon())
t.setDaemon(false);// Spécifiez que le thread n'est pas un thread démon
if (t.getPriority() != Thread.NORM_PRIORITY)
t.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);// Définir la priorité du thread à la priorité normale
return t;
}
}
Vous pouvez aussi définir vous - même un,RéalisationThreadFactoryUsine d'interface, Pour générer et vouloir des fils .
- RejectedExecutionHandler handler Politique de rejet:Quand la file d'attente est pleine、 Et tous les fils ( Thread maximum atteint )Tout est occupé, Exécuter la politique de rejet lorsque la tâche est ajoutée à nouveau .JDK Quatre politiques de refus sont disponibles par défaut ,Bien sûr, vous pouvez aussi personnaliser.

2.Scénario d'application de la politique de rejet par défaut
UtiliserDiscardOldest:Je vois.Task{i=2}A été jeté. UtiliserAbort:Lancer une exception
UtiliserAbort:Lancer une exception
UtiliserDiscardPolicy:Ne pas lancer d'exception,Mais pas d'exécution
UtiliserCallerRun: Parmain Le thread est programmé par mainExécution du thread
Il s'agit généralement d'une politique de rejet personnalisée , Par exemple, enregistrer l'information à Kfaka、MQAttendez., Faites le journal avant de le traiter , Lorsqu'il y a un grand nombre de tâches non traitées dans le journal , Il est temps d'ajouter la machine pour améliorer les performances .
Excutors Une usine qui peut être considérée comme un pool de Threads , Utilisé pour produire une grande variété de pools de Threads .
3.JDKMise en œuvre par défaut fournie
SingleThreadPool:Il n'y a qu'un seul thread dans le pool de Threads, On peut s'assurer que les tâches sont exécutées séquentiellement .
public class T07_SingleThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService service = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
for(int i=0; i<5; i++) {
final int j = i;
service.execute(()->{
System.out.println(j + " " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
}
}
}
Pourquoi avoir un pool de Threads avec un seul thread ? Le pool de Threads a une file d'attente de tâches , Avec une gestion complète du cycle de vie, etc .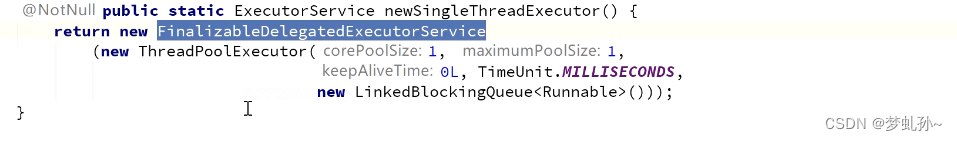
CachedThreadPool: Le nombre de fils de base est nul 、Le nombre maximum de fils estint Valeur maximale du type ,UtiliserSynchronousQueueFile d'attente, L'usine et la politique de rejet utilisent la valeur par défaut . Quand le fil n'est pas libre , En gros, une tâche commence par un fil (SynchronousQueue Est une capacité manuelle vide Queue Une tâche doit avoir un thread à enlever , Sinon, le thread qui soumet la tâche est bloqué )Caractéristiques:: Une mission doit être exécutée immédiatement .
Exemple de code:
public class T08_CachedPool {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
System.out.println(service);
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
service.execute(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
}
System.out.println(service);
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(80);
System.out.println(service);
}
}
FixedThreadPool:Nombre fixe de fils
Comment choisir un scénario : Disponible en cas de forte fluctuation de la valeur de crête de la tâche Cached、 Quand on sait combien de fils il faut hold Utilisation pendant le séjour Fixed.

Voici un exemple de code::
public class T09_FixedThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
getPrime(1, 200000);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
final int cpuCoreNum = 4;
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(cpuCoreNum);
MyTask t1 = new MyTask(1, 80000); //1-5 5-10 10-15 15-20
MyTask t2 = new MyTask(80001, 130000);
MyTask t3 = new MyTask(130001, 170000);
MyTask t4 = new MyTask(170001, 200000);
Future<List<Integer>> f1 = service.submit(t1);
Future<List<Integer>> f2 = service.submit(t2);
Future<List<Integer>> f3 = service.submit(t3);
Future<List<Integer>> f4 = service.submit(t4);
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
f1.get();
f2.get();
f3.get();
f4.get();
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
}
static class MyTask implements Callable<List<Integer>> {
int startPos, endPos;
MyTask(int s, int e) {
this.startPos = s;
this.endPos = e;
}
@Override
public List<Integer> call() throws Exception {
List<Integer> r = getPrime(startPos, endPos);
return r;
}
}
static boolean isPrime(int num) {
for(int i=2; i<=num/2; i++) {
if(num % i == 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
static List<Integer> getPrime(int start, int end) {
List<Integer> results = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=start; i<=end; i++) {
if(isPrime(i)) results.add(i);
}
return results;
}
}
Comparaison entre parallélisme et concurrence :concurrent vs parallel
Le parallélisme est un sous - ensemble de la concurrence, Et fait référence à la soumission des tâches , Parallélisme signifie l'exécution d'une tâche ,FixedThreadPool Est capable d'exécuter des tâches en parallèle .
ScheduledThreadPool:Pool de Threads de tâches programmées,Peut être utilisé pour effectuer des tâches programmées.DelayedWorkQueue Vous pouvez spécifier combien de temps après l'exécution .
Voici un exemple de code::
public class T10_ScheduledThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScheduledExecutorService service = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(4);
service.scheduleAtFixedRate(()->{
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}, 0, 500, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
4.Exemple de définition d'une politique de rejet

Doit être réaliséRejectedExecutionHandlerInterface,Voici un exemple de code::
public class T14_MyRejectedHandler {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService service = new ThreadPoolExecutor(4, 4,
0, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(6),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new MyHandler());
}
static class MyHandler implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
//log("r rejected")
//save r kafka mysql redis
//try 3 times
if(executor.getQueue().size() < 10000) {
//try put again();
}
}
}
}
边栏推荐
- 3 亿
- 你为什么会做测试/开发程序员?各路伙伴描述......
- Paper sharing, target detection, image segmentation, supervised learning, etc
- viewport缩放方法,解决移动端自适配
- Why do you work as a test / development programmer? Description of all partners
- PHP利用Redis 事务实现商品秒杀
- Didi was fined 8.026 billion yuan. Musk made toys with Barbie dolls. Dall-e invited millions of people to join the test. Today, more new things are here
- TZC 1283: simple sort - quick sort
- LeetCode刷题--点滴记录021
- Redis的主从复制
猜你喜欢

图解BERT、ELMo等 | NLP迁移学习开端
J9数字论:什么是 DAO?DAO 的起源是什么

Leetcode skimming -- bit by bit record 021

尾递归调用过程梳理

grafana 监控 node

MySQL insert ignore and replace into

删除文件夹中的相邻但名称不同的文件 && 适应于神经网络训练时的标签名称和图像名称相对应的情况

即看即用 && Reduction Ops && Pytorch官方文档总结 && 笔记 (五)

Human resource management software makes every employee's records within reach

Basic configuration of BGP
随机推荐
Pyinstaller packaging & problem solving about enum34 & reduced version
Leetcode skimming -- bit by bit record 021
[learning notes] take you to learn 01trie from 0
MySQL prefix index
查找和绘制轮廓(findContours and drawContours)&& 图像轮廓 (一) && cv2.boundingRect and cv2.rectangle
How can CIOs avoid stepping on the pit in the digital transformation of B2B enterprises
Apple lost 340million Yuan due to bad keyboard. SpaceX took the order. Webb's successor, meta, sued meta. Today, more new things are here
Tail recursive call process sorting
[brother hero July training] day 21: the smallest number in infinite concentration
LeetCode刷题--点滴记录020
Leetcode skimming -- drip record 020
A detail of MySQL varchar prefix index
Is the account of flush safe? How much is the Commission for opening an account at CITIC Securities
30出头成为复旦博导,陈思明:敲代码和写诗,我两样都要
即看即用 && 数学操作 ( Math operations) && Pytorch官方文档总结 && 笔记 (五)
(pc+wap) dream weaving template protective mask website
“洗钱”
flask 启动函数返回值的剖析
Routing policy-
基于SSM+MySQL+Bootstrap的在线教育课程课堂管理系统