当前位置:网站首页>15 SQL optimizations commonly used by experts
15 SQL optimizations commonly used by experts
2022-07-22 19:02:00 【Epiphyllum every month】

One 、 Avoid using select *
A lot of times , We write SQL When the sentence is , For convenience , Like to use directly select *, Find out the data of all columns in the table at one time .
Counter example :
select * from user where id=1;
In a real business scenario , Maybe all we really need to use is one or two columns . Checked a lot of data , But there's no need to , Wasted database resources , such as : Memory or cpu.
Besides , More data , Through the network IO In transit , It will also increase the time of data transmission .
Another most important question is :select * Do not overwrite index , There will be a lot of table back operations , And from the result of the query SQL The performance is very low .
that , How do you optimize it ?
Example :
select name,age from user where id=1;
SQL Statement query , Just look up the columns you need , There is no need to find out the redundant liegenben .
Two 、 use union all Instead of union
We all know SQL Statements use union The key word , You can get the data after weight removal .
And if you use union all keyword , You can get all the data , Contains duplicate data .
Counter example :
(select * from user where id=1)
union
(select * from user where id=2);
The process of weight removal needs to traverse 、 Sort and compare , It's more time-consuming , More consumption cpu resources .
So if you can use union all When , As far as possible need not union.
Example :
(select * from user where id=1)
union all
(select * from user where id=2);
Unless there are some special scenes , such as union all after , Duplicate data appears in the result set , In the business scenario, duplicate data is not allowed , You can use union.
3、 ... and 、 Small tables drive large tables
Small tables drive large tables , That is to say, the data set of a large table is driven by the data set of a small table .
If there is order and user Two tables , among order Table has 10000 Data , and user Table has 100 Data .
If you want to check , List of orders placed by all valid users .
have access to in Keyword implementation :
select * from order
where user_id in (select id from user where status=1)
You can also use exists Keyword implementation :
select * from order
where exists (select 1 from user where order.user_id = user.id and status=1)
The business scenario mentioned earlier , Use in Keywords to achieve business requirements , More appropriate .
Why? ?
Because if SQL The statement contains in keyword , Then it will give priority to in The subquery statement inside , And then execute in The sentence outside . If in The amount of data in it is very small , Faster query as a condition .
And if the SQL The statement contains exists keyword , It gives priority to exists The statement on the left ( That is, the main query statement ). Then make it a condition , To match the statement on the right . If match up , Then you can query the data . If it doesn't match , The data is filtered out .
In this demand ,order Table has 10000 Data , and user Table has 100 Data .order A watch is a big watch ,user A watch is a small watch . If order The watch is on the left , Then use in Better keyword performance .
To sum up :
- in Applicable to the large table on the left , Small watch on the right .
- exists Applicable to the small table on the left , Big watch on the right .
No matter how it is used in, still exists keyword , Its core idea is to use small tables to drive large tables .
Four 、 The batch operation
If you have a batch of data after business processing , Need to insert data , What should I do ?
Counter example :
for(Order order: list){
orderMapper.insert(order):
}
Insert data item by item in the loop .
insert into order(id,code,user_id) values(123,'001',100);
This operation requires multiple requests to the database , To complete the insertion of this batch of data .
But as we all know , We're in code , Every time you remotely request the database , It will consume some performance . And if our code needs to request the database multiple times , To complete this business function , It is bound to consume more performance .
So how to optimize ?
Example :
orderMapper.insertBatch(list):
Provide a method for batch inserting data .
insert into order(id,code,user_id)
values(123,'001',100),(124,'002',100),(125,'003',101);
In this way, you only need to remotely request the database once ,SQL Performance will be improved , More data , The greater the promotion .
But it should be noted that , It is not recommended to batch operate too much data at one time , If there is too much data, the database response will be slow . Batch operation needs to grasp a degree , It is recommended that each batch of data be controlled within 500 within . If the data is more than 500, It is processed in multiple batches .
5、 ... and 、 multi-purpose limit
occasionally , We need to query the first item in some data , such as : Query the first order placed by a user , Want to see his first single time .
Counter example :
select id, create_date
from order
where user_id=123
order by create_date asc;
According to the user id Query order , Sort by order time , First find out all the order data of the user , Get an order set . And then in the code , Get the data of the first element , That is, the data of the first order , You can get the first order time .
List<Order> list = orderMapper.getOrderList();
Order order = list.get(0);
Although this approach has no functional problems , But its efficiency is very low , You need to query all the data first , A bit of a waste of resources .
that , How do you optimize it ?
Example :
select id, create_date from order where user_id=123 order by create_date asc limit 1;
Use limit 1, Only the data with the smallest ordering time of the user can be returned .
Besides , When deleting or modifying data , In order to prevent misoperation , Results in the deletion or modification of irrelevant data , It can also be in SQL At the end of the sentence add limit.
for example :
update order set status=0,edit_time=now(3) where id>=100 and id<200 limit 100;
In this way, even if misoperation , For example id A mistake , It will not affect too much data .
6、 ... and 、in Too many values
For batch query interface , We usually use them in Keyword filter out data . such as : Want to pass some of the specified id, Batch query user information .
SQL The statement is as follows :
select id,name from category where id in (1,2,3...100000000);
If we don't make any restrictions , The query statement may query a lot of data at one time , It is easy to cause the interface to time out .
So what do you do ?
select id,name from category where id in (1,2,3...100) limit 500;
Can be in SQL Use... For data in limit Make restrictions .
However, we need more restrictions in business code , The pseudocode is as follows :
public List<Category> getCategory(List<Long> ids) {
if(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(ids)) {
return null;
}
if(ids.size() > 500) {
throw new BusinessException(" The maximum number of queries allowed at one time is 500 Bar record ")
}
return mapper.getCategoryList(ids);
}
Another solution is : If ids exceed 500 Bar record , You can use multithreading to query data in batches . Only check each batch 500 Bar record , Finally, summarize the queried data and return .
But this is only a temporary plan , Not suitable for ids There are too many scenes . because ids Too much , Even if you can find the data quickly , But if the amount of data returned is too large , Network transmission is also very performance consuming , The performance of the interface is always not good .
7、 ... and 、 Incremental query
occasionally , We need to query the data through the remote interface , Then synchronize to another database .
Counter example :
select * from user;
If you get all the data directly , And then sync it . Although this is very convenient , But it brings a very big problem , If there is a lot of data , Query performance will be very poor .
So what do you do ?
Example :
select * from user
where id>#{lastId} and create_time >= #{lastCreateTime}
limit 100;
Press id And time ascending , Only one batch of data is synchronized at a time , This batch of data only 100 Bar record . After each synchronization , Keep this 100 The largest of the data id And time , For synchronizing the next batch of data .
Through this incremental query , It can improve the efficiency of single query .
8、 ... and 、 Efficient paging
occasionally , When querying data on the list page , In order to avoid returning too much data at one time and affecting the interface performance , We usually do paging on the query interface .
stay MySQL Pagination is generally used in limit keyword :
select id,name,age from user limit 10,20;
If the amount of data in the table is small , use limit Keyword paging , No problem . But if there is a lot of data in the table , Using it will cause performance problems .
For example, now the paging parameter becomes :
select id,name,age from user limit 1000000,20;
MySQL We'll find out 1000020 Data , Then discard the front 1000000 strip , Just check the back 20 Data , This is a waste of resources .
that , How to page this huge amount of data ?
Optimize SQL:
select id,name,age from user where id > 1000000 limit 20;
First find the page with the largest number of pages last time id, And then use it id Index query on . But the plan , requirement id Is a continuous , And orderly .
Can also be used between Optimize paging .
select id,name,age from user where id between 1000000 and 1000020;
It should be noted that between To page on a unique index , Otherwise, the size of each page will be inconsistent .
Nine 、 Replace subquery with join query
MySQL If you need to query data from more than two tables , There are generally two ways to achieve it : Subquery and Link query .
An example of a subquery is as follows :
select * from orderwhere user_id in (select id from user where status=1)
Subquery statements can be through in Keyword implementation , The condition of one query statement falls on another select Statement in the query result . The program runs first in the innermost statement , Then run the outer statement .
The advantage of subquery statements is that they are simple , structured , If the number of tables involved is small .
But the disadvantage is MySQL When executing a subquery , You need to create a temporary table , When the query is finished , You need to delete these temporary tables again , There are some additional performance costs .
At this time, it can be changed to join query . Specific examples are as follows :
select o.* from order oinner join user u on o.user_id = u.idwhere u.status=1
Ten 、join Don't have too many watches
According to Alibaba developer manual ,join The number of tables should not exceed 3 individual .
Counter example :
select a.name,b.name.c.name,d.name
from a
inner join b on a.id = b.a_id
inner join c on c.b_id = b.id
inner join d on d.c_id = c.id
inner join e on e.d_id = d.id
inner join f on f.e_id = e.id
inner join g on g.f_id = f.id
If join Too much ,MySQL Selecting an index can be very complicated , It's easy to pick the wrong index .
And if you miss ,nested loop join Is to read a row of data from two tables and compare them , Complexity is n^2.
So we should try to control join Table number .
Example :
select a.name,b.name.c.name,a.d_name
from a
inner join b on a.id = b.a_id
inner join c on c.b_id = b.id
If you need to query the data in other tables in the business scenario , Can be in a、b、c Redundant special fields in the table , such as : In the table a Medium redundancy d_name Field , Save the data to be queried .
But I've seen some before ERP System , The amount of concurrency is small , But the business is more complex , need join Only a dozen tables can query the data .
therefore join The number of tables shall be determined according to the actual situation of the system , Can't generalize , As little as possible .
11、 ... and 、join Pay attention to
When it comes to the joint query of multiple tables , You usually use join keyword .
and join The most used is left join and inner join.
- left join: Find the intersection of two tables plus the remaining data in the left table .
- inner join: Find the data of the intersection of two tables .
Use inner join An example of this is :
select o.id,o.code,u.name
from order o
inner join user u on o.user_id = u.id
where u.status=1;
If two tables use inner join relation ,MySQL The small table of the two tables will be automatically selected , To drive the big watch , So there won't be much problem in performance .
Use left join An example of this is :
select o.id,o.code,u.name
from order o
left join user u on o.user_id = u.id
where u.status=1;
If two tables use left join relation ,MySQL Will default to left join The table on the left of the keyword , To drive the table on its right . If the table on the left has a lot of data , There will be performance problems .
Special attention should be paid to using left join When associating queries , Use a small watch on the left , You can use a big watch on the right . If it works inner join The place of , Use less as far as possible left join.
Twelve 、 Control the number of indexes
as everyone knows , Indexing can significantly improve query performance SQL Performance of , But the more indexes, the better .
Because when adding data to the table , You need to create an index for it at the same time , The index requires additional storage space , And there will be some performance consumption .
Alibaba's developer manual stipulates , The number of indexes in a single table should be controlled to 5 Within a , And the number of fields in a single index does not exceed 5 individual .
MySQL The use of B+ The structure of the tree to hold the index , stay insert、update and delete In operation , You need to update B+ Tree index . If there are too many indexes , It consumes a lot of extra performance .
that , The problem is coming. , If there are too many indexes in the table , More than the 5 What should I do ?
This problem should be viewed dialectically , If your system concurrency is not high , The amount of data in the table is not much , Actually more than 5 One can also , Just don't exceed too much .
But for some highly concurrent systems , Please be sure to observe that the number of indexes in a single table should not exceed 5 The limitation of .
that , How to optimize the number of indexes in highly concurrent systems ?
Able to build joint index , Don't build a single index , You can delete useless single indexes .
Migrate some query functions to other types of databases , such as :Elastic Seach、HBase etc. , Only a few key indexes need to be built in the business table .
13、 ... and 、 Select a reasonable field type
char Represents a fixed string type , This type of field has a fixed amount of storage space , It wastes storage space .
alter table order add column code char(20) NOT NULL;
varchar Represents variable length string type , The storage space of this type of field will be adjusted according to the length of the actual data , No waste of storage space .
alter table order add column code varchar(20) NOT NULL;
If it is a fixed length field , For example, the user's mobile phone number , It's usually 11 Bit , It can be defined as char type , The length is 11 byte .
But if it is the enterprise name field , If defined as char type , There's a problem .
If the length is defined too long , For example, it is defined as 200 byte , The actual enterprise length is only 50 byte , It will waste 150 Byte storage space .
If the length is defined too short , For example, it is defined as 50 byte , But the actual enterprise name is 100 byte , Will not be able to store , And throw an exception .
Therefore, it is suggested to change the enterprise name to varchar type , Variable length fields have small storage space , You can save storage space , And for queries , Searching in a relatively small field is obviously more efficient .
When we select the field type , This principle should be followed :
- Can use numeric type , No strings , Because character processing is often slower than numbers .
- Use as small a type as possible , such as : use bit Save Boolean , use tinyint Save enumeration values, etc .
- Fixed length string field , use char type .
- Variable length string field , use varchar type .
- The amount field is in decimal, Avoid loss of accuracy .
There are many principles , Here is not a list .
fourteen 、 promote group by The efficiency of
We have many business scenarios to use group by keyword , Its main function is de duplication and grouping .
Usually it will follow having Used together , It means that after grouping, the data is filtered according to certain conditions .
Counter example :
select user_id,user_name from ordergroup by user_idhaving user_id <= 200;
This writing method is not good , It first puts all orders according to the user id After grouping , Then filter users id Greater than or equal to 200 Users of .
Grouping is a relatively time-consuming operation , Why don't we narrow the data first and then , Group again ?
Example :
select user_id,user_name from orderwhere user_id <= 200group by user_id
Use where Condition before grouping , Just filter out the redundant data , In this way, the efficiency of grouping will be higher .
In fact, this is an idea , Not limited to group by The optimization of the . our SQL Statement before doing some time-consuming operations , The data range should be as narrow as possible , This can improve SQL Overall performance .
15、 ... and 、 Index optimization
SQL Optimization , There is a very important content is : Index optimization .
A lot of times SQL sentence , The index is gone , And didn't go , Execution efficiency varies greatly . So index optimization is regarded as SQL The first choice for optimization .
The first step in index optimization is : Check SQL The statement has no index .
that , How to view SQL Have you left yet ?
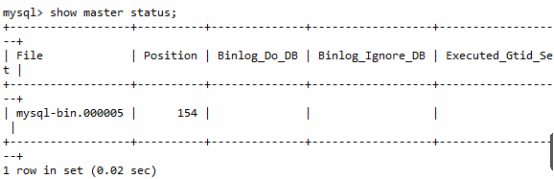
have access to explain command , see MySQL Implementation plan of .
for example :
explain select * from `order` where code='002';
result :
Through these columns, you can judge the index usage , The meaning of the columns included in the execution plan is shown in the figure below :

Tell the truth ,SQL The statement doesn't follow the index , Excluding no indexing , The biggest possibility is that the index fails .
Let's talk about the common causes of index failure :
If not for the above reasons , You need to further investigate other reasons .
Besides , Have you ever encountered such a situation : It's the same SQL, Only the input parameters are different . Sometimes I go a, Sometimes I just walk away b?
you 're right , occasionally MySQL The wrong index will be selected .
You can use when necessary force index To force a query SQL Go to an index .
边栏推荐
- Recursively find the partial sum of simple alternating power series (15 points)
- Sub database and sub table
- Design of hydraulic system for power slide of horizontal single side multi axis drilling combined machine tool
- Leetcode 653. sum of two IV - input BST
- 实现各个微服务间限制IP访问 的三种方式
- JVM-系统优化
- Sprintf rewriting of QT; The content under QT is scaled according to the scaling of the interface (without changing the font size)
- Tcpdump 简单用法
- Leetcode 114. expand binary tree into linked list
- 程序员面试金典面试题 01.05. 一次编辑
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Randomly query n pieces of data in various databases
MySQL statement execution order
Vlfeat, pydot configuration
Thymeleaf中一个页面怎么嵌套另一个页面,关于页面嵌套,标签告诉你应该知道的
各种技术资料汇总-MYSQL
JVM-系统优化
用LaTeX写论文时如何加资助信息
Sub database and sub table
NRF24L01 wireless module setting transmit receive mode method
数据存储分区--范围分区,哈希分区,列表分区,性能调优必不可缺少的部分
PTA exercise 8-8 judging palindrome string
Leetcode 105. constructing binary trees from preorder and inorder traversal sequences
IP地址、CIRD格式网址、主机名正则表达式
MNIST handwritten numeral recognition case tensorflow 2.0 practice
Bull column - blog summary
(C language) is array a special pointer?
LeetCode 693. 交替位二进制数
LeetCode 720. 词典中最长的单词
PTA basic question 7-23 currency conversion (20 points) (true)
1. Create a dynamic library of functions, 2. Howto create and deploy a sample DLL using MinGW






![[QT source code reuse] simulate the pop-up mode of qcompleter](/img/c3/805fe83c3f0b0affbbf0505b2bde13.png)