当前位置:网站首页>Binary tree OJ question, IO question
Binary tree OJ question, IO question
2022-07-22 16:42:00 【Placideo】
Binary tree OJ topic : Number of binary tree nodes / Number of leaf nodes 、 Find the number of binary trees k The number of layer nodes 、 Find a binary tree with a value of x The node of 、 Find the depth of the binary tree 、 Single valued binary trees 、 Same tree 、 Symmetric binary tree 、 Another subtree 、 Construction and traversal of binary tree (IO type )、 The former sequence traversal 、 In the sequence traversal 、 After the sequence traversal 、 Determine whether a binary tree is a complete binary tree
1. Number of binary tree nodes / Number of leaf knots --TreeSize
// The two methods
// Law 1.( Initial method )
int count = 0;// Empty it before each use
void TreeSize1(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
++count;
TreeSize1(root->left);
TreeSize1(root->right);
}
// Law 2.( Optimize )
int TreeSize2(BTNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 :
TreeSize2(root->left) + TreeSize2(root->right) + 1;
}
// Advanced
// Find the number of leaf nodes of the tree
int TreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (root->left== NULL && root->right == NULL)
return 1;
return TreeLeafSize(root->left) + TreeLeafSize(root->right);
}
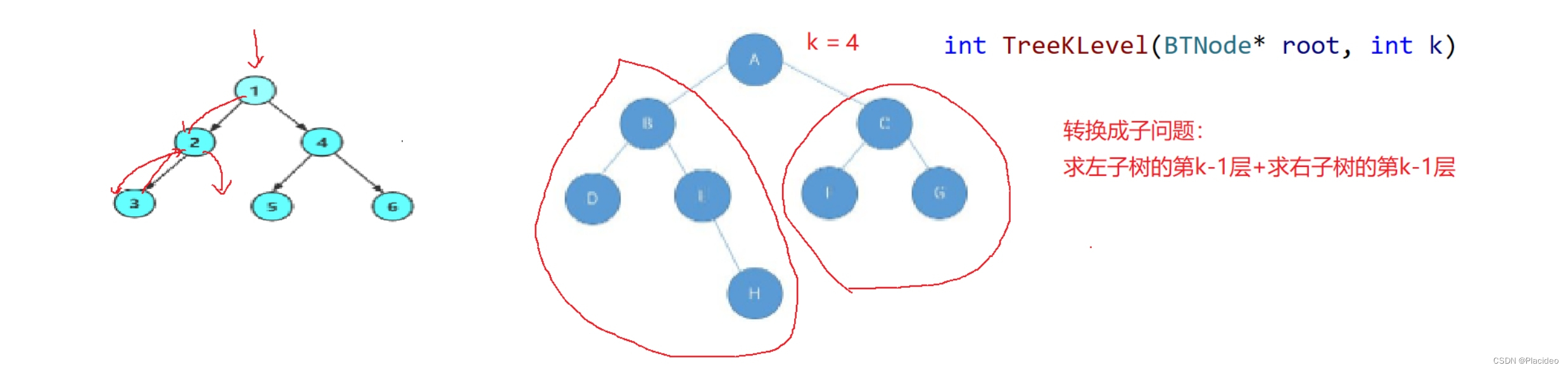
2. Please k The number of layer nodes --TreeKLevel
int TreeKLevel(BTNode* root, int k)
{
assert(k >= 1);
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (k == 1)
return 1;
return TreeKLevel(root->left, k - 1)
+ TreeKLevel(root->right, k - 1);
}
3. The binary tree lookup value is x The node of --TreeFind
// The binary tree lookup value is x The node of
BTNode* TreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
if (root->data == x)
return root;
BTNode* ret1 = TreeFind(root->left, x);
if (ret1)
return ret1;
BTNode* ret2 = TreeFind(root->right, x);
if (ret2)
return ret2;
return NULL;
}
4. Find the depth of the binary tree --TreeDepth
int TreeDepth(BTNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return 0;
}
else if(root!=NULL)
{
int leftDepth=TreeDepth(root->left)+1;
int rightDepth=TreeDepth(root->right)+1;
return leftDepth>rightDepth? leftDepth:rightDepth;
}
}
5. Single valued binary trees

// Law 1.
bool flag= true;
void PreOrderCompare(struct TreeNode* root, int val)
{
if(root==NULL||flag==false)
return ;
if(root->val !=val)
{
flag=false;
return;// There is one false It can be explained that it is not a single valued binary tree , You can just quit , No more traversal
}
PreOrderCompare(root->left,val);
PreOrderCompare(root->right,val);
}
bool isUnivalTree(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL)// First judge whether it is an empty tree
return true;
flag=true;//OJ Use global variables carefully , Static variables , Remember to reset
PreOderCompare(root,root->val);
return flag;
}
// Law 2.
bool isUnivalTree (struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL)
return true;
if(root->left&& root->left->val!=root->val)
return fasle;
if(root->right&&root->right->val!=root->val)
return fasle;
return isUnivalTree(root->left)&&isUnivalTree(root->right);
}
6. Same tree
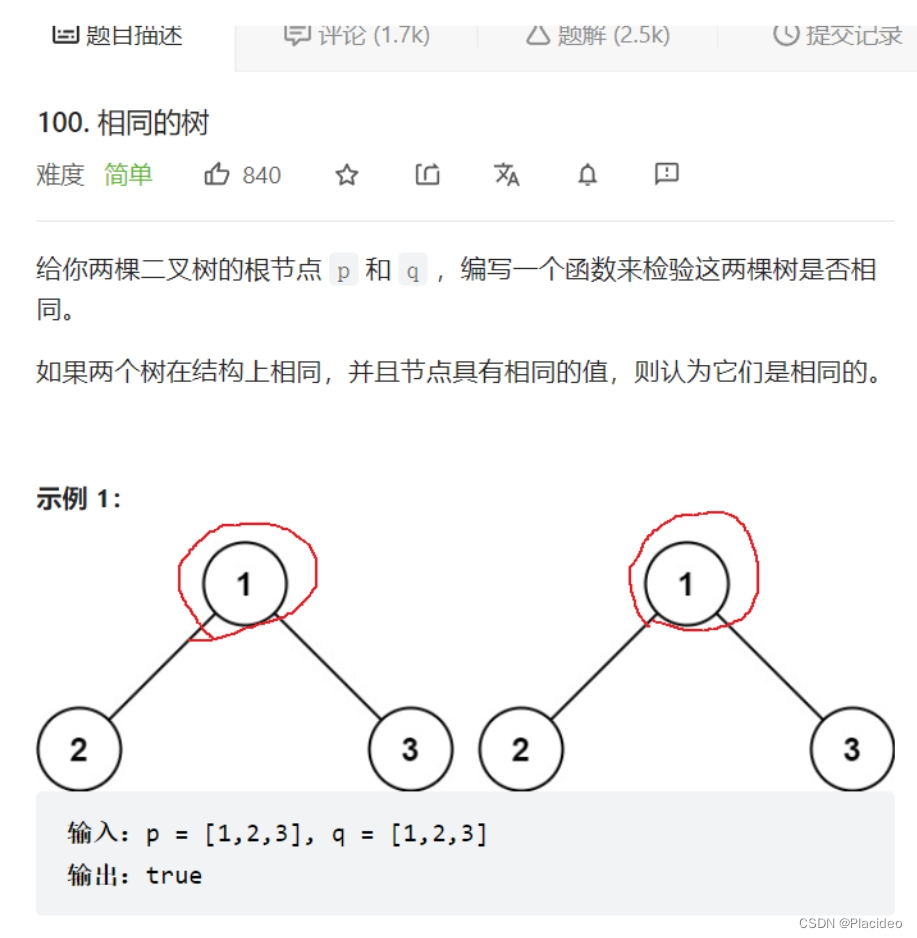
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q)
{
if(p==NULL&&q==NULL)// Both are empty
return true;
if(p==NULL||q==NULL)// There is only one blank
return false;
if(p->val!=!q->val)// Neither of the two here will be empty
return fasle;
// If root->val identical , Then enter the left and right subtree comparison
return isSameTree(p->left,q->right)&&isSameTree(p->right,q->right);
}7. Symmetric binary tree

Ideas : from Same tree Popularize Just put one of them root->left->val And another root->right->val Just compare . First judge whether the first root is NULL, If not for NULL, Then its subtree is divided into left and right subtrees to judge whether it is symmetrical -- Similar to the code of the same subtree .
bool isSymmetricSubTree(struct TreeNode* root1, struct TreeNode* root2)// Subtree symmetry
{
if(root1==NULL&&root2==NULL)// Are they the same NULL
return true;
if(root1==NULL|| root2==NULL)// One is empty , One is not empty , be false;
return false;
if(root1->val!=root2->val)// It's not empty. , But the value is different , Also for the false;
return false;
// It's not empty. , Same value , Then continue to compare subtrees
return isSymmetricSubTree(root1->left,root2->right)&&
isSymmetricSubTree(root1->right,root2->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root)// Symmetric tree
{
if(root ==NULL)// First judge whether the first root is empty
return true;
return isSymmetricSubTree(root->left,root->right);
}8. Another subtree
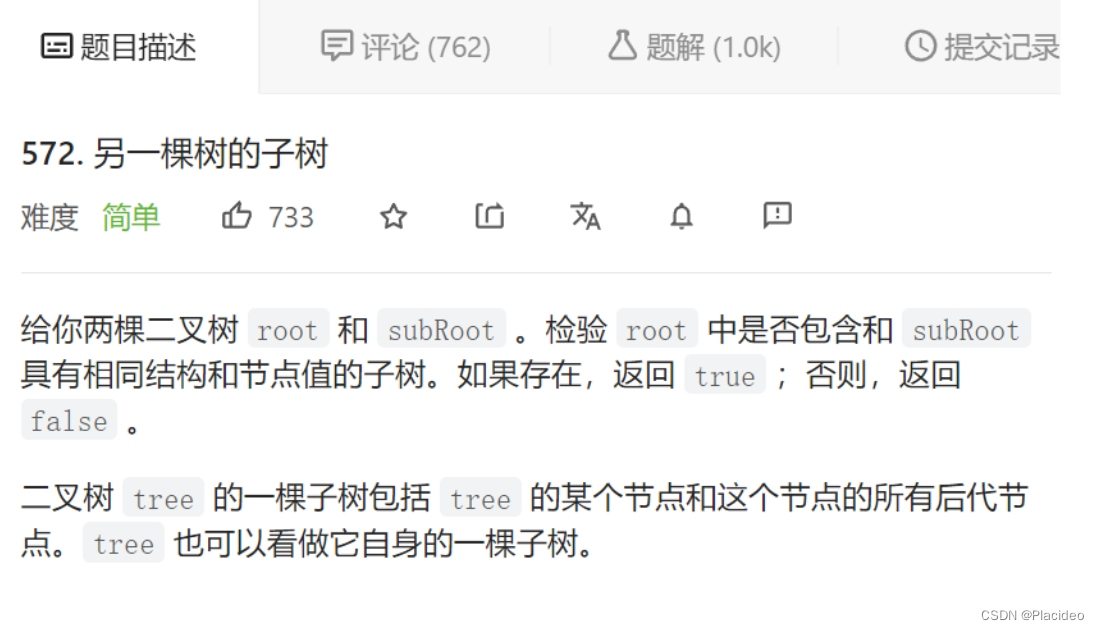

bool isSubtree(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* subRoot)//subRoot Not empty
{
if(root==NULL)// because subRoot Not empty , So if root==NULL, be root Our tree has no subtree
return fasle;
// Traverse , Follow root Compare all subtrees in
if(isSameTree(root, subRoot))
return true;
// Judge whether it is the subtree of the left subtree or the subtree of the right subtree
return isSubtree(root->left,subRoot)||
isSubtree(root->right,subRoot);
}ps:5->6->7->8 It is gradually advanced
9.IO Type questions -- Construction and traversal of binary tree


Ideas : First use The former sequence traversal take Sequence given Build a Trees . Then traverse in middle order .
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
BTDataType data;
}BTNode;
BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType x)
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
assert(node);
node->data = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
BTNode* CreateTree(char* str,int* pi)// Building tree -- Pre construction
{
if(str[*pi]=='#')
{
(*pi)++;
return NULL;
}
BTNode* root=BuyNode(str[(*pi)++]);
root->left=CreateTree(str,pi);
root->right=CreateTree(str,pi);
return root;
}
void InOrder(BTNode* root)// In the sequence traversal
{
if(root==NULL)
return;
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%c ",root->data);
InOrder(root->right);
}
int main()
{
char str[100];
scanf("%s",str);
int i=0;
BTNode* root=CreateTree(str,&i);// Build up trees -- Pre construction
InOrder(root);// In the sequence traversal
return 0;
}
10. The former sequence traversal

int TreeSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{
return root==NULL? 0: TreeSize(root->left) +TreeSize(root->right)+1;
}
void preorder(struct TreeNode* root,int *a,int* pi)
{
if(root==NULL);
return;
a[(*pi)++]=root->val;
preorder(root->left,a,pi);
preorder(root->right,a,pi);
}
int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root,int* returnSize)
{
*returnSize=TreeSize(root);
int* a=(int*)malloc(*returnSize * sizeof(int ));
int i=0;
preorder(root,a,&i);
return a;
}11. In the sequence traversal
12. After the sequence traversal
ps: The difference between pre -, mid -, and post order traversals is only in

Storage in val To a Different order in .
13. Judging whether a binary tree is a complete binary tree
Full binary tree :n The floor is full
Perfect binary tree : front n-1 Layer full , The first n Layer continuity
Ideas : Using sequence traversal BFS, Encounter empty , The back should be empty , Is a complete binary tree ;
If there is non empty after empty , Is not a complete binary tree .
void LevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q; // There are nodes in the queue ( Structure ) inconvenient
// Save pointer
QueueInit(&q);
if(root)// First put the first one in
{
QueuePush(&q,root);
}
while(QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front=QueueFront(&q); //front The value of the node in the accepted tree queue , The value of its node is stored as a pointer to the node of the tree
QueuePop(&q);//Pop Kill the node of the queue , It's not a node of a tree , Do not affect the nodes of the tree to find the left and right subtrees
if(front)
{
QueuePush(&q,front->left);
QueuePush(&q,front->right);
}
else // Encounter empty , Jump out of sequence traversal
break;
}
//1. If the back is all empty , Is a complete binary tree
//2. If there is non empty after empty , Is not a complete binary tree
while(!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front=QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if(front)
{
QueueDestroy(&q);
return false;
}
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
return true;
}边栏推荐
- 【Leetcode字符串--字符串下标排序】6121.裁剪数字后查询第 K 小的数字
- 【Leetcode数组--排序+辗转相除法最大公约数】6122.使数组可以被整除的最少删除次数
- STM32 single channel and multi-channel sampling of non DMA polling ADC based on Hal Library
- Repair the problem of adding device groups and editing exceptions on easycvr platform
- 复杂网络建模(网络上的传播现象 )
- 层序遍历BFS(广度优先)
- Win10 如何解决,应用商店打不开,错误代码0x80131500问题
- Pixels and colors
- Regular expression correlation
- C语言程序练习——(写一个函数,它的原形是int continumax(char *outputstr,char *intputstr))
猜你喜欢

ECCV 2022 | correction des dommages importants au rendement de la cible causés par le fpn: Vous devriez regarder tous les objets

Dc-4-range practice

JVM memory model: class loading process

模板学堂丨JumpServer安全运维审计大屏

JVM: parental delegation mechanism for class loading
![[leetcode array -- sorting + rolling division maximum common divisor] 6122. The minimum number of deletions that make the array divisible](/img/75/a1c2781ab259336411a3351ae7fc0e.png)
[leetcode array -- sorting + rolling division maximum common divisor] 6122. The minimum number of deletions that make the array divisible
![[ssm]ssm integration ③ (interface test)](/img/2c/09db4c058c7ce85df8710ab8b6a38b.png)
[ssm]ssm integration ③ (interface test)

Operation tutorial: UOB camera registers the detailed configuration of easycvr platform through gb28181 protocol

Popular science | how to create a Dao?

Fastjson code execution cve-2022-25845
随机推荐
Win10系统打开什么都是反应比平时慢,转圈等待1分钟如何解决?
二叉树OJ题,IO题
Execute function semicolon immediately
用c语言编写一个函数用来删除字符串中的空格并返回空格个数
SQL Server2008 database query admin password
[ssm]ssm integration ② (development of functional modules)
QUuid
Application level questions of computer network
JVM memory model: PC program counters
Glide source code analysis
JVM memory model: virtual machine stack
LeetCode 每日一题——814. 二叉树剪枝
信息学奥赛一本通 1977:【08NOIP普及组】立体图 | 洛谷 P1058 [NOIP2008 普及组] 立体图
Leetcode 172. zero after factorial
[JS] scope and scope chain
[leetcode array -- sorting + rolling division maximum common divisor] 6122. The minimum number of deletions that make the array divisible
Rsync downlink synchronization +inotify real-time synchronization deployment
Distributed scheduling framework elastic job
洛谷_P1112 波浪数_思维_进制 / 构造 / 枚举
Screen command use