当前位置:网站首页>Several common locks (mutex lock, spin lock, optimistic lock, pessimistic lock)
Several common locks (mutex lock, spin lock, optimistic lock, pessimistic lock)
2022-07-20 09:10:00 【JYCJ_】
Mutexes and spinlocks
The mutex After the lock failed , Threads will Release CPU , To other threads ;
spinlocks After the lock failed , Threads will Busy waiting , Until it gets the lock ;
The mutex , It's a kind of 「 An exclusive lock 」, When locking fails , From user mode to kernel state , Let the kernel switch threads for us ;
What is the context of thread switching ?
When two threads belong to the same process , Because virtual memory is shared , So when switching , Virtual memory, these resources remain stationary , Only the private data of the thread needs to be switched 、 Data that is not shared, such as registers
spinlocks , It's through CPU Provided CAS function (Compare And Swap), stay 「 User mode 」 Complete locking and unlocking operations , No active thread context switch is generated , So compared to mutexes , It's going to be faster , It's also less expensive .
Mutexes and spinlocks are the most basic locks , Read write lock can choose one of these two locks according to the scene .
If you can be sure that the locked code has a short execution time , You shouldn't use mutexes , Instead, spin locks should be used , Otherwise use mutex .
Optimistic lock and pessimistic lock
Concept
Optimism lock : Optimistic lock is very optimistic when operating data , Think other people won't change the data at the same time . So optimistic locks don't lock , It's just to judge whether someone else has modified the data during the update : If someone else modifies the data, they give up the operation , Otherwise, perform the operation .
Pessimistic locking : Pessimistic lock is more pessimistic when operating data , Think that others will modify the data at the same time . Therefore, when operating data, lock the data directly , The lock will not be released until the operation is completed ; No one else can modify the data during locking .
Realization
Optimism lock : There are two main ways to achieve this :CAS Mechanism and Version number mechanism
Pessimistic locking : The implementation method is locking , Lock can be a code block lock ( Such as Java Of synchronized keyword ), It can also be data locking ( Such as MySQL The platoon lock in )
Applicable scenario
Functional limitation
Compared with pessimistic lock , There are more restrictions on the application of optimistic lock , Whether it's CAS Or version number mechanism .
for example ,CAS Only atomicity of single variable operation can be guaranteed , When multiple variables are involved ,CAS There's nothing we can do , and synchronized Then we can lock the whole code block to deal with . Another example is the version number mechanism , If query When it comes to watches 1, and update When it comes to watches 2, It's also hard to implement optimistic locks with simple version numbers .
The intensity of the competition
When the competition is not fierce ( The probability of concurrency conflict is small ) when , Optimistic lock has more advantages , Because pessimistic locks lock code blocks or data , Other threads cannot access at the same time , Affect concurrency , In addition, adding and releasing locks need to consume extra resources
When the competition is fierce ( There is a high probability of concurrent conflicts ) when , Pessimistic lock has more advantages , Because optimistic locks often fail when performing updates , Need to keep retrying , waste CPU resources , Exit mechanism can be introduced , If the number of retries exceeds a certain threshold, it fails to exit . Of course , More importantly, avoid using optimistic locks in a highly competitive environment .
Questioning
Optimistic lock plus lock ? Optimistic lock itself is not locked , But sometimes optimistic locking may cooperate with locking operation (MYSQL It's locked )
CAS What are the disadvantages ? ABA problem , That is, a thread changes the data in memory , however CAS The compared value is returned to the original value by the thread ,CAS Operation succeeded , The more effective solution is to introduce version number , Every time the value in memory changes , Version No +1, It's going on CAS In operation , Not only compare values in memory , Also compare version numbers , Only when neither of them has changed ,CAS To execute successfully
边栏推荐
- YOLOv1详解
- MPPT电源控制器设计
- JS中 绑定事件总结 以及注意事项
- Tensorflow学习笔记--张量与会话
- ShardingJDBC
- Summary of margin consolidation issues
- VLQ的介绍
- 响应式布局【Responsive】 与 自适应布局 【adaptive】、单页面【SPA】 和多页面【MPA】
- Generate crud restful API by configuring zero code without programming
- 【论文导读】Self-Supervised Learning with Data AugmentationsProvably Isolates Content from Style
猜你喜欢

YOLOv1论文中英文对照翻译

YOLOv3详解
MPPT power controller design

模拟图像加密、解密

Generate crud restful API by configuring zero code without programming
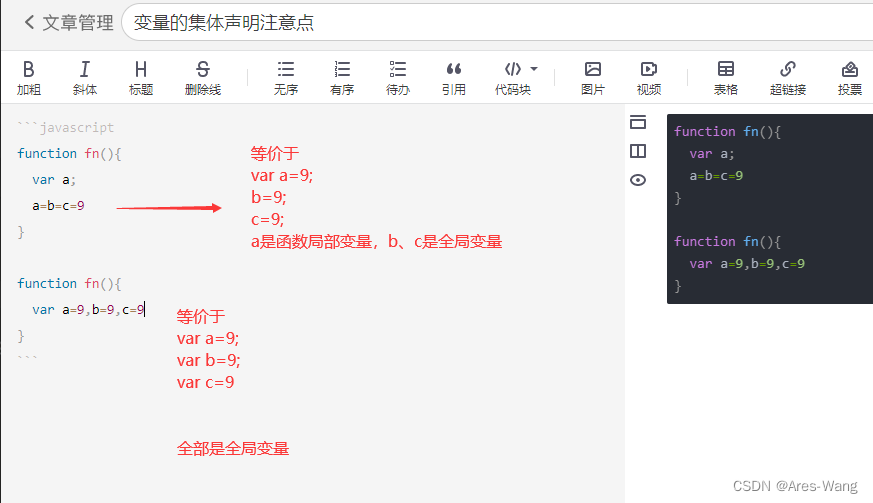
变量的集体声明注意点

Android studio executes kotlin throwing com android. builder. errors. Solution to evalissueexception problem

Talk about how to install openfire

uniapp中引入自定义图标

106 Polkadot substrate: fork free upgrade
随机推荐
单片机2——数码管动态显示的简单原理
单片机1-流水灯的拓展
事务处理(结合分布式事务)
Want to try Web3 work? It's enough to read this article
ShardingJDBC
Rich text set picture size and font size
EXCEL中VLOOKUP的使用
说说 Redis 缓存删除策略
电源学习(1)——电源系统测试
H5页面导出成pdf文件
102 Polkadot substrate: proof of existence
Asp.NET <%=%> <%#%> <% %> <%@%>
【深度学习】-Imdb数据集情感分析之模型对比(4)- CNN-LSTM 集成模型
【无标题】mysql之binlog数据恢复流程
Vivado error code [usf-xsim-62] [xsim 43-4316] solution
【深度学习】-Imdb数据集情感分析之模型对比(2)- LSTM
TCP三次握手和四次挥
10m Polkadot substrate: your first contract
Google Chrome 浏览器快捷键说明大全
margin 合并问题总结