当前位置:网站首页>August 30, 2020: naked write algorithm: the nearest common ancestor of two nodes in a binary tree.
August 30, 2020: naked write algorithm: the nearest common ancestor of two nodes in a binary tree.
2020-11-06 21:50:00 【Fuda Dajia architect's daily question】
Fogo's answer 2020-08-30:
1. recursive
Algorithm
Left node sub function return value is not empty , The return value of the sub function in the right node is null , Return to left node .
Left node sub function return value is null , The return value of the sub function in the right node is not empty , Back to the right node .
Left node sub function return value is not empty , The return value of the sub function in the right node is not empty , Returns the current node .
Complexity analysis :
Time complexity O(N) : among N Is the number of binary tree nodes ; In the worst case , You need to recursively traverse all the nodes of the tree .
Spatial complexity O(N) : In the worst case , The depth of recursion reaches N , System use O(N) The size of the extra space .
2. Store the parent node
Ideas
We can use a hash table to store the parent nodes of all nodes , Then we can use the parent node information of the node from p The nodes start to jump up , And record the nodes that have been visited , Again from q The nodes start to jump up , If you encounter a node that has been visited , So this node is the nearest public ancestor we're looking for .
Algorithm
Traverse the whole binary tree from the root node , Use hash table to record the parent node pointer of each node .
from p The node begins to move towards its ancestors , And use the data structure to record the visited ancestor nodes .
Again , Let's go from q The node begins to move towards its ancestors , If any ancestors have been visited , That means it's p and q The deepest public ancestor , namely LCA node .
Complexity analysis
Time complexity :O(N), among N It's the number of nodes in a binary tree . All nodes of the binary tree have and will only be accessed once , from p and q The number of ancestor nodes that the node jumps up will not exceed N, So the total time complexity is O(N).
Spatial complexity :O(N), among N It's the number of nodes in a binary tree . The stack depth of recursive calls depends on the height of the binary tree , In the worst case, a binary tree is a chain , Now the height is N, So the space complexity is zero O(N), The hash table stores the parent node of each node, which also needs O(N) Spatial complexity of , So the final total space complexity is O(N).
3. iteration
Ideas
Depth-first traversal , Traverse to two values , The answer comes out .
Complexity analysis
Time complexity O(N) : among N Is the number of binary tree nodes ; In the worst case , You need to recursively traverse all the nodes of the tree .
Spatial complexity O(Level) : Level It's the maximum depth of the tree .
The code to use go Language writing , as follows :
package test35_lowestcommonancestor
import (
"fmt"
"testing"
)
//go test -v -test.run TestLowestCommonAncestor
func TestLowestCommonAncestor(t *testing.T) {
root := &TreeNode{}
root.Val = 3
root.Left = &TreeNode{}
root.Left.Val = 5
root.Right = &TreeNode{}
root.Right.Val = 1
root.Right.Left = &TreeNode{}
root.Right.Left.Val = 0
root.Right.Right = &TreeNode{}
root.Right.Right.Val = 8
root.Left.Left = &TreeNode{}
root.Left.Left.Val = 6
root.Left.Right = &TreeNode{}
root.Left.Right.Val = 2
root.Left.Right.Left = &TreeNode{}
root.Left.Right.Left.Val = 7
root.Left.Right.Right = &TreeNode{}
root.Left.Right.Right.Val = 4
p := root.Right.Right
q := root.Left.Right.Right
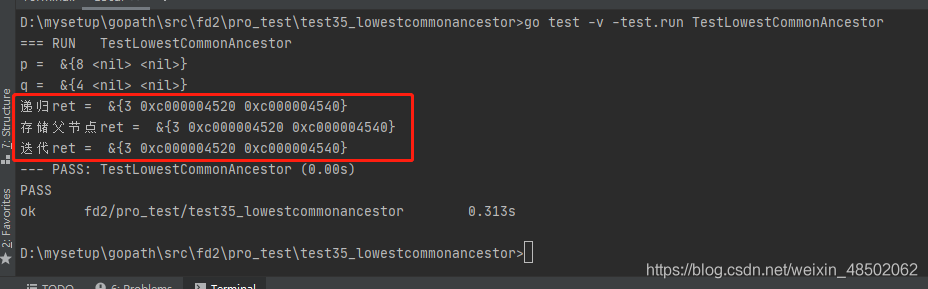
fmt.Println("p = ", p)
fmt.Println("q = ", q)
ret := LowestCommonAncestor1(root, p, q)
fmt.Println(" recursive ret = ", ret)
ret = LowestCommonAncestor2(root, p, q)
fmt.Println(" Store the parent node ret = ", ret)
ret = LowestCommonAncestor3(root, p, q)
fmt.Println(" iteration ret = ", ret)
}
//Definition for a binary tree node.
type TreeNode struct {
Val int
Left *TreeNode
Right *TreeNode
}
// recursive
func LowestCommonAncestor1(root, p, q *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
if root == nil || root == p || root == q {
return root
}
left := LowestCommonAncestor1(root.Left, p, q)
right := LowestCommonAncestor1(root.Right, p, q)
if left == nil && right == nil { //root It's a leaf node
return nil
}
// The left node cannot be searched , The right node is the root node
if left == nil {
return right
}
// The right node cannot be searched , The left node is the root node
if right == nil {
return left
}
// There are... On the left and right , explain root It's the root node
return root
}
// Store the parent node
func LowestCommonAncestor2(root, p, q *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
parent := map[int]*TreeNode{}
visited := map[int]bool{}
var dfs func(*TreeNode)
dfs = func(r *TreeNode) {
if r == nil {
return
}
if r.Left != nil {
parent[r.Left.Val] = r
dfs(r.Left)
}
if r.Right != nil {
parent[r.Right.Val] = r
dfs(r.Right)
}
}
dfs(root)
for p != nil {
visited[p.Val] = true
p = parent[p.Val]
}
for q != nil {
if visited[q.Val] {
return q
}
q = parent[q.Val]
}
return nil
}
// iteration
func LowestCommonAncestor3(root, p, q *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
if root == nil || root == p || root == q {
return root
}
//push root
stack := make([]*TreeNode, 0)
stack = append(stack, root)
stackvisited := make([]int, 0) // Record stack Access status of
stackvisited = append(stackvisited, 0) //0 Not accessed 1 The left node has accessed 2 The right node has accessed
var cur *TreeNode = nil
var ret *TreeNode = nil
for len(stack) > 0 {
cur = nil
if stackvisited[len(stackvisited)-1] == 0 { // Not accessed
stackvisited[len(stackvisited)-1] = 1
if stack[len(stack)-1].Left != nil {
stack = append(stack, stack[len(stack)-1].Left)
stackvisited = append(stackvisited, 0)
cur = stack[len(stack)-1]
}
} else if stackvisited[len(stackvisited)-1] == 1 { // Left node visited
stackvisited[len(stackvisited)-1] = 2
if stack[len(stack)-1].Right != nil {
stack = append(stack, stack[len(stack)-1].Right)
stackvisited = append(stackvisited, 0)
cur = stack[len(stack)-1]
}
} else { // The right node has accessed
if ret != nil {
if stack[len(stack)-1] == ret {
ret = stack[len(stack)-2]
}
}
//pop
stack = stack[0 : len(stack)-1]
stackvisited = stackvisited[0 : len(stackvisited)-1]
}
if cur != nil {
if cur == p {
if ret != nil { // The second time
break
} else { // for the first time
ret = cur
}
}
if cur == q {
if ret != nil { // The second time
break
} else { // for the first time
ret = cur
}
}
}
}
return ret
} knock go test -v -test.run TestLowestCommonAncestor command , The results are as follows :
版权声明
本文为[Fuda Dajia architect's daily question]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
边栏推荐
- #JVM 类加载机制
- Git remote library rollback specified version
- The isolation level of transaction and its problems
- All the way, I was forced to talk about C code debugging skills and remote debugging
- Understanding formatting principles
- Exclusive interview of guests at | 2020 PostgreSQL Asia Conference: Wang Tao
- The role of theme music in games
- 统计项目代码行数
- Exclusive interview with Alibaba cloud database for 2020 PostgreSQL Asia Conference: Zeng Wenjing
- C calls SendMessage to refresh the taskbar icon (the icon does not disappear at the end of forcing)
猜你喜欢

超高频RFID医疗血液管理系统应用

C calls SendMessage to refresh the taskbar icon (the icon does not disappear at the end of forcing)

递归、回溯算法常用数学基础公式

实验一

Qt音视频开发46-视频传输UDP版

With this artifact, quickly say goodbye to spam messages

1万辆!理想汽车召回全部缺陷车:已发生事故97起,亏损将扩大

How much disk space does a new empty file take?

Zero basis to build a web search engine of its own

谷歌浏览器实现视频播放加速功能
随机推荐
Git remote library rollback specified version
Python 100 cases
Bitcoin once exceeded 14000 US dollars and is about to face the test of the US election
Some operations kept in mind by the front end foundation GitHub warehouse management
STM32F030K6T6兼容替换灵动MM32F031K6T6
Qt音视频开发46-视频传输UDP版
An article takes you to understand CSS pagination examples
Common syntax corresponding table of mongodb and SQL
Junit测试出现 empty test suite
统计项目代码行数
Why is the LS command stuck when there are too many files?
C calls SendMessage to refresh the taskbar icon (the icon does not disappear at the end of forcing)
ado.net and asp.net The relationship between
ES6 learning notes (4): easy to understand the new grammar of ES6
Exclusive interview of guests at | 2020 PostgreSQL Asia Conference: Wang Tao
An article will take you to understand CSS3 fillet knowledge
Js数组-数组的用法全在这里(数组方法的重构、数组的遍历、数组的去重,数组的判断与转换)
2020-09-09:裸写算法:两个线程轮流打印数字1-100。
2020-08-14:数据任务的执行引擎用的哪些?
The legality of IPFs / filecoin: protecting personal privacy from disclosure