当前位置:网站首页>二叉树OJ题,IO题
二叉树OJ题,IO题
2022-07-22 04:25:00 【Placideo】
二叉树OJ题:二叉树节点数/叶子节点数 、求二叉树第k层节点个数、 查找二叉树中值为x的节点 、求二叉树深度、 单值二叉树、 相同的树、对称二叉树、 另一棵子树、 二叉树的构建和遍历(IO型)、 前序遍历 、 中序遍历、 后序遍历、 判断二叉树是否为完全二叉树
1.二叉树节点数/叶子结点数--TreeSize
//两种方法
//法1.(初始方法)
int count = 0;//每次使用前都要置空一下
void TreeSize1(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
++count;
TreeSize1(root->left);
TreeSize1(root->right);
}
//法2.(优化)
int TreeSize2(BTNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 :
TreeSize2(root->left) + TreeSize2(root->right) + 1;
}
//进阶
//求树的叶子节点的数量
int TreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (root->left== NULL && root->right == NULL)
return 1;
return TreeLeafSize(root->left) + TreeLeafSize(root->right);
}
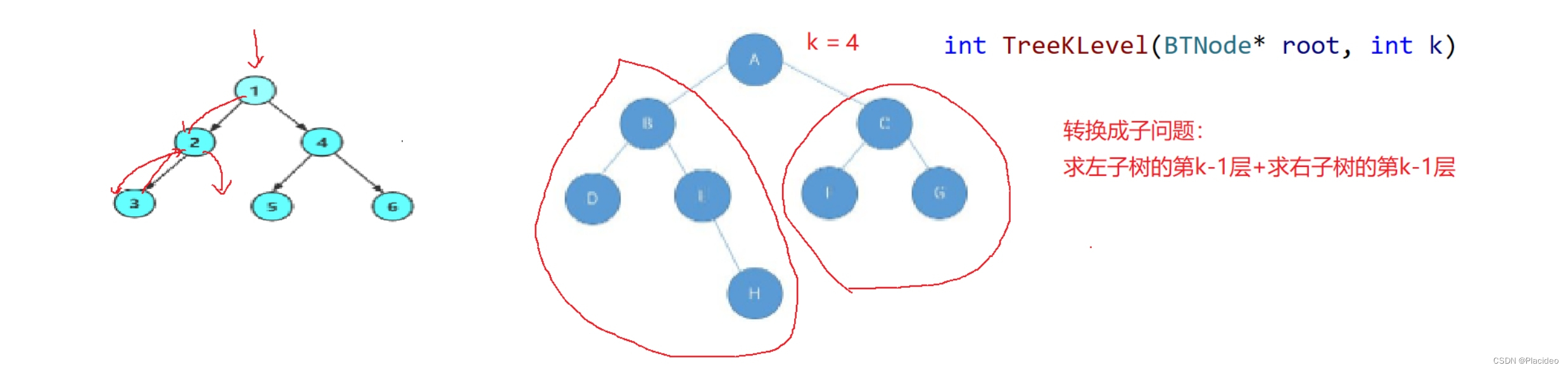
2.求第k层节点个数--TreeKLevel
int TreeKLevel(BTNode* root, int k)
{
assert(k >= 1);
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (k == 1)
return 1;
return TreeKLevel(root->left, k - 1)
+ TreeKLevel(root->right, k - 1);
}
3.二叉树查找值为x的节点--TreeFind
// 二叉树查找值为x的结点
BTNode* TreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
if (root->data == x)
return root;
BTNode* ret1 = TreeFind(root->left, x);
if (ret1)
return ret1;
BTNode* ret2 = TreeFind(root->right, x);
if (ret2)
return ret2;
return NULL;
}
4.求二叉树的深度--TreeDepth
int TreeDepth(BTNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return 0;
}
else if(root!=NULL)
{
int leftDepth=TreeDepth(root->left)+1;
int rightDepth=TreeDepth(root->right)+1;
return leftDepth>rightDepth? leftDepth:rightDepth;
}
}
5.单值二叉树

//法1.
bool flag= true;
void PreOrderCompare(struct TreeNode* root, int val)
{
if(root==NULL||flag==false)
return ;
if(root->val !=val)
{
flag=false;
return;//有一个false就可以说明不是单值二叉树了,可以直接退出,不用继续遍历了
}
PreOrderCompare(root->left,val);
PreOrderCompare(root->right,val);
}
bool isUnivalTree(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL)//先判断是否为空树
return true;
flag=true;//OJ题中慎用全局变量,静态变量,记得要重置
PreOderCompare(root,root->val);
return flag;
}
//法2.
bool isUnivalTree (struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL)
return true;
if(root->left&& root->left->val!=root->val)
return fasle;
if(root->right&&root->right->val!=root->val)
return fasle;
return isUnivalTree(root->left)&&isUnivalTree(root->right);
}
6.相同的树
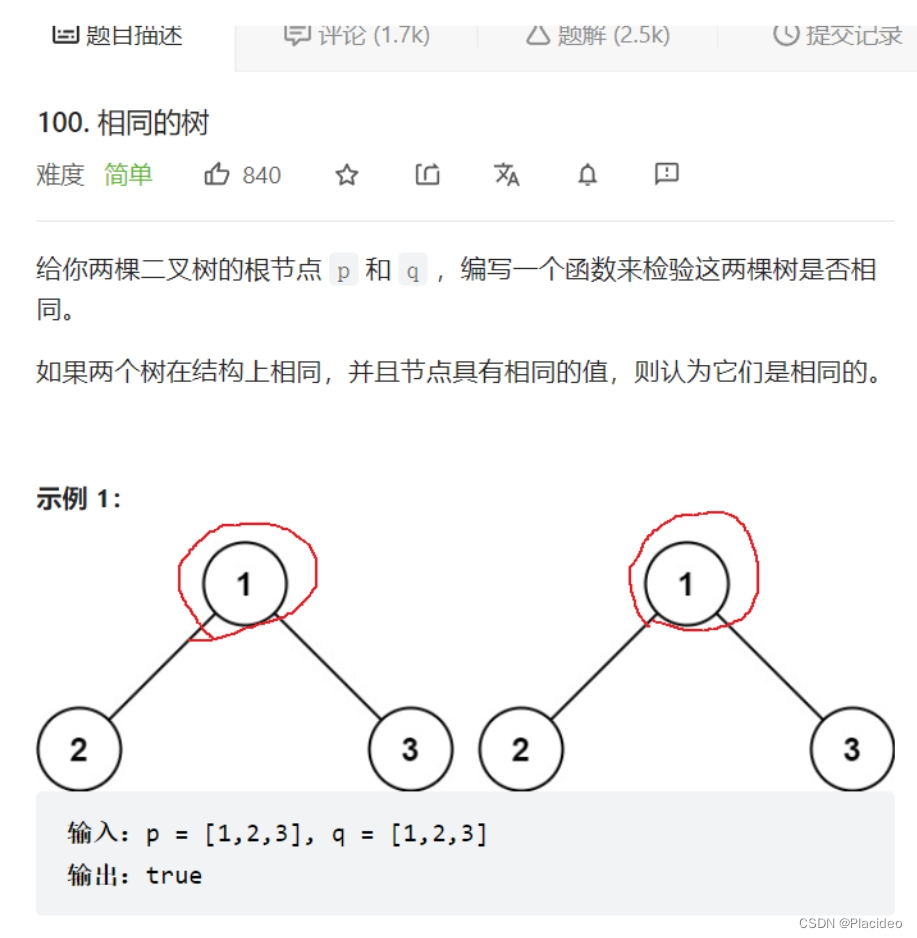
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q)
{
if(p==NULL&&q==NULL)//两个都为空
return true;
if(p==NULL||q==NULL)//在这只有一个为空
return false;
if(p->val!=!q->val)//这里的两个都不会为空
return fasle;
//如果root->val相同,则进入到左右子树比较
return isSameTree(p->left,q->right)&&isSameTree(p->right,q->right);
}7.对称二叉树

思路:由 相同的树 推广而来 只要将其一的root->left->val和另一root->right->val 进行比较即可。先判断首根是否为NULL,如果不为NULL,则将其子树分为左右子树来判断是否对称--和相同子树的代码类似。
bool isSymmetricSubTree(struct TreeNode* root1, struct TreeNode* root2)//子树对称
{
if(root1==NULL&&root2==NULL)//是否同为NULL
return true;
if(root1==NULL|| root2==NULL)//有一个为空,一个不为空,则false;
return false;
if(root1->val!=root2->val)//都不为空,但是值不同,也为false;
return false;
//都不为空,值相同,则继续比较子树
return isSymmetricSubTree(root1->left,root2->right)&&
isSymmetricSubTree(root1->right,root2->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root)//对称树
{
if(root ==NULL)//先判断首根是否为空
return true;
return isSymmetricSubTree(root->left,root->right);
}8.另一棵子树
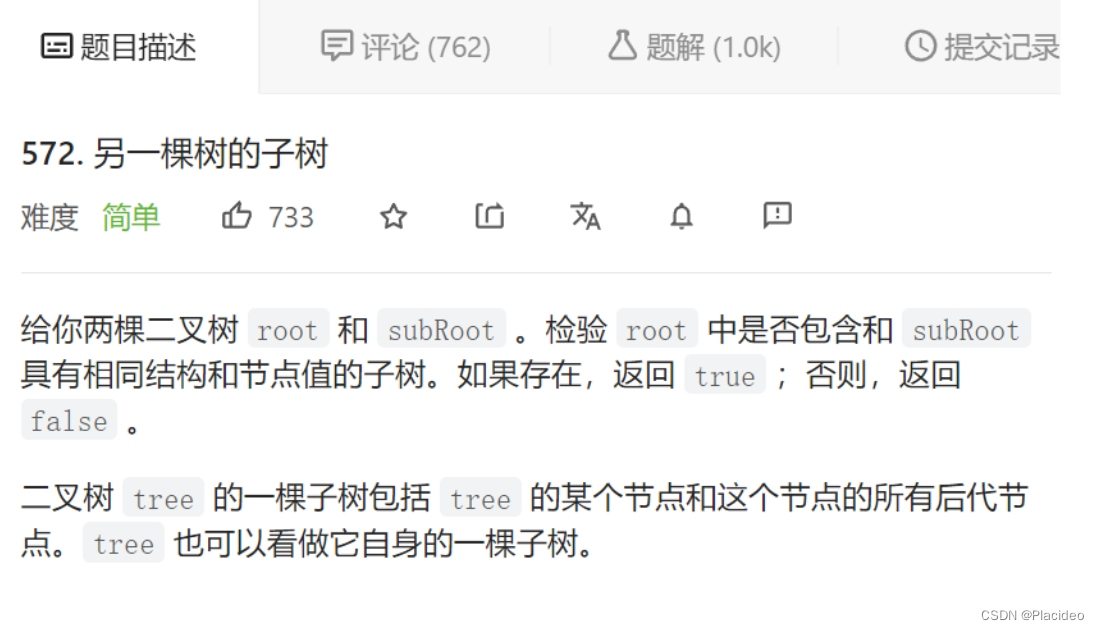

bool isSubtree(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* subRoot)//subRoot不为空
{
if(root==NULL)//因为subRoot不为空,所以如果root==NULL,则root的树没有子树
return fasle;
//遍历,跟root中所有子树都比较一遍
if(isSameTree(root, subRoot))
return true;
//判断是左子树的子树或者右子树的子树
return isSubtree(root->left,subRoot)||
isSubtree(root->right,subRoot);
}ps:5->6->7->8是慢慢进阶的
9.IO型题--二叉树的构建和遍历


思路:先用 前序遍历 将 已给序列 建成一个 树。再中序遍历。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
BTDataType data;
}BTNode;
BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType x)
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
assert(node);
node->data = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
BTNode* CreateTree(char* str,int* pi)//构建树--前序构建
{
if(str[*pi]=='#')
{
(*pi)++;
return NULL;
}
BTNode* root=BuyNode(str[(*pi)++]);
root->left=CreateTree(str,pi);
root->right=CreateTree(str,pi);
return root;
}
void InOrder(BTNode* root)//中序遍历
{
if(root==NULL)
return;
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%c ",root->data);
InOrder(root->right);
}
int main()
{
char str[100];
scanf("%s",str);
int i=0;
BTNode* root=CreateTree(str,&i);//建树--前序构建
InOrder(root);//中序遍历
return 0;
}
10. 前序遍历

int TreeSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{
return root==NULL? 0: TreeSize(root->left) +TreeSize(root->right)+1;
}
void preorder(struct TreeNode* root,int *a,int* pi)
{
if(root==NULL);
return;
a[(*pi)++]=root->val;
preorder(root->left,a,pi);
preorder(root->right,a,pi);
}
int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root,int* returnSize)
{
*returnSize=TreeSize(root);
int* a=(int*)malloc(*returnSize * sizeof(int ));
int i=0;
preorder(root,a,&i);
return a;
}11.中序遍历
12.后序遍历
ps:前中后序遍历的不同之处只是在

中的存储val到a中的顺序的不同。
13.判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
满二叉树:n层都满的
完全二叉树:前n-1层满,第n层连续
思路:用层序遍历法BFS,遇到空后,后面应该是全空,才是完全二叉树;
如果空后面还有非空,则不是完全二叉树。
void LevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q; //队列里存是节点(结构体)不方便
//改存指针
QueueInit(&q);
if(root)//先把首根放进去
{
QueuePush(&q,root);
}
while(QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front=QueueFront(&q); //front接受的树队列中节点的值,其节点的值存的就是树的节点的指针
QueuePop(&q);//Pop干掉的队列的节点,不是树的节点,不影响树的节点找左右子树
if(front)
{
QueuePush(&q,front->left);
QueuePush(&q,front->right);
}
else //遇到空后,跳出层序遍历
break;
}
//1.如果后面全是空,则是完全二叉树
//2.如果空后面还有非空,则不是完全二叉树
while(!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front=QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if(front)
{
QueueDestroy(&q);
return false;
}
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
return true;
}边栏推荐
- 嵌入式IDE原理 OpenOCD介绍 以及stlink如何连接stm32板子
- Informatics Olympiad all in one 1977: [08noip popularization group] stereogram | Luogu p1058 [noip2008 popularization group] stereogram
- Fastjson 代码执行 CVE-2022-25845
- Switch and router technology: Standard ACL, extended ACL and named ACL
- DNS interview questions of computer network
- SQL Server2008 database query admin password
- Repair the problem of adding device groups and editing exceptions on easycvr platform
- CF464E The Classic Problem
- The principle of embedded IDE, openocd introduction and how stlink connects STM32 board
- JVM memory model: class loading process
猜你喜欢

【Leetcode栈与队列--最小栈】155.最小栈

交换机与路由器技术:OSPF路由重分发、OSPF的NSSA区域和OSPF虚链路

交換機與路由器技術:標准ACL、擴展ACL和命名ACL
Chant Developer Workbench 2022

Diversified distribution methods of NFT

Technologie des commutateurs et des routeurs: ACL standard, ACL étendu et ACL nommé
Lesson 3 shell syntax

服务器与本地资料互传的命令行代码

梅科尔工作室——HarmonyOs第二次作业

分布式调度问题
随机推荐
Diversified distribution methods of NFT
C ftp detects whether the directory exists and creates a folder
交換機與路由器技術:標准ACL、擴展ACL和命名ACL
JVM memory model: class loading process
记一个composer依赖问题requires composer-runtime-api ^2.0.0 -> no matching package found
How far can TTL, RS232 and 485 transmit?
C#上传文件到共享文件夹
Elephant Swap的LaaS方案迅速崛起,构建全新DeFi2.0协议
STM32 single channel and multi-channel sampling of non DMA polling ADC based on Hal Library
[solution] solve the importerror: library "Glu" not found
C#服务器NFS共享文件夹搭建与上传图片文件
梅科尔工作室——HarmonyOs第二次作业
进程和线程面试问题
How can the easycvr platform access special devices without authentication?
Character encoding problem
CF464E The Classic Problem
Transparent transmission of punctual atom Lora wireless serial port point-to-point communication and Its Precautions
Command line code for server and local data transmission
C language pthread_ Join() function
网络层面试题