当前位置:网站首页>Understand the original Gan loss and hinge Gan loss
Understand the original Gan loss and hinge Gan loss
2022-07-21 03:44:00 【daimashiren】
original Gan Loss
m i n G m a x D V ( D , G ) = E x ∼ P d a t a [ l o g D ( x ) ] + E z ∼ P z ( Z ) [ l o g ( 1 − D ( G ( Z ) ) ) ] \mathop{min}\limits_{G}\space \mathop{max}\limits_{D}\space V(D,G) = E_{x\sim P_{data}}[log\space D(x)] + E_{z \sim P_z \space (Z)}[log(1-D(G(Z)))] Gmin Dmax V(D,G)=Ex∼Pdata[log D(x)]+Ez∼Pz (Z)[log(1−D(G(Z)))]
The Loss Our goal is to optimize two opposing goals at the same time , namely maximize V(D) and minimize V(G).
First , Maximize V(D) when , The function images are


therefore , If you want to Maximize V(D), It only needs D(x) → 1,D(G(Z)) → 0 that will do , Even for real images Discriminator The output probability of D(x) Tend to be 1, And for the generated image Discriminator The output probability of is close to 0, To maximize V(D) So as to optimize the purpose of the discriminator .
secondly , To optimize Generator, Minimize V(G), Because the first term in the formula E x ∼ P d a t a [ l o g D ( x ) ] E_{x\sim P_{data}}[log\space D(x)] Ex∼Pdata[log D(x)] Not included G, So just minimize E z ∼ P z ( Z ) [ l o g ( 1 − D ( G ( Z ) ) ) E_{z \sim P_z \space (Z)}[log(1-D(G(Z))) Ez∼Pz (Z)[log(1−D(G(Z))) that will do , From the function image , To minimize the V(G) Just need to make D(G(Z)) →1 that will do . Train the generator and the discriminator respectively for a period of time , Then train together , That is to say Gan Network optimization process .
Hinge Gan Loss
Hinge Gan Loss yes Hinge Loss And traditional Gan Loss A combination of , First understand Hinge Loss.

H i n g e L o s s = m a x ( 0 , 1 − t y ) Hinge Loss = max(0, 1- ty) HingeLoss=max(0,1−ty) The image of is shown in the above figure , t y ≧ 1 ty \geqq 1 ty≧1 The parts of all become 0 , among t t t Indicates the desired output tag ± 1 \pm 1 ±1 , and y Express SVM Direct input of, such as y = w ∗ x + b y = w*x + b y=w∗x+b. It can also be expressed by the following formula :
H i n g e L o s s = { 1 − t y , i f t y < 1 0 , o t h e r w i s e Hinge Loss = \begin{cases} 1- ty \hspace{2em} ,if \hspace{1em} ty<1 \\0 \hspace{4em},otherwise\end{cases} HingeLoss={ 1−ty,ifty<10,otherwise
The meaning of the above formula is , If the predicted label is correct ( namely t And y Same number ), And ∣ y ∣ \vert{y}\vert ∣y∣ >1 when ,loss by 0
If the predicted label is wrong ( namely t And y Different sign ), be loss With y Linear growth . Allied , When ∣ y ∣ \vert{y}\vert ∣y∣ <1 when , Even if t And y Same number ( Correct classification ), But there will still be losses due to insufficient spacing .
Hinge Loss variant
Hinge Loss There are also the following variants :
L ( y , y ^ ) = m a x ( 0 , m − y + y ^ ) L(y,\hat y) = max(0,m-y+\hat y) L(y,y^)=max(0,m−y+y^)
among : y y y Express positive ( real ) Sample scores , y ^ \hat y y^ Express negative ( forecast ) Sample scores ,m Represents the minimum spacing between positive and negative samples (margin).
Hinge Loss Our goal is to try our best to widen the score gap between positive and negative samples , In the above variants, the minimum score spacing of positive and negative samples should meet margin Conditions ( Suppose in a classification problem , The machine learned nothing , Give the same score for each class , This is the time margin The existence of has a role , bring loss At least m, Instead of being 0).
Hinge Gan Loss
V ( D , G ) = L D + L G V(D,G) = L_D + L_G V(D,G)=LD+LG
L D = E [ m a x ( 0 , 1 − D ( x ) ) ] + E [ m a x ( 0 , 1 + D ( G ( z ) ) ) ] L_D = E[max(0,1-D(x))] + E[max(0,1+D(G(z)))] LD=E[max(0,1−D(x))]+E[max(0,1+D(G(z)))]
Optimization objectives : D(x) → 1,D(G(z)) → 0
For discriminators , Only D ( x ) < 1 D(x)<1 D(x)<1( The probability of real samples is less than 1) and D ( G ( z ) ) > − 1 D(G(z))> -1 D(G(z))>−1( The probability of forging samples is greater than 0) These two situations will produce loss, Need to be optimized , Other cases loss by 0, Thus, the training of the discriminator is stabilized to a certain extent .
L G = − E [ D ( G ( z ) ) ] L_{G} = -E[D(G(z))] LG=−E[D(G(z))]
Optimization objectives : D(G(z)) → 1
Reference resources
https://zh.wikipedia.org/zh-cn/Hinge_loss
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/72195907
边栏推荐
- (10) Pytorch deep learning: convolutional neural network (simple residual convolutional neural network)
- (五)PyTorch深度学习:Logistic回归
- Antd mobile form validation RC form usage
- Five basic data types of redis (super detailed)
- 二分图
- Select all on the current page of Ali vector Gallery
- Dameng DEM deployment
- About encoding (ASCII / Unicode / utf8)
- 电脑端微信有很多垃圾可以清理
- Li Hongyi 2020 machine learning notes -- P10 classification
猜你喜欢
![[camp d'entraînement can] essai de mise en œuvre du Gan basé sur Shengsi](/img/e1/964ba73d4dbdb6da8219565b116d13.png)
[camp d'entraînement can] essai de mise en œuvre du Gan basé sur Shengsi

Package (.Py) files into (.Exe) files in pychart

(四)PyQt5系列教程:使用Pycharm对PyQt5在串口助手参数选项进行内部逻辑设计(一)
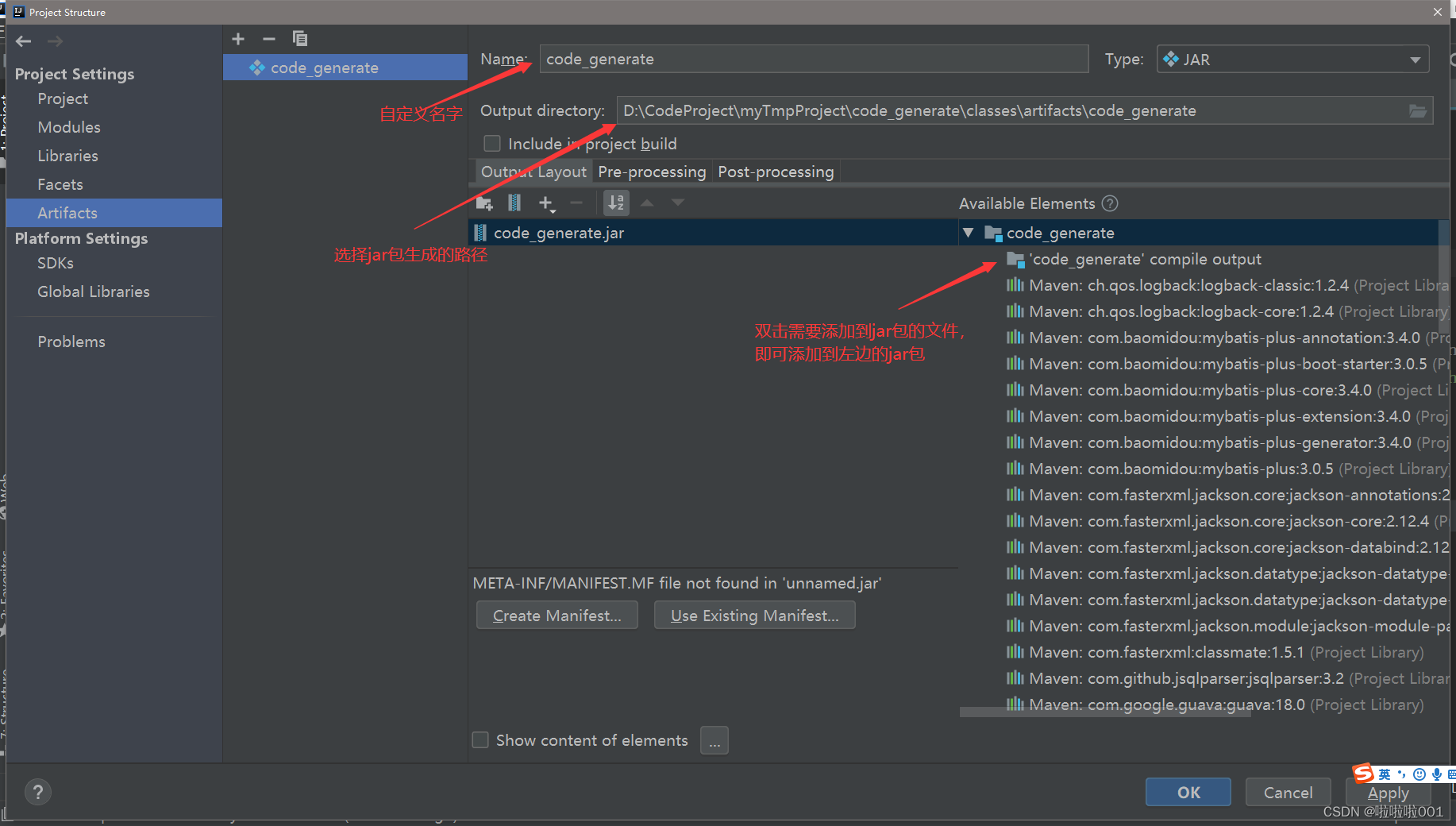
How to use idea to make jar packages

Li Hongyi machine learning 2020---p12 brief introduction of DL & p15 why DL

Flink datastream API (XIV) Flink output to MySQL (JDBC)

Realization of data warehouse technology
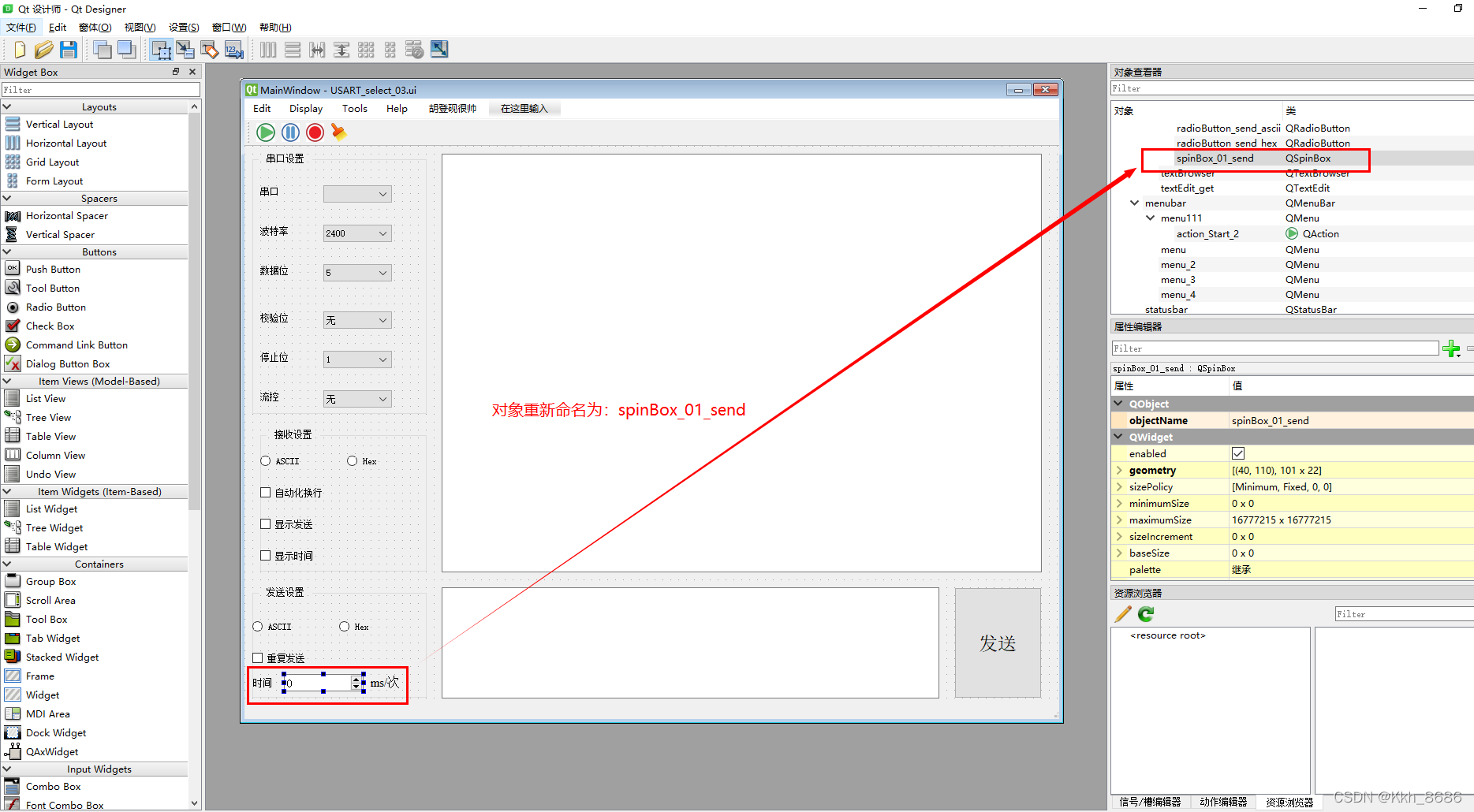
(5) Pyqt5 series tutorials: use pychart to design the internal logic of pyqt5 in the serial port assistant parameter options (II)

点云SSD模型

MIMO-OFDM无线通信技术及MATLAB实现(2)-SISO下的室外信道模型
随机推荐
MIMO-OFDM無線通信技術及MATLAB實現(2)-SISO下的室外信道模型
Detection model of 2D target detection overview (2)
xcode编译 build号自增
Li Hongyi machine learning 2020---p12 brief introduction of DL & p15 why DL
Non parametric statistical learning for urllc transmission rate control
Flink watermark
基于弹性云服务器的昇腾AI应用开发随笔【与云原生的故事】
Redis publishing and subscription
Data warehouse OLAP OLTP modeling method
(6) Pytorch deep learning: logistic regression (multi-layer and multi-dimensional feature input)
(四)PyQt5系列教程:使用Pycharm对PyQt5在串口助手参数选项进行内部逻辑设计(一)
Docker remote connection MySQL
Paper learning -- resource allocation in urllc with online learning for mobileusers
Neural networks: a review of 2D target detection
Li Hongyi 2020 machine learning -- P11 logistic progression
二分图
Realization of data warehouse technology
PyQt5 使用自定义ToolTip解决QTableWidget数据显示不全问题
Five basic data types of redis (super detailed)
李宏毅2020机器学习笔记---P10 Classification