当前位置:网站首页>Scala 高阶(八):集合内容汇总(下篇)
Scala 高阶(八):集合内容汇总(下篇)
2022-07-20 13:23:00 【百思不得小赵】
大家好,我是百思不得小赵。
创作时间:2022 年 7 月 18 日
博客主页: 点此进入博客主页
—— 新时代的农民工
—— 换一种思维逻辑去看待这个世界
今天是加入CSDN的第1234天。觉得有帮助麻烦点赞、评论、️收藏
在上一篇集合的分享中,讲解了Scala中集合的基本概述以及常用集合的基本操作,本次住要分享Scala中集合更高级的操作。
一、集合常用函数
基本操作
- 获取集合长度和大小:线性集合
length,所有集合都有size - 循环遍历:
for (elem <- collection) - 迭代器:
for (elem <- collection.iterator) - 生成字符串:
list.toString / mkString - 判断包含:
list.contains()
代码实操:
// 创建集合
val list = List(12,21,98,78,65,90)
// 长度
println(list.length)
// 大小
println(list.size)
// 遍历
list.foreach(println)
for (elem <- list){
println(elem)
}
for (elem <- list.iterator){
println(elem)
}
// 生成字符串
println(list.mkString("-"))
// 判断包涵
println(list.contains(12))
衍生集合
获取集合的头
head,除过头之外的都是尾tail集合最后一个数据
last,除过最后一个元素的初始数据init反转
reverse取前(后)n 个元素
take(n) takeRight(n)去掉前(后)n 个元素
drop(n) dropRight(n)并集
list1.union(list2)Set做并集的话会进行去重操作。交集
list1.intersect(list2)差集
list1.diff(list2)拉链
list1.zip(list2)将两个集合对应位置的元素进行配对成一个二元组,大小不匹配会丢掉其中一个集合不匹配的多余部分。滑窗.
list.sliding(n, step = 1)框住特定个数元素,方便移动和操作,得到的是一个迭代器,进行遍历输出结果。步长:当前窗口每次滑动的范围,窗口之间相隔的距离为滑动步长
代码实操:
val list1 = List(12, 34, 56, 32, 24, 45)
val list2 = List(45, 23, 89, 97, 56, 36)
// 头
println(list1.head)
// 尾
println(list1.tail)
// 最后一个元素
println(list1.last)
// 除过最后一个元素
println(list1.init)
// 反转
println(list1.reverse)
// 前(后)n 个元素
println(list1.take(2))
println(list1.takeRight(4))
// 去掉前(后)n 个元素
println(list1.drop(1))
println(list1.dropRight(1))
// 交集
println(list1.intersect(list2))
// 并集
println(list1.union(list2))
// 差集
println(list1.diff(list2))
// 拉链
println(list1.zip(list2))
// 滑窗
println(list1.sliding(3, 2).foreach(println))
简单计算函数
- 求和
sum求乘积product最大值min最小值max maxBy(函数)可以传入一个函数来获取元素返回比较依据的值。元组默认判断第一个元素进行比较,可以修改比较规则使用第二个元素进行判断。- 排序
sorted默认从小到大排序,从大到小排序list.sorted(Ordering[Int].reverse) sortBy(函数)对一个属性或多个属性进行排序,传入隐式参数逆序排序sortBy(函数)(Ordering[Int].reverse)sortWith(比较规则)基于函数的排序,通过一个 comparator 函数,实现自定义排序的逻辑。
实操代码:
object Test_SimpleFunction {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 创建集合
val list = List(12, 90, 45, 34, 23, 65)
val list2 = List(("a", 1), ("b", 4), ("c", 5), ("d", 2), ("e", 9))
// 求和
println(list.sum)
// 求乘积
println(list.product)
// 最大值
println(list.max)
println(list2.maxBy((tuple: (String, Int)) => tuple._2))
println(list2.maxBy(_._2))
// 最小值
println(list.min)
println(list2.minBy(_._2))
// 排序
// 默认从小到大排列
val sorted = list.sorted
println(sorted)
// 从大到小排列
println(list.sorted.reverse) // 效率太低
// 传入隐式参数排序 改变排序规则 默认从小到大
list.sorted(Ordering[Int].reverse)
println(list2.sortBy(_._2))
println(list2.sortBy(_._2)(Ordering[Int].reverse))
// sortWith
println(list.sortWith( (a: Int,b: Int) => a < b ))
println(list.sortWith( (a,b) => a < b ))
println(list.sortWith( _<_ ))
}
}
高级计算函数
- 数据处理的核心为两个方面:规约和映射。
Map操作:
- 过滤
filter(过滤条件):遍历一个集合并从中获取满足指定条件的元素组成一个新的集合 - 映射
map(自定义映射函数):将集合中的每一个元素映射到某一个函数 - 扁平化
flatten将集合中集合元素拆开,去掉里层集合,放到外层中来. - 扁平映射
flatMap(). 相当于先进行map操作,在进行flatten操作 - 分组
groupBy(分组规则)按照指定的规则对集合的元素进行分组
Reduce操作:
- 简化/规约
reduce对所有数据做一个处理,规约得到一个结果. - 折叠
fold给定一个初始值,从弟一个元素开始计算
实操代码:
val list = List(12, 23, 78, 65, 34)
// 过滤 选取偶数
println(list.filter((elem: Int) => elem % 2 == 0))
// 简化
println(list.filter(_ % 2 == 0))
// 狭义上的Map操作,把每一个元素做一个转化得到新的集合,相当于集合的映射关系
// 每个元素️2
list.map(elem => elem * 2)
// 扁平化
val newList = List(List(1, 2, 3), List(4, 5, 6), List(7, 8, 9))
println(newList.flatten)
// 扁平映射
// 将一组字符串进行分词,并保存成单词的列表
val strings = List("hello world", "hello scala", "hello java")
// 分词
val splitList = strings.map(string => string.split(" "))
// 打散 扁平化
println(splitList.flatten)
println(strings.flatMap(_.split(" ")))
// 分组 groupBy
// 分成奇偶两组
println(list.groupBy(_ % 2))
println(list.groupBy(data => if (data % 2 == 0) "偶数" else "奇数"))
val wordList = List("asd", "cdffd", "bfrf", "ascd")
println(wordList.groupBy(_.charAt(0)))
val list = List(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
// reduce
println(list.reduce(_ + _))
println(list.reduceLeft(_ + _))
val list2 = List(3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 80)
println(list2.reduce(_ - _))
println(list2.reduceLeft(_ - _))
// 底层由递归实现
println(list2.reduceRight(_ - _)) //3 - (4 - (5- (7- (8-90))))
//fold
println(list.fold(10)(_ - _)) // 10-1-2-3-4-5
println(list.foldLeft(10)(_ - _))
println(list.foldRight(11)(_ - _))
WordCount案例
案例需求
单词计数:将集合中出现的相同的单词,进行计数,取计数排名前三的结果
分析过程
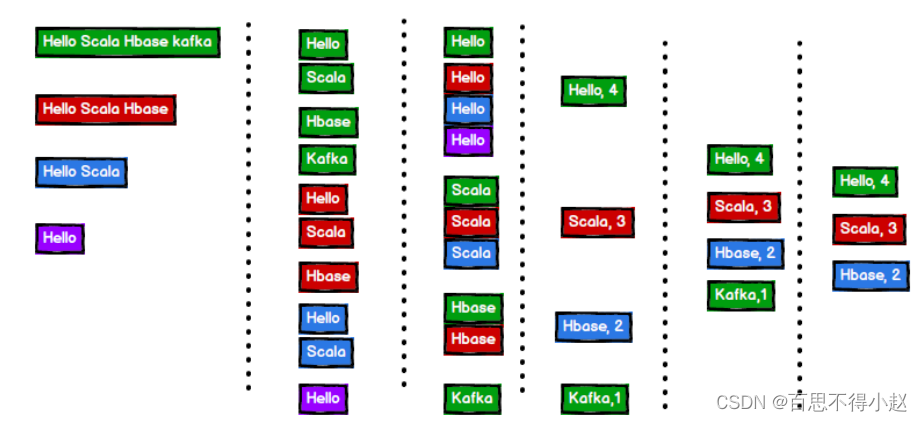
实操代码:经典版本的wordCount
object Test_CommonWordCount {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 创建单词集合
val strings = List(
"hello",
"hello world",
"hello scala",
"hello scala spark",
"hello scala spark flink"
)
// 对字符串进行拆分
val wordList = strings.flatMap(_.split(" "))
// 相同单词分组
val groupMap = wordList.groupBy(word => word)
// 对分组后List取长度,得到单词的个数
val countMap = groupMap.map(kv => (kv._1, kv._2.length))
// 将map转换为List , 通过count进行排序 取前三
val sortList = countMap.toList
.sortWith(_._2 > _._2)
.take(3)
println(sortList)
}
}
复杂版的wordCount
object Test_ComplexWordCount {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 创建单词集合
val tupleList = List(
("hello", 1),
("hello world", 3),
("hello scala", 4),
("hello scala spark", 7),
("hello scala spark flink",5)
)
// 解法一:直接展开为普通版本
val stringList = tupleList.map(
kv => {
(kv._1.trim + " ") * kv._2
}
)
val wordCountList = stringList
.flatMap(_.split(" "))
.groupBy(word => word)
.map(kv => (kv._1, kv._2.length))
.toList
.sortBy(_._2)(Ordering[Int].reverse)
.take(3)
println(wordCountList)
// 解法二:基于预统计的结果进行转换
// 将字符串打散为单词
val preCountlist=tupleList.flatMap(
tuple => {
val tuples = tuple._1.split(" ")
.map(word => (word, tuple._2))
tuples
}
)
// 对二元组进行单词进行分组
val preCountMap = preCountlist.groupBy(tuple => tuple._1)
// 叠加每个单词统计的个数值
val countMap = preCountMap.mapValues(
tupleList => tupleList.map(_._2).sum
)
// 转换成List 排序输出
val countList = countMap.toList
.sortWith(_._2 > _._2)
.take(3)
println(countList)
}
}
二、队列
Scala 也提供了队列(Queue)的数据结构,队列的特点就是先进先出。进队和出队的方法分别为 enqueue 和 dequeue。
实操代码:
// 创建 可变队列
val queue = new mutable.Queue[String]()
// 入队操作
println(queue.enqueue("a", "b", "c"))
// 出队操作
println(queue)
println(queue.dequeue())
println(queue)
println(queue.dequeue())
println(queue)
// 创建不可变的队列
val queue2 = Queue("q","b","c")
// 入队列
val queue3 = queue2.enqueue("d")
println(queue3)
// 出队
val dequeue = queue2.dequeue
println(dequeue)
三、并行集合
Scala 为了充分使用多核 CPU,提供了并行集合(有别于前面的串行集合),用于多核环境的并行计算。
实操代码:
object Test_Parallel {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 串行
val result = (1 to 100).map(
x => Thread.currentThread().getName
)
println(result)
// 并行计算
val result2 = (1 to 100).par.map(
x => Thread.currentThread().getId
)
println(result2)
}
}
本次Scala集合总结分享到这里就结束了,希望对大家学习Scala语言有所帮助!!!
边栏推荐
- How much do you know about the questions often asked by redis in Alibaba's interview?
- 水调歌头·明月几时有
- 六石管理学:流程只是便于推脱责任,对解决问题无帮助
- Hj76 nikochus theorem
- 二.uni-app页面基础[新建文件规范、页面生命周期]
- Repeaters, hubs, bridges, switches, routers
- When will the moon appear
- Learning canoe from scratch (16) -- graphics
- Google 為造芯再掀“搶人大戰”,英特爾 17 年老將加入
- Control the operation of the test module through the panel in canoe (Advanced)
猜你喜欢

GCC getting started manual
Hand rolling third person character controller - unity makes soul game notes 01

Google lance une autre bataille pour construire des noyaux, rejoignant Intel, un vétéran de 17 ans
MySQL Basic (Multi - table query, transaction)

Klocwork部署的安全最佳实践
Automation sequences of canoe simulation functions

ProSci 抗CD22抗体Epratuzum28流式细胞术展示
CANoe的数据回放(Replay Block),还是要结合CAPL脚本才能说的明白

水调歌头·明月几时有

亮点抢先看!2022开放原子全球开源峰会定于7月25-29日在北京举办
随机推荐
Learning canoe from scratch (16) -- graphics
网易游戏 Flink SQL 平台化实践
docker清理缓存脚本怎么写
When will the moon appear
MySQL Foundation (multi table query, transaction)
十年烧光1300亿,垂直电商终将走进历史尘埃
Google 為造芯再掀“搶人大戰”,英特爾 17 年老將加入
mybats中xml参数类型的设置
【漏洞复现】Apache Log4j2 远程代码执行漏洞
windows安全加固--关闭非必要端口
sql 盲注
Chapter3 : Fighting COVID-19 with Artificial Intelligence
HJ107 求解立方根
Latex笔记
Recommend 5 powerful tools for data visualization
这款IDE插件3.0让你成为公司最懂安全的程序员
Limit the input type and length in the input box
Control the operation of the test module through the panel in canoe (Advanced)
HJ107 solve cube root
Hj17 coordinate movement
