当前位置:网站首页>Process and planned task management
Process and planned task management
2022-07-20 10:25:00 【1701y】
Catalog
Difference between process and thread
top Shortcut keys of full screen operation interface
View relevant configuration files
Special representation of time value
Check the process
Kernel functions : Process management 、 memory management 、 file system 、 Network function 、 The driver 、 Safety function, etc
For all operating systems , All have basic functions
Program
Save on hard disk 、 Executable code and data in media such as CD
Statically saved code
process
stay CPU And the program code running in memory
Dynamically executed code
Father 、 Subprocesses ( Each program can create one or more processes )
Difference between process and thread
Thread running under process
A process can contain multiple threads
Multiple threads can share data
PS command
ps -aux
a: Display all processes on the terminal , Include other users' processes
u: Represents the user who lists the processes
x: Show all terminal processes
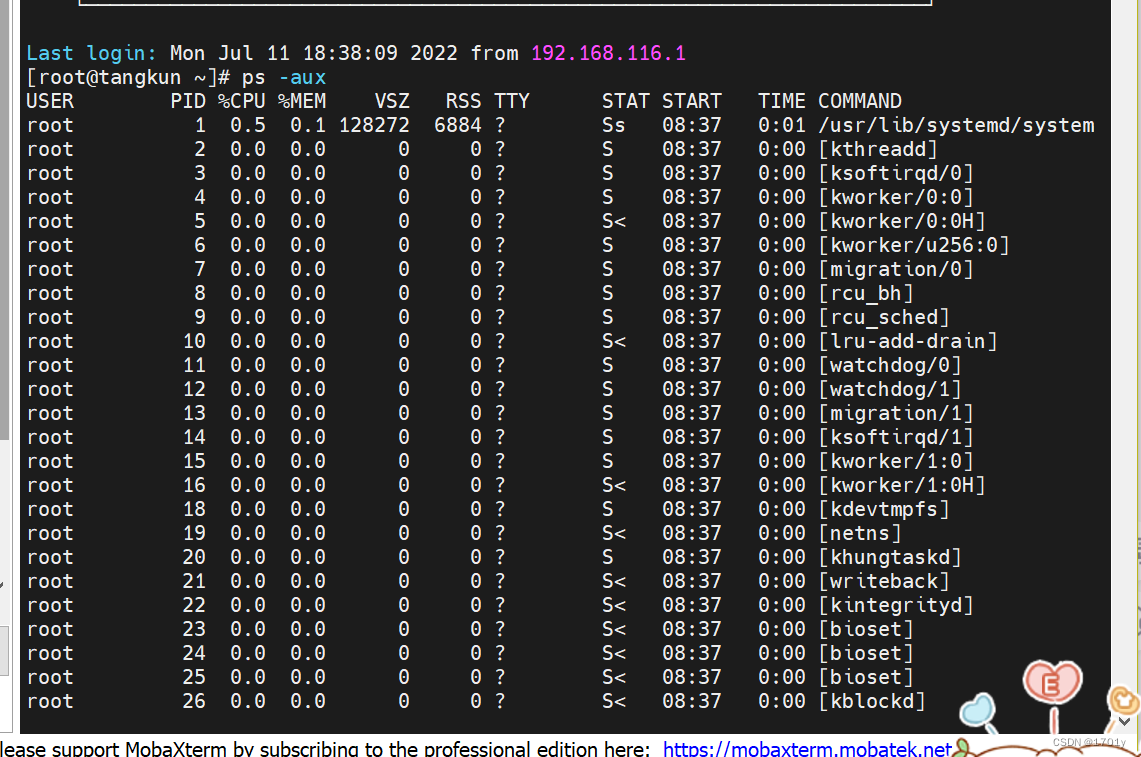
USER : The name of the user account that started the process
PID : The number of processes in the system ID Number , It is the only one in the system of the day .
%CPU : upc Percentage occupied
%MEM : Percentage of memory used
VSZ : The amount of virtual memory used by the process (KB)
RSS : The amount of physical memory consumed by the process (KB)
TTY : Indicates which terminal the process is running on . Processes that are not started from the terminal are displayed as ?
STAT : The state of the process (D: Non terminal sleep state R: Running state S: In a dormant state , Can be awakened
T: Stop state , It may be suspended in the background or the process is in trace debugging state Z: Zombie process
The process has been aborted , But some programs are still in memory )
START: Time to start the process
TIME : The process Zhaoyong CPU Time for
COMMAND: The name of the command that started the process
ps -elf
-e: The system displays all your progress information
-l: Use long format to display process information
-f: Display process information in full format

F : The system token that the kernel assigns to a process
S : State of process
UID : The user who started these processes
PID : Process of process ID, Every process has a unique PID
PPID : The process number of the parent process ( If the process is started by another process )
C : In the life cycle of a process CPU utilization
PRI : Priority of the process ( The higher the number, the lower the priority )
NI : Humility value is used to participate in determining priority
ADDR : The memory address of the process
SZ : If the process is called , The approximate size of the swap space required
WCHAN: If the process is dormant , The system function name in sleep is displayed
STIME: System time when the process started
TTY : The terminal device when the process starts
TIME : The cumulative amount required to run the process CPU Time
CMD : The start command of the process
add grep You can check whether the program is running
TOP command
View process dynamic information

Express meaning
start :
8:59:15 : Current time
up 21min : The time the system runs
1 user : Number of current login users
load average : System load , The average length of the task queue . The three are 1min ,5min ,15min
The average from minutes ago to now
Tasks : System task information :total The total number of processes ;running, Number of running processes ;
sleeping Number of dormant processes ;stopped Number of processes aborted ;zombie The number of dead and unresponsive processes
%CPU Occupancy information :us User occupied ;sy Kernel occupancy ;ni Priority scheduling occupies ;id Free CPU;wa I/O Waiting for occupation
hi Hardware interrupt occupation ;si Software interrupt occupancy ;st Virtualization takes up .
KiB Mem Memory :total Total memory space ;free Free memory ;used Used memory ;buff/cache Physical memory and swap Total number of stored buffers .
KiB Swap :total Total swap space ;free Space exchange space ;used Used swap space ;avail Mem Available physical space
PID : process ID
USER : User name of the process owner
PR : priority
NI : Humility value Negative value indicates high priority , A positive value indicates a low priority
VIRT : Total virtual memory used by the process , Company kb
RES : The amount of physical memory used by the process , Company kb
SHR : Shared memory size , Company kb
S : Process status
%CPU : Last updated to now CPU Percentage of time used
%MEM : Percentage of physical memory used by the process
TIME : Used by process CPU The sum of time , Company 1/100 second
COMMAND: Command name , Command line
top Shortcut keys of full screen operation interface
s : Change the refresh time , Press space to refresh immediately Default 3s Refresh once
p : Press CPU Sort
M : Sort by memory
T : Sort by time
P : process IP, Check the status of a process
N : Sort according to startup time
1 : Show the... For each kernel CPU Usage rate u/U: Specify the user to display
h : You can get top Online help information for the program
q : sign out
pgrep command
-l : At the same time, output the corresponding process name and PID
-U : Query the process of a specific user
-t : Designated terminal

pstree command
View the process tree
-p : You can list the corresponding PID Number
-u : You can list the corresponding user names
-a : You can list complete command information 

Control process
The process startup mode is manual startup and scheduling startup
Manual start
The front desk starts : The user enters the command , Direct execution of the program
Background start : In the command At the end of the line Join in “&” Symbol ( The reason for putting it in the background is that some programs are relatively large , May not finish , So it should be run in the background , In this way, other operations can be carried out at the same time .)

Restore the background process
bg : You can resume the task of the command suspended in the background , Continue to execute in the background
fg : You can restore the background task to the foreground .
CTRL+Z You can put the task in the background and pause

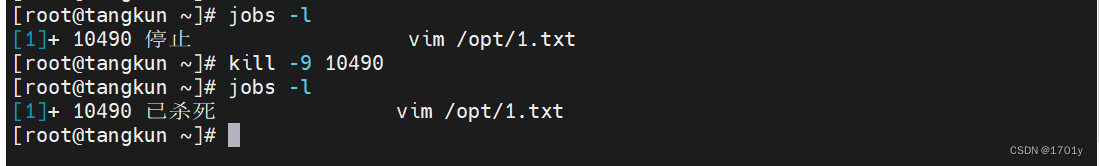
jobs
View the list of tasks in the background
-l The process can be displayed at the same time
kill
The specified information can be sent to the program
1 (HUP): Reload process .
9 (KILL): Kill a process .
15 (TERM): Normally stop a process .( The default value is )
killall command
Terminate the process by its name
When the system needs to end multiple processes with the same name , This command is much more convenient
Can directly kill all at the same time vim The process of

pkill command
According to the name of the process 、 The user running the process 、 The terminal where the process is located, etc. to end the process
-U : Designated user
-t : Designated terminal
for example
pgerp -l -U “zhangsan” Find out the process of user Zhang San
pkill -9 -U “zhangsan” Specify the user to kill the process
Planning task management
at
date Display current time
at 16:10 ( Only write the time to indicate the day )
enter
Then write down the commands that need to be executed And then go back
ctrl+d Submit run ctrl+c Exit not run
crontab command
According to the preset time period ( Time sharing day month week ) Repeat the user specified command operation
It belongs to periodic tasks
-e Start planning tasks
-l View scheduled tasks
-r Delete scheduled task
View relevant configuration files

Special representation of time value
* This is an arbitrary range of time
, Represents multiple discontinuous time points of an interval
- Represents a continuous time range
/ Specify the time and frequency of the interval
minute :0-59
Hours :0-23
date :1-31
month :1-12
week :0-7(0 and 7 It means Sunday )
Configuration format
minute Hours date month week command
Let's experiment
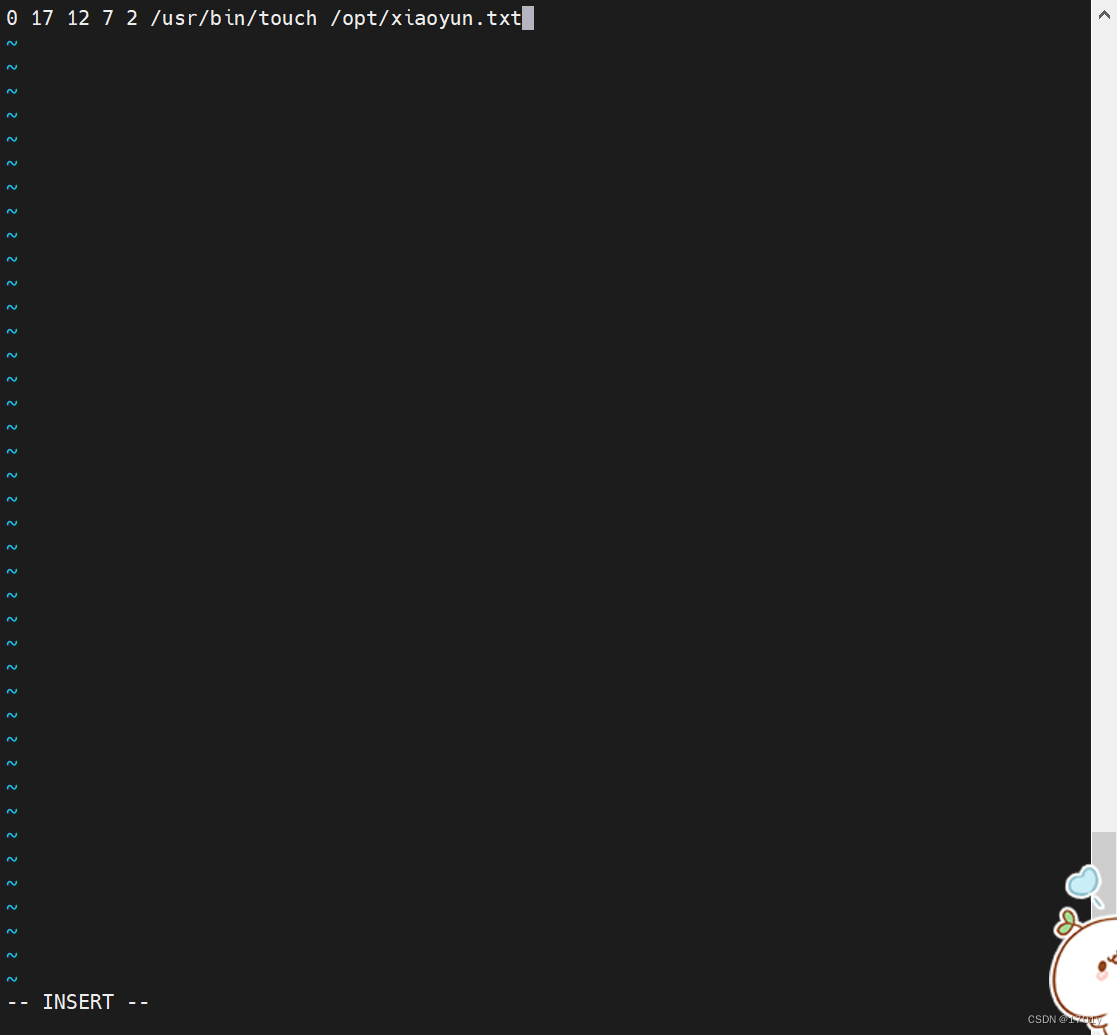
If you don't know the absolute path of the command Can pass which+ Query by command name
Create an annual 7 month 12 Week of the th 2 17 spot 0 branch stay /opt Create one in the directory xiaoyun.txt file

边栏推荐
- ceph详解之mon_osd_max_split_count
- ZTE ZXR10 5250 command hints
- Nju Nanjing University elevation course: battlecity
- 在线问题反馈模块实战(七):安装部署swagger2
- 第三天实验
- RedHat 7 replace Yum source
- Insert cross column pictures under the title of the home page of latex IEEE paper, and solve the footnote problem
- 使用 gst-launch 小记
- Notes on using GST launch
- openstack queens创建固定IP虚拟机
猜你喜欢

Network Security Learning (XXIV) transport layer protocol

Network Security Learning (XXIII) firewall

第三天实验

DHCP原理与配置

Overview of key core technologies of intelligent operation and maintenance aiops worth seeing
![[resource record] VAE learning notes](/img/b4/a357968335d1d02cc9af1e1d1f8281.png)
[resource record] VAE learning notes

ZABBIX automatically discovers and monitors CEPH OSD

静态路由工作原理与配置

Variable influence notes from UCB CS 285 Sergey Levine

Scala案例(伴生对象)
随机推荐
zabbix 自动发现并监控ceph osd
在线问题反馈模块实战(七):安装部署swagger2
系统安全和运用
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'cv2'
Server hardware and RAID configuration and Practice
论文笔记:Look Back and Predict Forward in Image Captioning# Look Back and Predict Forward in Image Capti
FIO test hard disk performance
The difference between overload and override
六大集合List、Set、Map、Queue、Deque、Stack的遍历方式总结
Network Security Learning (XXIII) firewall
【记录资源&想法】如何评估聚类效果 i.e. Clustering performance evaluation/Clustering validity assessment.
黑马程序员线程通信【了解】
VLAN概述
CEPH detailed mon_ osd_ max_ split_ count
【资源记录】Invertible Neural Networks 可逆神经网络是什么,与VAE,GAN的关系;什么是Bits per pixel,Bits per dim
黑马程序员方式一实现多线程
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'gflags'
tensorflow tf.where使用方法,大于某个值为1,小于为0
[resource record] what is reversible neural networks and its relationship with VAE and Gan; What are bits per pixel, bits per dim
传输层协议
