当前位置:网站首页>C language 2022 Shanxi upgraded C language knowledge points
C language 2022 Shanxi upgraded C language knowledge points
2022-07-21 21:10:00 【Guo Guo's learning journey】
Catalog
3、 ... and 、 Selection structure
Four 、 Three circulation structures
8、 ... and 、 Structure 、 Shared body 、 enumeration
One 、 The basic definition
One 、 Concept
1. machine language ( The computer can directly compile and recognize ) link --> Semiotic language ( assembly language ) compile --> High-level language ( compile );
2. compiler : After a compilation, there is no need to recompile [c Language 、c++、java];
3. Interpreter : Every time, it needs to be reinterpreted [pyhton];
4. Program structure : Sequential structure 、 Selection structure 、 Loop structure ;
5. The procedures are all based on main() The function starts executing , There is and only one main function , Then proceed from top to bottom ( When encountering a cycle, do a cycle , When you meet a choice, make a choice , When you encounter a function, do a function );
6. The data of the computer is stored in binary form in the computer ;
7.C Keywords of language (auto break case char const continue default do)
①. Data type key : char double enum float int long short signed struct union unsigned void
②. Control statement keywords : for do while break continue return if else goto switch case default
③. Storage type key : auto extern register static
④. Other keywords : const// Declare read-only variable sizeof typedef volatile// Variables can be changed implicitly in the execution program
Two 、 Often test concepts
1. Preprocessing #define PI 3.14 No c Part of the language , No running time , Without a semicolon ,c A program compiled in a language is called a source program , It uses ASCII The code is stored in a text file ;//#define PI 3.14; This writing is wrong , Semicolons should not appear in preprocessing
2. Every c In language programs main There is and only one function ;
3. Functions can be called nested, but not defined nested ;
4. The implicit storage type for variables is auto;
5. The implicit storage type of the function is extern: Expand the scope ;
6. The main function can be divided into two parts : Function description part and main function body ;

- Any non main function can call any other non main function ;

( A function that directly or indirectly calls the function itself is called a recursive call of a function )
7.c The steps and methods of language execution :.c[ Source program ]--- compile --->.obj[ Target file ]--- Connect --->.exe[ Executable file ];
(.c--->.obj--->.exe)//.c and .obj Files can't run ,.exe Before running, compile , Back connection , Last run ;
8.c A program written in is called a source file , Also known as compilation unit ;
9. If a statement has only one semicolon ; This statement is empty ;
10. identifier :
(1) Must consist of alphanumeric underscores , The beginning can only be letters or underscores ;
(2) Identifiers are divided into keywords 、 Predefined identifiers 、 User identifier ;
(3) Keywords cannot be used as user identifiers ( Identifiers defined by users themselves are called user identifiers );
(4)main、define、scanf、printf None of them are keywords (!!!);
(5) Confuse If Can be used as an identifier ( because if The initials are capitalized , So it's not keywords );
(6) Predefined identifiers are define、scanf 、printf、include;
(7) Predefined identifiers can be used as user identifiers ;
11. The difference between a statement and an expression is whether there is a semicolon , Statements have semicolons , The expression doesn't have ;
12. The operand of an expression can be a constant 、 Function call 、 Variable ;
13.c The basic unit of a program is a function ;
3、 ... and 、 Algorithm
1. Characteristics of the algorithm : Fineness 、 deterministic 、 effectiveness 、 There is one or more outputs , Zero or more inputs ;
2. How to describe an algorithm ?
Express the algorithm in natural language 、
Use the program flow chart to represent the algorithm 、
- S The flowchart represents the algorithm 、
Using pseudocode to represent algorithm 、
Express algorithm in computer language ;
3. Algorithm : No input , But there must be output ;
Four 、 Hexadecimal conversion
1. All hexadecimal conversions are converted to binary and then to other hexadecimal ;
2. Octal to binary according to 3 Bit calculation , 16 bits to binary according to 4 Bit calculation ;
3.c There are only eight in the language 、 Ten 、 Hexadecimal , No binary . But when it's running , All the bases must be converted to binary for processing .
4. Regulations
A.c The language stipulates that octal should start with 0 start .018 It's illegal. , Octal No Yes 8 Meet 8 Into the 1;
B .c The language stipulates that hexadecimal should start with 0x start , Output lowercase %x, Output uppercase %X;

Two 、 Sequential programming
One 、 Constant
1. Integer constant :
134( Decimal number )、 034( Octal number )、 0XA2( Hexadecimal number )、
45L( Long plastic surgery )、 7UL( Unsigned long shaping )、8U( Unsigned shaping )
U representative unsigned L representative long
- Real constant :
1.3(double type )、 1.5f、1.5F(float type )、
1.4e3( The index means )、1.4E-3( Capitalizable );
float Effective precision 6 position double Effective precision 15 position ;
a. 2.333e-1 It's legal , And the data is 2.333*10 Primary
b. Test formula :e front e There must be a few in the future ,e Must be an integer after
3. character constants :‘a’( character a)、 ‘\n’( Escape character )、 ‘\101’(\ Followed by octal numbers )、 ‘\x46’(\x Followed by hexadecimal ) example :‘\n’ ‘\t’ ‘\\’ ‘\’ ‘\0’;
Possible mistakes in the exam :
a. The wrong form of a single character :‘65’“1”;
B. Characters can be used for arithmetic operators :‘0’- 0 = 48;
c. How to convert upper and lower case letters :‘a’- 32 = ‘A’;
d.‘a’ Of ASCII Code for 97,‘A’ Of ASCII Code for 65,‘0’ Of ASCII Code for 48‘ ’( Space ) Of ASCII Code for 32‘\0’ Of ASCII Code for 0;
e.‘z’-‘a’= 25;// The difference between letters 25 position ;
4. String constant :
“abcde” Hide a behind ‘\0’;
example :strlen(“abcde”)=5;
sizeof(“abcde”)=6;
strlen(“abcde\0abcde”)=5 //strlen encounter \0 end
sizeof(“abcde\0abcde”)=12;
strlen(“a\nb\t\101dc”)=7 a \n b \t \101 d c =7;
5. Symbolic constant #define PI 3.14 // Remember that there is no semicolon after pretreatment
(1) The definition of constants can also be used const Definition for example :const int a;// Defined a constant a Constant a Will open up space ;
(2) The value of a constant cannot be changed ;
Two 、 Variable :
Define before use .// The purpose of defining variables : Make room for variables in memory .
(1)int (4Byte) short=(short int)(2Byte) long(long int)(4Byte)
char(1Byte) float(4Byte) double (8Byte)
1.. Reference type ( Derived type )
Array :( An array type * Number for example int a[10]=int *10=(40Byte))
The pointer :( stay 64 In a bit computer 8Byte,32 Bit computers account for 4Byte)
Structure :(struct) Separate space for each byte ;
Shared body :(union) Shared memory space , Total memory opened by the largest member ;
2.. Function type
(1) Enumeration type (enum): Limited plastic surgery
(2)void Empty type
(3) Unsigned type :unsigned
example :
(1)unsiged long int a=10;// Unsigned long
(2)unsiged b=10;// Unsigned shaping
(3)unsiged int c=10;// Unsigned shaping
(4)unsiged long d=10;// Unsigned long shaping
3. Assignment operator 、 Arithmetic operator 、 Relational operator 、 Logical operators
The remainder operator %
Be careful :% The left and right sides must be integers , The divisor is negative Whether the divisor is positive or negative , The results are all negative
example : -17%3=-2 17%3 =2 17%-3=2 -17%-3=-2
357%10=7 357/10=35 357/10%10=5
- Arithmetic expressions :+ 、 - 、* 、/
- Be sure to pay attention during the exam 3/2=1;
- 3.0/2=1.5
- Assignment compound expression
int a=2;
a*=2+3// Equivalence and a=a*(2+3)
Be sure to pay attention to , In the first 2+3 Put parentheses on ,(2+3) recompute ;
- ++、- - expression ( Self adding and self subtracting expression )
formula :++ Add before use ,++ First use later +( Subtraction is the same thing )
- Comma expression
‘ ,’ The lowest priority , Output the value after the last comma
example :
printf(“%d”,1,2,3);// The output is 3;
z=(2,3,4)// The whole assignment expression z The received value is 4;
z=2,3,4// The whole thing is a comma expression z The received value is 2;
- Logical operators
Logical expression :&&( And )、||( or )、!( Not )
!> && >||( Priority level )
c True use and non use in language 0 To express , False use 0 To express ;// Not 0 It can be expressed as an integer 、 decimal ;
For relational operators : The result represented by logical operators :1 It's true ,0 For false ;
stay c Execute expressions in language a&&b, If && False before ,&& Do not execute after , If && The former is the real talent, and the latter ;
stay c Execute expressions in language a||b, If || The former is true ,|| Do not execute after , If || The former is false before the latter ;
notes : Empty statements cannot be executed at will , Will lead to logical errors ;
The note is not c Language , No running time , There's no semicolon , You can't nest !
- Conversion between different types
int+int=int char+int=int
As long as there are floating-point types involved in the operation , All for double type
- Cast
example (int)((double)(7/2)+3.5) The value of is 6
Calculate first 7/2=3 3+3.5=6.5 transformation int=6
4. Standard type input and output
printf(“a=%d\nb=%d”,1,2);// The result is a=1
b=2
Standard input and output types :( Positive and negative can refer to the number axis , Left minus right positive )
%d( Shaping input and output decimal numbers )、
%3d( The input and output occupy three spaces on the right )、
%-3d( The input and output occupy three spaces on the left )、
%c( Input and output characters )、
%s( Input and output string Just need the first element address )、
%e( Input output exponential form )、
%o( Input output octal )、
%x( Input / output hex )、
%u( I / O unsigned form )、
%f( I / O floating point )、
%lf( Input double Type use )、
%hd ( Output shaping )、
%p ( Output address format )、
%10.5f( Proportion of output 10 grid The decimal point is one place Keep the precision of five decimal places Four Round to the right )、
%-10.5f( Proportion of output 10 grid The decimal point is one place Keep the precision of five decimal places Round to the left );
%%( Output one %)、
![]() %#o( Octal with leading )、
%#o( Octal with leading )、
![]() %#x( Hexadecimal with leading );
%#x( Hexadecimal with leading );
Be careful : At the time of input , Input in strict accordance with the input format
example :scanf(“a=%d”,&a);// When inputting, you need to input a=1;
In this way, we can assign a value to a;
When inputting real data ,float According to %f Input ,double According to %lf Input ;
When there is a definition int a,b;
scanf(“%3d%d,&a,&b);// Input 12345 123 The received a=123,b=45;
scanf(“%d%3d,&a,&b);// Input 12345 123 The received a=12345,b=123;
notes :char s[30],s2[30];
Use scanf(“%s %s”,s,s1);// Spaces must be used between , Do not use other characters ;
Common output functions :
getchar()、// Receive input of one character ;
putchar( )、// Output a character ;
gets()、// Enter a string ;
puts();// Output a string ;
How to put two variables a,b The value of the swap ?a=t;a=b;b=t;
a=a^b;b=a^b;a=a^b; Bitwise XOR ;// To eight bit binary operation

How to put two variables a,b Sort from small to large or from small to large , This formula has generalization significance !
3、 ... and 、 Selection structure
- if...else...
1. about if...else if...else... Only the conditions that are satisfied first can be selected to execute , Others are not implemented ,else Always closest to him if Connected to a ;
notes :if(a>5);// This sentence is empty , There is only one semicolon ;
- Pay attention to differences :
- if(a>b)t=a;a=b;b=t;
- if(a>b){t=a;a=b;b=t;}
These two sentences mean different things , Pay attention to distinguish ,if If there is no {}, Then his executive sentence can only be followed by his first sentence ; end
// therefore , In programming or problem solving , Be sure to see if The scope of the statement ;
- Conditional expression (c The only ternary operator in the language )
The general form is :( expression 1)? expression 2: expression 3;
The execution direction is from right to left ;
formula : Before the truth and after the falsehood ;
stay C In language , result 1 and result 2 Must be of the same type
example

- switch sentence
- First of all, we should clarify his format

- The process of execution must be understood ;
- Yes no break The difference between :
- No, : As long as there is one case To satisfy the , From case Start and continue
- Yes : encounter break Just jumped out switch sentence ;
break stay c Language is breaking up , make a clean break with ;
- switch Only with break Use it together ,continue Can not be ;
- Since everyone knows switch The nature of , Then let's do a problem

Is this correct ?
The answer is right ,continue It's for the circulatory body , about switch No effect
And the output result is 1*3*5*
switch It is a compulsory exam every year , Be sure to use skilled
Four 、 Three circulation structures
- while loop :while( The loop condition ){ The loop body ;}
- do while loop :do{ The loop body }while( The loop condition ;);// Remember that there is a semicolon at the end
- for loop :for( initial value ; The loop condition ; Cycle increment ){ The loop body ;}
- The concept of circulation
1.while Circulation and do while Difference between cycles :do while Will unconditionally cycle once and then judge ;
2.for There are two semicolons in the loop ;
3. When writing programs, you must pay attention to writing cycle conditions , Otherwise, it will become an endless cycle ;
3、 ... and 、break And continue The difference between
1.break:break It means to break , Destroy the whole cycle , So I met break Just jump out of this layer ;
2.continue:continue It means to continue , But to end this cycle , The remaining statements in the loop body are no longer executed , Jump to the beginning of the cycle , Then judge the conditions , Continue to cycle ;
5、 ... and 、 Array
One 、 The concept of array
1. Basic concept of array : A continuously stored collection , All element types must be the same
[ Basic data type 、 Structure ];
give an example :struct Stu{....};struct Stu a[10];
int a[10];
- Only constants or expressions can be used to define the number of arrays , It can't be a variable ;
for example int a[10];
int a[5+5];
#define N 5 int a[N+4];
int n=10; int a[n];// Wrong definition of array method
Two 、 One dimensional array
1. Definition : data type Array name [ Constant expression ];//auto int a[10];
2.struct Stu{....};struct Stu a[10];// Array a Every element is Stu Type of
a Is the address of the first element of the array ;10 Represents the number of array elements ; Every element in the array In memory They are stored continuously ;
- Initialization of one-dimensional array and use of array :4 In the form of .
- int a[10]={...};// Initialize the value for each element of the array
- int a[10]={0};// All elements of the array are initialized to 0
- int a[10];a[0]=1;// Assign initial values to one or more elements of the array , The other elements are uncertain values
- int a[10]={1,2};// Assign initial values to one or more elements of the array , The rest of the elements are 0
Be careful :int a[5]={1,2,3,4,5,6}; It's wrong. , The subscript crossing the line ;
- Two dimensional array
- int a[3][4]; Altogether 3*4(12) Elements , Every element is int Type of , The array name is the address of the first element of the array ; This array has three rows and four columns ;
- Each element of a two-dimensional array is stored continuously in memory by row ;
- Initialization of 2D array :
- int a[3][4]={...};// Initialize the value for each element of the array
- int a[3][4]={1,2};// Assign initial values to one or more elements of the array , The rest of the elements are 0
- int a[3][4]={0};// All elements of the array are initialized to 0
- int a[3][4];a[0][0]=1;// Assign initial values to one or more elements of the array , The other elements are uncertain values
- int a[][4]={...};// Assign initial values to each element of the array , Omit the number of lines
- A character array
- Array of strings
(1) The way of string input and output :
Input gets();// You can receive any string with a space in the middle
scanf();// Cannot receive strings with spaces in the middle. Use spaces as spacers
Output
puts();
printf();
2. Two dimensional array of strings
char a[4][10]={"aaaa","bbbb","cccc","dddd"};// Every line in the array is a string
- Character array common functions
From header file #include<stdio.h>
a=getchar();// Receive a character on the keyboard and assign it to a
putchar(a);// Output a Stored characters
gets();// Receive a string
puts();// Output a string
#include<string.h>// Remember to add header before use
strcat( character string 1, character string 2);// take 2 Connect to 1 after
strcpy( character string 1, character string 2);// take 2 Copy to 1
strcmp( character string 1, character string 2);// Compare 1 and 2 Size ,
Such as a string 1> character string 2 Returns a positive integer ,
character string 1== character string 2 return 0,
character string 1< character string 2, Returns a negative integer ;
strlen(a);// A character array a The length of ( barring ‘\0’);
sizeof(a);// Need header file #include<stdio.h>, Array a Occupied memory space ;
strlwr(a);// Turn all uppercase letters in the character array into lowercase ;
strupr(a);// Turn all lowercase letters in the character array into uppercase ;
6、 ... and 、 function
- The concept of function
- A function represents a function module , yes c The basic unit of language ;
- One c A program is made up of one or more program modules , Each program module acts as a source file ; A source file is composed of one or more functions and other contents .
- All functions are parallel , Mutually independent ;
- Functions are divided into library functions (string.h or math.h) And user defined functions ;
- The form of function is divided into nonparametric function and parametric function ;


- Calling procedure of function
- The formal parameter variable specified in the definition function , When there is no function call , They do not occupy storage , Only when a function call occurs , Only the formal parameters in the function are allocated to the memory unit ;
- Argument and formal parameter passing :
- When all variables : Single value transmission ;
- When all are arrays : One way address delivery ;
- If the function has return sentence , You can use the return Bring the function value back to the main function ;
- After call , The formal parameter unit will be released ;
notes : When defining a function with a return value , We should avoid the following situation :

!!! When a<0 when , The return value of the function is uncontrollable ;
notes : Arguments can be constant 、 Variable or expression , But they are required to have certain values 、 Assign the value of the argument to the formal parameter variable when calling , If the parameter is an array name , Then the address of the first element of the array is passed ;
- Nesting of functions
- You cannot define another function within a function , But you can call another function ;
- Functions cannot be nested , Calls can be nested
- Recursion of a function
- In the process of calling a function, it occurs to call the function itself directly or indirectly , Become a recursive call to a function ;
- A recursive function includes two necessary conditions :1. Exit of function ;2. Recurrence of functions ;

- Global variables and local variables ( Internal variables )
- Global variables are all valid in this source program from the definition ;
- Local variables are only valid in the defined function body ;
- In the same function, if there are global variables and local variables with the same name , Global variables are masked , Local variable priority > Global variables
Ingenious notes : The smaller the scope ; The greater the power ;
example : There are five classes in grade three , There are two people named Zhang San in junior high school , But in a class , There is only one Zhang San , So I went to a class , Zhang San is only effective for Zhang San in this class , So in local variables , Global variables are masked ;
- All variables defined in a function are local variables ( Unless otherwise stated ), No default ;
- All variables defined outside the function are global variables , Default assignment 0;
example : The integer global variable is assigned 0;
The floating-point global variable is assigned 0.0;
Assign a value of ‘\0’;
All array global variables are assigned 0;
- How variables are stored
- Automatic variable :auto: Variables defined when not declared are automatic variables ;
At the end of the calling function , These variables are automatically released ; Keywords can be omitted when defining ;
- Static variables :static: Variables will not be released after use ; Continue saving values
- Register variables :register: Variables stored in registers , It can be used to improve the operation speed ;
- External variables :extern: The default type of the function
The examination site of this chapter :

The declaration of function should pay attention to the type of function , Name of function , The parameter type of the function ;

Remember some library functions that you often use :
Library functions in the contents of the array
#include<math.h>// Remember to add header
abs()// Find the absolute value ( plastic );
fabs()// Find the absolute value ( floating-point );
sqrt()// Find the square root ( The return type is double);
pow( , )//2 The three times of can be pow(2,3) To calculate ;
sin()// Find the value corresponding to the degree of trigonometric function ;
7、 ... and 、 The pointer
- The concept of pointer
1. A pointer is the address of a variable in memory ;
2. If there is a variable dedicated to the address of another variable , Called pointer variables ;
3. The pointer stores the address of another variable , The values of all pointer variables are Address ;
4. The general form of pointer variables
Type name * Pointer variable name ;
5. stay 64(32) The memory occupied by pointers in bit computers is 8(4) Bytes ;
6. A pointer variable can only point to variables of the same type ;
7. If you want to assign a value to a pointer variable , Then it must point to a variable ;
8. When the parameter of the function is pointer type , His role is to put a The address of the variable Pass to function ;
9. There are two ways to return the value of a function : adopt return Return value or use pointer to return value ;
Two 、 Notes on using pointer variables
1. What type of pointer variable points to what type of data ;
2. When defining a pointer variable , The pointer variable must be given an initial value, otherwise the wild pointer will appear and cause memory leakage ;
3. If a pointer variable is defined without an initial value assigned to NULL;
4. Pointer variables only receive addresses ;
5. Pointer variables do not receive constants ;
6. Pointers can perform relational operations 、 Subtraction , You can't add ;
*p++ It means to take out p The value of the pointer address and then the address plus 1;
++*p It means to take out p The value of the pointer address is then added 1;
(*p)++ It means to take out p The value of the pointer address and then add the value of the address 1;
*++p It means to first p My address plus 1, Then take out the value
*(p++) It means to take out p The value of the pointer address and then the address plus 1;
3、 ... and 、 Reference a string with a pointer
char *p// You can't be right *p assignment
char p[10]// You can re assign values to the array
Address of two-dimensional array : It will convert the row address into the address of the first element of the row, point to the pointer of the function and return the pointer value ;
Be proficient in using pointers to point to one-dimensional arrays and two-dimensional arrays ;

8、 ... and 、 Structure 、 Shared body 、 enumeration
- There are three ways to define a structure




ps: When initializing structure variables , To assign values to structure members one by one , Cannot skip previous member variables , And directly assign initial values to the following members , But you can only assign the first few , For the following unassigned variables , If it's numerical , It will be automatically assigned to 0, For character type , The initial value will be automatically assigned to NULL, namely ‘\0’;
- Array of structs
Every element in the array is a variable of the same custom type .
- Structure pointer : Defining a structure pointer can be used to point to each item of the structure array ;
Four 、 Type of community (union)
1. In some algorithms C In language programming , Several different types of variables need to be stored in the same memory unit . That is, using coverage technology , Several variables cover each other . This kind of several different variables occupy a memory structure , stay C In language , It's called “ Shared body ” Type structure , Abbreviation: common body , It's also called a consortium .
2. The general form of the common body :

- Key knowledge points
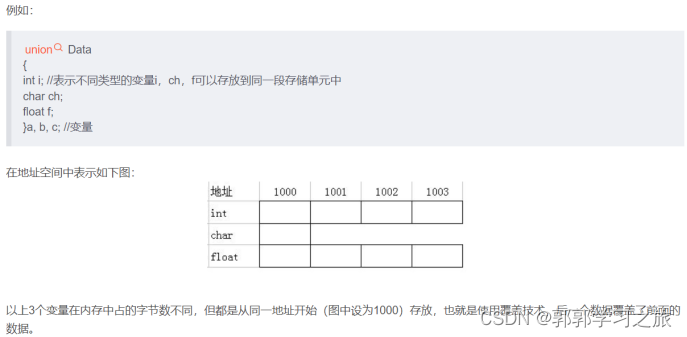
4. The active member in the common variable is the last member to be assigned , After assigning a value to a member in the community variable , The value in the original variable storage unit is replaced .
- The common body at any moment , Only one member is meaningful . also , Assign values to common variables , Only one variable can be assigned at any one time .
- The size of the community is the size of the widest basic member , But divide by the widest basic member size .
- Enumeration type (enum)
- Is a named set of integer constants
- Enumeration is not a number , But constant aggregate , That is, it may be one or more integer constants .
3. integer : Namely int , It means that he can't be float Other types .
constant : It shows that several numbers in this set cannot be changed .
- nickname (typedef)
1.C Language allows a new alias for a data type , It's like giving people “ nickname ” equally .
2. Use typedef The names that were nicknamed before are still valid ;
for example : Xiao Ming was nicknamed alarm , that “ Alarm ” It can also represent Xiao Ming ,“ Xiao Ming ” It can also represent Xiao Ming ;
Nine 、 file
- Concept of documents
- According to how the data is stored , Files can be divided into Binary and text file ;
- text file :ASCII file , Each byte stores one ASCII code Characters are easy to operate on characters . Such documents are in the form of EOF end .
- Binary : The data is stored according to its storage form in memory, which is convenient for storing intermediate results .
- The concept of flow
It is divided into character stream or byte stream
- file name
1. The composition of the document
- File path (2) File backbone (3) file extension
- Use file name
stay c In language ‘\’ For escape characters , So when writing a program, it needs to be written as ‘\\’
for example D:\str.doc For the file address to be used , It needs to be written as “D:\\str.doc”;
- The file pointer
- The file pointer actually points to a Structure Pointer to type , This structure contains : The address of the buffer 、 The position of the currently accessed character in the buffer 、 To the file is “ read ” still “ Write ”、 Is it wrong 、 Whether you have encountered the end of file information flag and other information .
- The general form of defining file type pointer variables is :FILE * Pointer variable name ;
- The file pointer comes from the header file #include<stdio.h>
- Open and close files
- The keyword to open the file is :fopen( file name ,“ How to open the file ”);

- The keyword to close the file is fclose( The file pointer );
- buffer : In order to improve the transmission efficiency ;
Ten 、 Preprocessing
- Macro definition #define

- Macro definition format
#define < Macro name / identifier > < character string >
3、 ... and 、 Description of simple macro definition
1. Macro names are usually capitalized ;
2. No points are added at the end of the macro definition Number ;
3. Macro definitions can be nested
4. Macro replacement is performed before compilation , Don't allocate memory , Variable definition allocate memory , Function calls are made when the compiled program runs , And allocate memory
5. Preprocessing is before compiling , One of the tasks of compiling is grammar checking , Preprocessing does not do grammar check check .
Four 、 Macro definition with parameters
1. There can't be spaces between the parentheses of macro name and parameter ;
2. Macro replacement does not calculate , No expression solving ;
3. There is no type in the combination of macros , There is no type conversion ;
4. Macro expansion does not take up running time , It only takes compile time , Function calls occupy running ;

边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
文件操作上(C语言)
Redis(六) - Redis企业实战之商户查询缓存
Solana项目学习(一):Hello World
Write a sushi MasterChef in Solana
Easy language learning notes (4) -- JS decryption, graphic verification code, slider, fishbone multithreading
Pawningshop: an implementation of NFT mortgage lending
Cannot convert from "boost:: shared\u PTR < pcl:: rangeimage >" to "const std:: shared\u PTR < const pcl:: pointcloud < pcl:: pointwit"
[intranet penetration] OpenSSL rebound traffic encrypted shell
并发编程(二十一)-ReentrantLock 中断原理
Redis(七) - 封裝Redis工具類
Attack and defense World Web Zone difficulty level: 3 (ics-05, MFW, easytornado)
25. [method of judging whether it is a prime number]
[file upload bypass] - Secondary rendering
并发编程(二十六)-ReentrantLock应用
易语言学习笔记(三)
佛萨奇2.0-Metaforce原力链上操作抢跑教程
[vulnerability recurrence] cve-2022-22954 VMware workspace one access vulnerability analysis
[intranet penetration] MSF rebound traffic encryption session
Rust short notes: solutions to four different quoted variables
【内网渗透】cobaltstrike流量加密


![[PHP code audit] Introduction analysis of vulnerabilities in Pikachu shooting range](/img/23/bb16865d56129e1f53bbd2a9348879.png)


![[file upload bypass] - Secondary rendering](/img/4b/d7ad3c7b693c2d30c99173c96f4669.png)



