当前位置:网站首页>【外部排序】归并思想完成外部排序
【外部排序】归并思想完成外部排序
2022-07-22 05:56:00 【pass night】
问题描述
利用归并排序思想,实现外排。
算法思想

- 当输入缓存为空时,读取磁盘
- 归并输入缓存,保存结果在输出缓存
- 当输出缓存为空时,写入磁盘
算法实现
缓存类
struct Cache
{
int *cache;
int capacity;
//the start position of the cache in disk
//when the cache is empty, startPosition = endPosition = 0
int diskStartPosition;
int diskEndPosition;
//when Cache is not filled, endPosition - startPosition != capacity
//for tempCache, endPosition - startPosition == capacity 并不完全成立
int startPosition;
int endPosition;
int size;
};
- 声明缓存类管理缓存,同时保存部分相关数据;但因为数组位置信息保存在数组类当中,所以不提供读写操作
数组类的实现
class ExternalArray
{
friend class ExternalArrayTest;
private:
int length = 0;
Cache inputCache1;
Cache inputCache2;
Cache outputCache;
fstream fio;
string filePath;
size_t diskIOCount = 0;
string tempFilePath;
};
- 数组类包含对应的各个缓存
- 使用
fstream进行文件操作 - 使用
diskIOCount计算磁盘IO数量
算法思路
- 当输入缓存为空时,读取磁盘
- 归并输入缓存,保存结果在输出缓存
- 当输出缓存为空时,写入磁盘
缓存操作函数
写缓存:
// write to disk
// automatically set the start position and the end position of the cache
// if the sequencial is true, than set the disk start position and the disk end position of the disk last write
// if the sequencial is false, than set the start position and the end position of the disk to -1
void writeCache(Cache &cache, int diskStartPosition, int startPosition, int endPosition, bool sequencial = true)
{
cache.diskStartPosition = diskStartPosition;
fio.seekp(diskStartPosition * sizeof(int), ios::beg);
for (int i = startPosition; i < cache.size; i++)
{
fio.write((char *)&cache[i], sizeof(int));
}
cache.diskEndPosition = diskStartPosition + cache.size;
fio.clear();
if (!sequencial)
{
cache.diskEndPosition = -1;
cache.diskStartPosition = -1;
}
diskIOCount++;
// cout << "write cache " << cache << "now the array is ";
print();
}
读缓存:
// basic read method
// read from disk
// if the disk is empty or shorter than cache, then fill with zero
// the append parameter is used to determine whether the cache is appended to the old data
// when read from disk, the status flag(those position) is automatically set
// return count number of data
int readCache(Cache &cache, int start, int end, int diskStartPosition, bool append = false, bool sequencial = true)
{
fio.seekg(diskStartPosition * 13, ios::beg);
int i = start, count = 0;
if (!append)
cache.size = 0;
for (; i < end && fio.peek() != EOF; i++, count++)
{
fio >> cache[i];
cache.size++;
}
if (append)
{
// cache.cacheStartPosition is equal to old one
cache.endPosition += count;
// cache.diskStartPosition is equal to old one
cache.diskEndPosition += count;
}
else
{
cache.startPosition = start;
cache.endPosition = start + count;
cache.diskStartPosition = diskStartPosition;
cache.diskEndPosition = diskStartPosition + count;
}
for (; i < end; i++)
cache[i] = 0;
if (!sequencial)
{
cache.diskEndPosition = -1;
cache.diskStartPosition = -1;
}
fio.clear();
diskIOCount++;
return count;
}
临时文件操作
- 为了降低算法的复杂度,将归并后的数据写入临时文件,临时文件的操作如下:
void appendToTempFile(Cache &cache)
{
ofstream fout(tempFilePath, ios::binary | ios::app);
for (int i = cache.startPosition; i < cache.endPosition; i++)
{
fout.write((char *)&cache[i], sizeof(int));
}
fout.close();
}
void append(Cache &cache, int value)
{
if (cache.isFilled())
{
appendToTempFile(cache);
// cout << "write temp file " << tempFilePath << " now the array is ";
// print(tempFilePath);
cache.size = 0;
cache.startPosition = 0;
cache.endPosition = 0;
}
cache.append(value);
}
数据代理
- 为了将磁盘操作抽象为内存操作,重载获取数据函数
// if left = true, read from input cache 1, else read from input cache 2
int &get(int i, bool left)
{
if (i > length)
throw invalid_argument("i is larger than length");
if (left)
{
if (inputCache1.diskStartPosition <= i && i < inputCache1.diskEndPosition)
{
return inputCache1[i - inputCache1.diskStartPosition];
}
else
{
readCache(inputCache1, i, min(inputCache1.capacity, length - i));
// cout<<"read input cache 1, now the cache is "<<inputCache1;
return inputCache1[0];
}
}
else
{
if (inputCache2.diskStartPosition <= i && i < inputCache2.diskEndPosition)
{
return inputCache2[i - inputCache2.diskStartPosition];
}
else
{
readCache(inputCache2, i, min(inputCache2.capacity, length - i));
// cout<<"read input cache 2, now the cache is "<<inputCache2;
return inputCache2[0];
}
}
}
int &operator()(int i, bool left)
{
return get(i, left);
}
归并实现
- 在实现上述代理后,同内存归并排序一样实现归并排序即可
- 为了降低实验复杂度,只实现了输入缓存大小相同的情况 不同的情况也无实际意义
void merge(int leftDiskStartPosition, int leftDiskEndPosition, int rightDiskStartPosition, int rightDiskEndPosition)
{
int i = leftDiskStartPosition;
int j = rightDiskStartPosition;
while (i < leftDiskEndPosition || j < rightDiskEndPosition)
{
if (i < leftDiskEndPosition && j < rightDiskEndPosition)
{
if (get(i, true) < get(j, false))
{
append(outputCache, get(i, true));
i++;
}
else
{
append(outputCache, get(j, false));
j++;
}
}
else if (i < leftDiskEndPosition)
{
append(outputCache, get(i, true));
i++;
}
else
{
append(outputCache, get(j, false));
j++;
}
}
}
void mergeSort()
{
for (int step = 2; step / 2 < length; step *= 2)
{
// cout << "step = " << step << endl;
tempFilePath = "./cache/tempArray.dat";
remove(tempFilePath.c_str());
outputCache.reset();
inputCache1.reset();
inputCache2.reset();
for (int i = 0; i < length; i += step)
{
int mid = i + step / 2;
if (mid < length)
{
//右子区间存在元素则合并
merge(i, mid, mid, min(i + step, length));
}
}
appendToTempFile(outputCache);
fio.close();
remove(filePath.c_str());
rename(tempFilePath.c_str(), filePath.c_str());
fio.open(filePath, ios::out | ios::in | ios::binary);
// cout << "after one round, the arr is ";
// print();
// cout << endl;
}
}
实验结果与分析
测试类
class ExternalArrayTest
{
public:
// the merge
void test2()
{
// ExternalArray arr(50, 30, 80);
// srand(time(NULL));
// for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++)
// {
// arr.inputCache1[i] = rand() % 1000;
// }
// for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++)
// {
// cout << arr.inputCache1[i] << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
// for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++)
// {
// arr.inputCache2[i] = rand() % 1000;
// }
// for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++)
// {
// cout << arr.inputCache2[i] << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
// arr.inputCache1.endPosition = 50;
// arr.inputCache2.endPosition = 30;
// arr.inputCache1.size = 50;
// arr.inputCache2.size = 30;
// arr.merge(arr.inputCache1, arr.inputCache2, arr.outputCache);
// arr.outputCache.print();
}
// enough cache to sort
int test3()
{
ExternalArray arr(50, 50, 100);
arr.addRandomNumber(100);
arr.mergeSort();
return arr.isAccendent();
}
// not enough cache to sort
int test4()
{
ExternalArray arr(3, 3, 5);
arr.addRandomNumber(20);
// cout << "the array to be sorted is " << arr;
arr.mergeSort();
return arr.isAccendent();
}
// run all test
void runTest()
{
if (test3() == -1)
{
cout << "test1 success" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "test1 failed" << endl;
}
if (test4() == -1)
{
cout << "test2 success" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "test2 failed" << endl;
}
if (test7() == -1)
{
cout << "test3 success" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "test3 failed" << endl;
}
if (test8() == -1)
{
cout << "test4 success" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "test4 failed" << endl;
}
}
void experience()
{
for (int length = 1000; length < 3000; length += 500)
{
for (int inputCacheSize = 100; inputCacheSize < 400; inputCacheSize += 100)
{
for (int outputCacheSize = 100; outputCacheSize < length; outputCacheSize += 300)
{
ExternalArray arr(inputCacheSize, inputCacheSize, outputCacheSize);
arr.addRandomNumber(length);
arr.mergeSort();
cout << "length = " << length << ", input cache size = " << inputCacheSize << ", output cache size = " << outputCacheSize << ", disk IO count = " << arr.diskIOCount << endl;
}
}
}
}
// test the os file system
void test5()
{
ExternalArray *a = new ExternalArray(0, 0, 0, "array.dat");
ExternalArray *temp = new ExternalArray(0, 0, 0, "temp.dat");
a->fio.close();
temp->fio.close();
cout << remove(a->filePath.c_str());
rename(temp->filePath.c_str(), a->filePath.c_str());
}
// file out
void test6()
{
ExternalArray arr(0, 0, 0, "array.dat");
arr.addRandomNumber(100);
arr.print();
}
//large number
int test7()
{
ExternalArray arr(5000, 5000, 100000);
arr.addRandomNumber(1000000);
arr.mergeSort();
return arr.isAccendent();
}
// asymmetric cache size
int test8()
{
ExternalArray arr(3, 3, 5);
arr.addRandomNumber(20);
// cout << "the array to be sorted is " << arr;
arr.mergeSort();
return arr.isAccendent();
}
};
实验结果
正确性分析
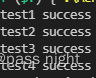
实验结果

实验分析
读取过程中,有两个缓存,其平均缓存大小为 i n p u t C a c h e 1. c a p a c i t y + i n p u t C a c h e 2. c a p c c i t y 2 \frac{inputCache1.capacity + inputCache2.capccity}{2} 2inputCache1.capacity+inputCache2.capccity,总读取次数固定为 ⌈ log 2 ( l e n g t h ) ⌉ \lceil\log_2(length)\rceil ⌈log2(length)⌉,所以平均磁盘读取次数为 2 e n g t h ⌈ log 2 ( l e n g t h ) ⌉ i n p u t C a c h e 1. c a p a c i t y + i n p u t C a c h e 2. c a p c c i t y \frac{2ength\lceil\log_2(length)\rceil}{inputCache1.capacity + inputCache2.capccity} inputCache1.capacity+inputCache2.capccity2ength⌈log2(length)⌉
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
NVIDIA hardware architecture
Cross domain problem (CORS) detailed description and solution

UART通信实验(查询方式)

活动推荐| Apache Pulsar 在 vivo 的探索与实践 即将开播
Xshell Plus6下载及安装使用的方法

Win11闪白屏无法控制如何解决?
Pytorch深度学习实践 第11讲(CNN)
UE4 set night (update skysphere according to directionallight direction)

Polygon chain matic concept and underlying mechanism

Digital path and practical thinking
随机推荐
UE4 level blueprint realizes door opening and closing
Spark高级特性,220720,
MySQL foundation +mysql cluster review
[paper translation] generalized radio representation learning via cross supervision between images
flask框架添加异步任务处理模型任务
服务器buffer/cache 的产生原因和释放buffer/cache
Write a sequencer plug-in sequence subtitle (1)
Pytorch深度学习实践 第11讲(CNN)
JWT学习
Enthusiasm and expertise fly together | Microsoft's most valuable expert project, attracting Microsoft technology contributors!
牛客网 Fibonacci数列
Can0 transceiver + receive interrupt configuration and baud rate calculation of gd32f470 (detailed)
牛客网 替换空格
Digital path and practical thinking
Anaconda download link
tf.placeholder
MVC模式和三层架构
【机器学习】pytorch如何加载自定义数据集并进行数据集划分
-bash-4.2$
分支语句和循环语句