当前位置:网站首页>Pyspark: conversion operation and action operation of dataframe
Pyspark: conversion operation and action operation of dataframe
2022-07-21 06:50:00 【Sun_ Sherry】
Spark edition :V3.2.1
Keep adding
preface
Spark DataFrame For the creation and common column operations in, please refer to blog :https://blog.csdn.net/yeshang_lady/article/details/89528090
Text
because Spark DataFrame Is based on RDD Created , therefore DataFrame The operation of can also be divided into two types : Transformation operation and action operation . The conversion operation can convert Spark DataFrame Convert to new DataFrame, Without changing the original data . Conversion operations are inert , It will not be calculated immediately . The action operation will trigger the actual evaluation of all conversion operations .
1. Action operations
1.1 show Display data
show Methods can be shown in the form of tables DataFrame Data in , The method mainly has the following parameters :
- n: Number of data rows to display ;
- truncate: Whether to truncate the string , You can also directly use this field to specify the length of the displayed string ;
- vertical: Whether to display vertically DataFrame The lines in the ;
Examples of its usage are as follows :
from pyspark.sql.types import *
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
from pyspark.sql import functions as func
import pandas as pd
from pyspark.sql.functions import pandas_udf
data=[['Alice',26],['Jessica',23],['Shirely',33]]
df=spark.createDataFrame(data,['Name','age'])
df.show(2,truncate=3)
df.show(vertical=True)
The result is as follows :
1.2 Get all data to array
show Method can only DataFrame Show the data in , But you cannot use variables to receive DataFrame. To get data , have access to collect Methods will DataFrame The data in is saved to List In the object . The usage is as follows :
data=[['Alice',26],['Jessica',23],['Shirely',33]]
df=spark.createDataFrame(data,['Name','age'])
df_array=df.collect()
print(df_array)
The result is as follows :
One thing to note ,collect Method will put DataFrame All data of is retrieved to a node , So the memory of a single node is not enough to save the whole DataFrame Memory overflow error will be reported when all the data in .
1.3 Get several rows of records
first、head、take、tail These four methods can obtain DataFrame Several lines of records in . These four methods are similar , among :
- first: This method gets DataFrame Of the 1 rows .
- head: This method gets DataFrame Before n n n rows . This method only applies to DataFrame The amount of data is small , And all data is saved in memory .
- take: obtain DataFrame Before n n n rows .
- tail: obtain DataFrame After n n n rows .
Only with take Take as an example to explain the usage ( The results are no longer displayed ):
data=[['Alice',26],['Jessica',23],['Shirely',33]]
df=spark.createDataFrame(data,['Name','age'])
res_1=df.take(2)
print(res_1)
1.4 take DataFrame conversion pandas.DataFrame
toPandas Method can spark DataFrame Turn into Pandas DataFrame. Usage is as follows :
data=[['Alice',26],['Jessica',23],['Shirely',33]]
df=spark.createDataFrame(data,['Name','age'])
dt=df.toPandas()
print(dt)
The result is as follows :
2. Transformation operation
Before introducing the conversion operation in detail , The following points need to be explained :
- Spark DataFrame The data type of the field name parameter in the conversion operation method in is generally :String Type and Column object , Or these two objects List object . When the method can receive multiple field names at the same time ,String The type and Column Can't mix .
- Spark DataFrame The results returned by the conversion operation of are Spark DataFrame type , So these methods can be used continuously .
2.1 decribe Get the statistics of the specified field
describe Method receives one or more String type (Column Type is not allowed ) Field name , Return the statistical value of the corresponding field , Include :Count、Mean、Stddev、Min、Max. This method can also be used without specifying the field name , At this time, the statistical information of all fields is returned . The usage is as follows :
data=[['Alice',26],['Jessica',23],['Shirely',33]]
df=spark.createDataFrame(data,['Name','age'])
df.describe(['Name','age']).show()
The result is as follows :
2.2 where/filter Filter data
where and filter It's the same thing , All right DataFrame The data are filtered . Here is just where Methods as an example to illustrate .where(condition) Medium condition Two parameter types can be accepted . As follows :
- When the received parameter is String When it's type , Its writing refers to SQL In language where Clause ;
- When the received parameter is Column Type , The filtering requirements for each field need to be described separately , Then use logical operations to combine ( And or is written as :&、|、~).
Examples of its usage are as follows :
data=[[34,None,'Shirely'],
[24,89,'Alice'],
[30,90,'Mark']]
df=spark.createDataFrame(data,['C1','C2','C3'])
# Conditions : C2 And is not null C1 Greater than 25
df.where('C2 is not null and C1>25').show()
# Conditions : C2 It's empty
df.where(func.isnull('C2')).show()
# Conditions : C2 And is not null C3 Longer than 3
df.where(~func.isnull('C2')).where(func.length('C3')>3).show()
# Conditions : C2 Not empty or C1 Greater than 25
df.filter((~func.isnull('C2'))|(func.col('C1')>25)).show()
The result is as follows :
2.3 select/selectExpr Query specified column
select and selectExpr It's the same thing , The difference is that the two methods receive different parameter types . As follows :
- select: This operation receives Sting type ( Name )、Column or List The parameters of type . If you want to query all columns , You can also use ∗ * ∗;
- selectExpr: This operation receives SQL expression , You can perform function processing on specific fields at the same time ;
Examples of its usage are as follows :
data=[[34,None,'Shirely'],
[24,89,'Alice'],
[30,90,'Mark']]
df=spark.createDataFrame(data,['C1','C2','C3'])
# Query all columns
df.select('*').show()
# Multiple Column Columns of List
df.select([func.length('C3'),func.lower('C3')]).show()
# receive SQL expression
df.selectExpr('length(C3)','C1>25').show()
The result is as follows :
2.4 drop Delete the specified column
drop In the method, you can connect String The parameters of type , You can also use Column Type parameter . When using the former , You can delete multiple columns at the same time , When using the latter, only one column can be deleted at a time . Examples of its usage are as follows :
data=[[34,None,'Shirely'],
[24,89,'Alice'],
[30,90,'Mark']]
df=spark.createDataFrame(data,['C1','C2','C3'])
df.drop('C1').show()
df.drop('C1','C2').show() # Note that it can't be written as List
df.drop(df.C1).show()
The result is as follows :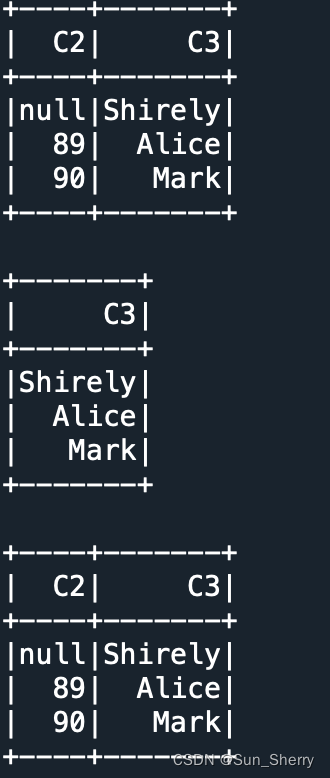
2.5 limit Before acquisition n rows
limit Method to get the specified DataFrame Before n rows , Its usage is as follows :
data=[[34,None,'Shirely'],
[24,89,'Alice'],
[30,90,'Mark']]
df=spark.createDataFrame(data,['C1','C2','C3'])
df.limit(2).show()
The result is as follows :
2.6 orderBy/sort/sortWithinPartitions Sort by specified field
orderBy and sort The methods are the same , and sortWithinPartitions Methods can be applied to every Parition Sort , Here is just sort Take an example to illustrate .sort Method can accept two types of parameters , Different parameter types , Sorting is described in different ways . As follows :
- In the use of Column Type parameter , stay Column Back plus .desc() Representation of descending order ,.asc() Expressing ascending order ( You can also use functions In bag asc and desc Method ).
- When using String Type variable , Use ascending Parameter to specify the sorting direction .
Specific usage examples are as follows :
data=[[34,None,'Shirely'],
[24,89,'Alice'],
[30,90,'Mark']]
df=spark.createDataFrame(data,['C1','C2','C3'])
df.sort(['C1','C2'],ascending=[0,1]).show()
df.sort([func.desc('C2'),func.asc('C3')]).show()
The result is as follows :
2.7 groupBy Group and aggregate fields
groupBy Method can group data , What it gets is GroupedData Type object . The object API Provides some aggregation operations . As follows :
- avg、max、min、mean、count、sum Method
The method here can only connect String Variable name of type , And will automatically ignore non numeric fields . Usage is as follows :
schema=StructType([StructField('State', StringType()),
StructField('Color', StringType()),
StructField('Count', IntegerType())])
df=spark.read.csv('data/mnm_dataset.csv',
schema=schema,
header=True)
df.groupby('State').min('Count').show(5)
df.groupby('State').sum('Count').show(5)
df.groupby('State').count().show(5)
The result is as follows :
- agg: Custom aggregate functions .
agg Method can use avg、max And other built-in aggregation functions , You can also use pyspark.sql.functions.pandas_udf Defined GROUPED_AGG Function of type . Examples are as follows :
@pandas_udf('int')
# Count the number of different values
def agg_func1(x:pd.Series) -> int:
return (~x.duplicated()).sum()
df.groupby('State').agg({
'Color':'count','Count':'sum'}).show(5)
df.groupby('State').agg(agg_func1('Color')).show(5)
The result is as follows :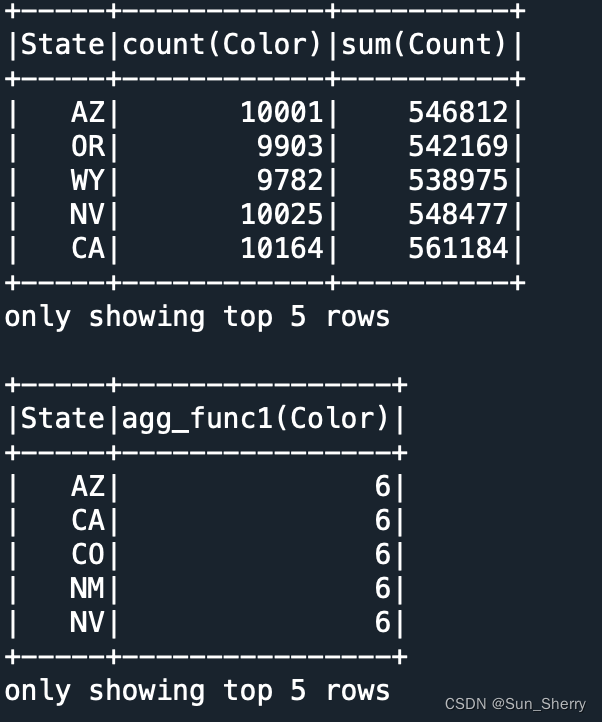
- apply/applyInPandas: Use Pandas The function in
applyInPandas and apply The method works the same , but apply In the future Spark The version will be discarded , And compared with applyInPandas Method ,apply The definition of functions in is a little troublesome . This is only about applyInPandas Usage of . As follows :
def new_func(pdf:pd.DataFrame)-> pd.DataFrame:
pdf['Count']=(pdf['Count']-pdf['Count'].mean())/pdf['Count'].std()
return pdf[['State','Count']]
df.groupby('State').applyInPandas(new_func, schema='State string,Count float').show(5)
The result is as follows :
Be careful applyInPandas Methods schema What is specified in the parameter is the type information of the return value of the custom function , This parameter can be used DDL Format strings can also be used pyspark.sql.types.DataType Type object .
- pivot: PivotTable
pivot The object type returned by the method is still GroupedData type , therefore agg、avg And other methods can still be used . Examples are as follows :
df.groupby('State').pivot('Color').sum('Count').show()
The result is as follows :
2.8 Deduplication
Spark DataFrame Two de duplication operations are provided in , As follows :
- distinct: Returns a... That does not contain duplicate records DataFrame.
- drop_duplicates: De duplicate according to the specified field .
The usage is as follows :
data=[[1,2],
[1,2],
[3,4],
[1,3]]
df=spark.createDataFrame(data,['A','B'])
df.distinct().show()
df.drop_duplicates(['A']).show()
The result is as follows :
2.9 Merge operation
Spark DataFrame For two DataFrame There are ways to merge :union、unionAll and unionByName. As follows :
- union、unionAll For two fields with the same number DataFrame A merger . The two methods do not check when merging DataFrame Field type and field name , Only merge according to the position of the field . The method and SQL in Union all The same effect . Examples are as follows :
data1=[[1,2],
[1,2],
[3,4],
[1,3]]
df1=spark.createDataFrame(data1,['A','B'])
data2=[['a',6],
['b',8]]
df2=spark.createDataFrame(data2,['C','D'])
df1.union(df2).show()
The result is as follows :
- unionByName: This method will follow two DataFrame Merge field names with the same name in , This method does not require two DataFrame The number of fields is the same . As follows :
data1=[[1,2],
[1,2],
[3,4],
[1,3]]
df1=spark.createDataFrame(data1,['A','B'])
data2=[[5,6],
[7,8]]
df2=spark.createDataFrame(data2,['B','A'])
df1.unionByName(df2).show()
data3=[[4],[5]]
df3=spark.createDataFrame(data3,['C'])
df1.unionByName(df3,allowMissingColumns=True).show()
The result is as follows :
2.10 join operation
join The role of SQL Medium join The operation is similar , I won't repeat it here . Examples of usage are as follows ;
data1=[[1,2],
[5,4],
[7,3]]
df1=spark.createDataFrame(data1,['A','B'])
data2=[[5,6],
[7,8]]
df2=spark.createDataFrame(data2,['A','B'])
df1.join(df2,df1['A']==df2['A'],how='outer').select(df1.A,df1.B,df2.B.alias('B_1')).show()
The result is as follows :
2.11 stat Get the statistics of the specified field
stat Method can calculate statistics between specified fields or between specified fields , Like variance 、 covariance 、 Frequent element sets, etc .DataFrame.stat The sub call interfaces under are shown in the following table :
| Method | effect |
|---|---|
| approxQuantile | Calculate the approximate percentile of the numerical column ( There are still some unsolved problems about this function , Add later ) |
| corr | Calculate the correlation between the two fields |
| cov | Calculate the covariance of two fields |
| crosstab | Crossover table |
| freqItems | Calculate a set of frequently occurring values in a column or columns ,support The parameter specifies the minimum support of frequent items |
| sampleBy | Sample the specified column data , You need to specify the sampling proportion of a specific column |
Examples are as follows :
df=spark.read.csv('/data/mnm_dataset.csv',
schema=schema,
header=True)
df.stat.freqItems(cols=['State','Color'],support=0.9).show()
df.stat.sampleBy('Color',fractions={
'Yellow':0.001}).show()
df.stat.crosstab('State','Color').show()
The result is as follows :
2.12 Collection class operation
Spark DataFramet The provided collection class operations are as follows :
- intersect\intersectAll: Get two DataFrame Common records ;
- exceptAll: Get one DataFrame There's another one DataFrame Data records not found in ;
The specific usage is as follows :
data1=[[1,2],[3,4],[4,5]]
df1=spark.createDataFrame(data1,['A','B'])
data2=[[1,2]]
df2=spark.createDataFrame(data2,['A','B'])
data3=[[2,1]]
df3=spark.createDataFrame(data3,['B','A'])
df1.intersect(df2).show()
df1.intersectAll(df3).show()
df1.exceptAll(df2).show()
The result is as follows :
Here we need to pay attention to , Two DataFrame Column names are not checked during set operations , It depends on the position of the column , therefore df1 and df3 The intersection result of is empty .
2.13 Operation field name
Spark DataFrame Common methods of operating field names mainly include the following two :
- withColumnRenamed: Yes DataFrame A column in is renamed ;
- withColumn: Yes DataFrame Add a new column ;
Its usage is as follows :
data1=[[1,2],[3,4],[4,5]]
df1=spark.createDataFrame(data1,['A','B'])
df1.withColumn('C',(df1['A']>3).alias('C')).show()
df1.withColumnRenamed('A','A_1').show()
The result is as follows :
2.14 Handle null Columns
na Method can process row data with null columns , It provides three treatment methods , As follows :
- drop: Delete the null value row of the specified column , It can also be used directly dropna Method .
- fill: Replace the value of the specified null value column with the specified value . By passing in the column name of the specified null value column and the replacement value of the null value column Map Object to fill Method to replace the value of the specified null value column . The method and fillna The method works the same .
- replace: Replace the value ;
Examples are as follows :
data=[[1,None,None],
[2,4,8],
[9,None,11]]
df=spark.createDataFrame(data,['A','B','C'])
df.show()
# Delete data - Only if there is a null value, the row data will be deleted
df.na.drop(how='any').show()
# Delete data - If the number of null values in a row of data >=thresh, Then the record in this line is deleted
df.na.drop(thresh=2).show()
# use 0 Fill with null values
df.na.fill(0).show()
# Different columns are filled with different values
df.na.fill({
'B':0,'C':1}).show()
# Data substitution - take A In column 2 Replace with 4,9 Replace with 8
df.na.replace([2,9],[4,8],'A').show()
The result is as follows :
边栏推荐
- Section 10 of Chapter 1: conditional judgment if
- PostgreSQL是什么?StackOverflow上开发者最爱和最想要的关系型数据库
- 铁钉扎头、酸奶瓶“咬”舌……广东消防:暑期儿童安全不容忽视
- Industrial control safety PLC firmware reverse I
- “我放弃编程,写了一本130万字的硬科幻小说”
- Custom persistence layer framework myormframework (II) - Framework Design
- 标量、向量、矩阵微积分
- 笔记。。。。
- Huawei computer test: Student matrix
- kvm虚拟化作业
猜你喜欢

2022年7月8日

Win10 boot PS1 script

静态页面和动态页面的原理及区别详解

NC | chenghuan Institute zhuyongguan team - potential of marine plastic circles in the process of nitrogen geochemical cycle

换装MG黑色标识 名爵将推新产品序列

用 emoji 学安全上网小常识?看 Google 新玩法

理解什么是配置中心?

Wps2019 all macros are forbidden. You have to pay for enabling macros. How to use them for free
在 Excel 内使用 ODBC 消费 SAP ABAP CDS view

历史上的今天:Kotlin 语言首次被公开;IMAP 协议之父出生;CT 成像实现新突破...
随机推荐
Jackson 动态过滤属性,编程式过滤对象中的属性
CSRF攻击原理场景
后深度学习时代,推荐系统向何处去?
《网络安全测试实验室搭建指南》—第1章1.5节关键术语
华人女婿小野三太成密西根大学首位亚裔校长,年薪超650万!
Custom persistence layer framework myormframework (III) - framework implementation
Iron nails pierce the head, yogurt bottles "bite" the tongue... Guangdong fire: Summer children's safety can not be ignored
Huawei computer test: Student matrix
Section 9 of Chapter 1: the simplest user interaction
Golang利用反射设置结构体中的项, Json数据源
在 Excel 内使用 ODBC 消费 SAP ABAP CDS view
工控安全PLC固件逆向二
Function introduction
【Go开源宝藏】基于 Golang 语法的性能调优技巧(数组的遍历)
PostgreSQL是什么?StackOverflow上开发者最爱和最想要的关系型数据库
IDEA手动编写Servlet详解
深入理解String类
Section 12 of Chapter 1: use of break and continue
如何向服务器上传文件
What is an IP SSL certificate and how to apply for it?