当前位置:网站首页>leetcode:460. LFU least commonly used cache
leetcode:460. LFU least commonly used cache
2022-07-20 22:38:00 【Oceanstar's study notes】
Title source
Title Description



class LFUCache {
public:
LFUCache(int capacity) {
}
int get(int key) {
}
void put(int key, int value) {
}
};
title
The size of the cache is limited , When the cache is full, new elements need to be added , You need a way to delete some elements from the cache , The deletion strategy is the elimination algorithm of cache . There are two commonly used elimination algorithms :
- LRU(Least Recently Used) Least recently used algorithm , It is based on Time Dimension to select the elements to be eliminated , That is, delete the elements that have not been accessed for the longest time .
- LFU(Least Frequently Used) The least commonly used algorithm recently , It is based on frequency Dimension to select the elements to be eliminated , That is, delete the element with the lowest access frequency . If two elements have the same access frequency , Eliminate the elements that have not been accessed for the longest time .
in other words LFU When eliminated, two dimensions will be selected :
- Compare first frequency , Select the element with the least frequent access ;
- If the frequency is the same , Then press Time Dimension eliminates the oldest element .
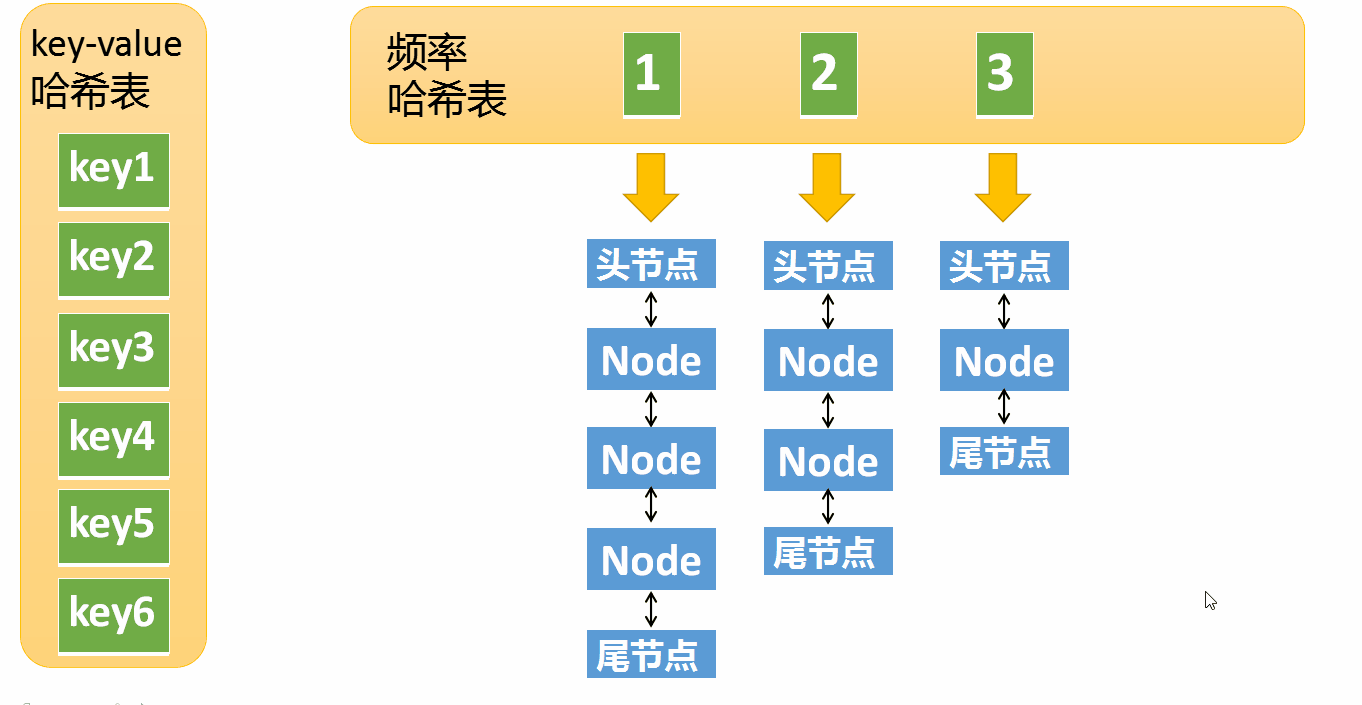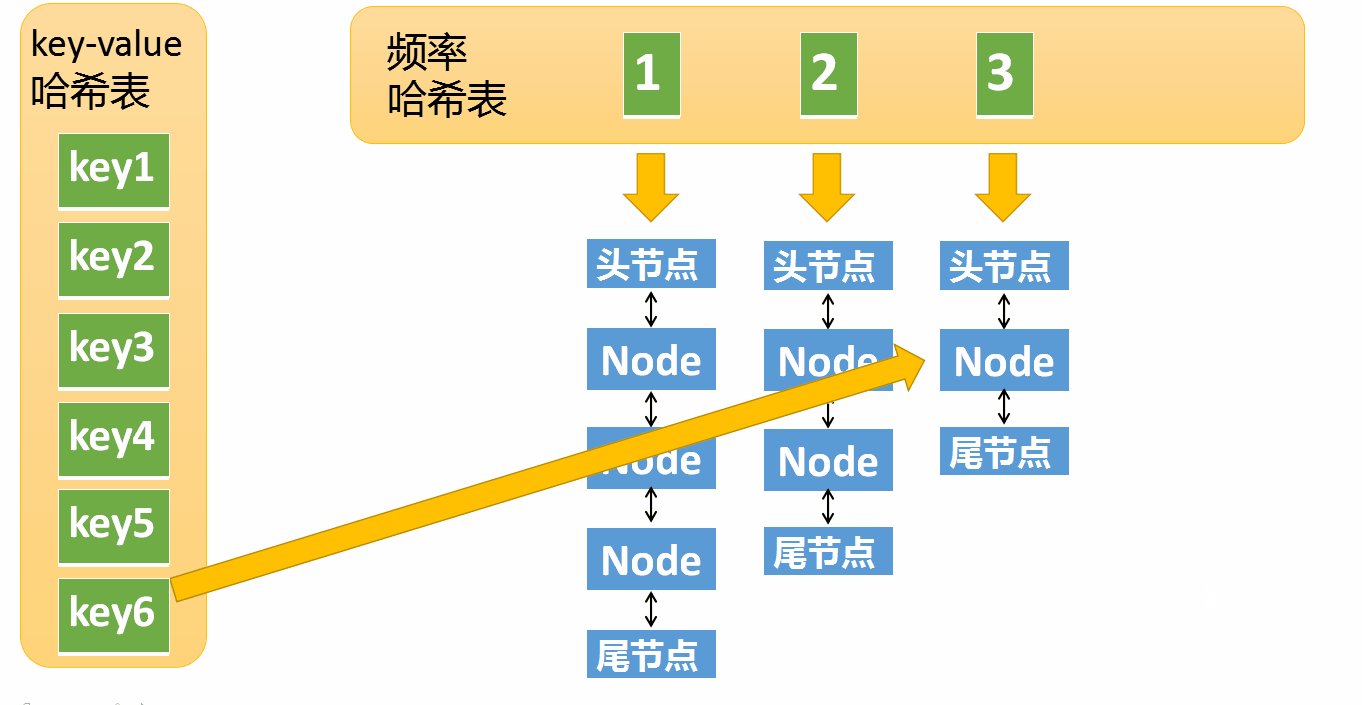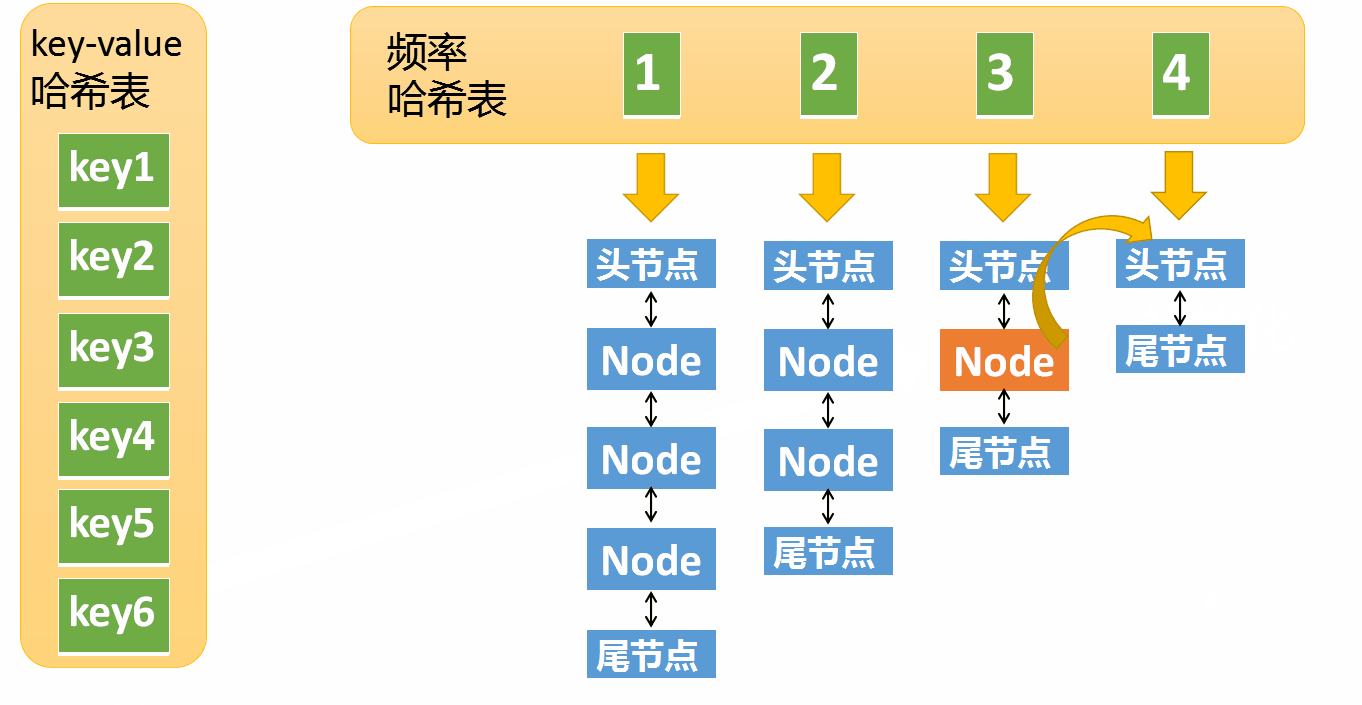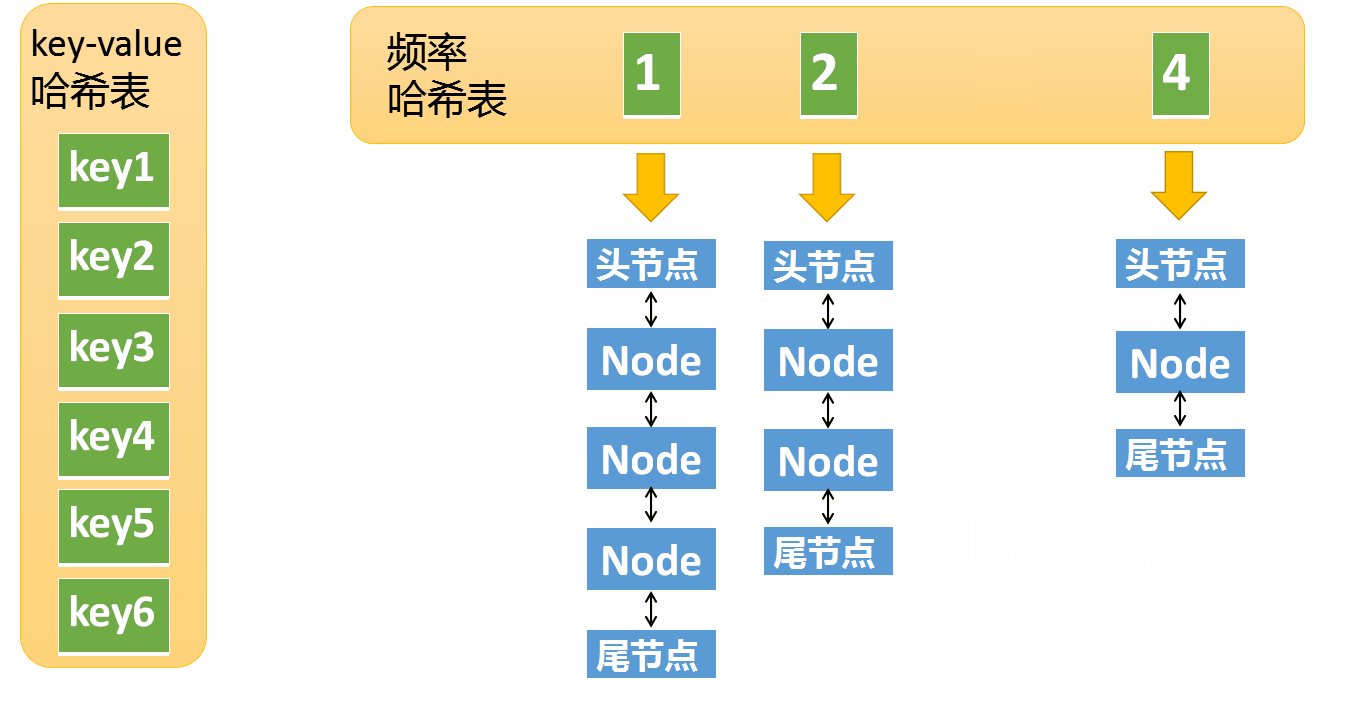
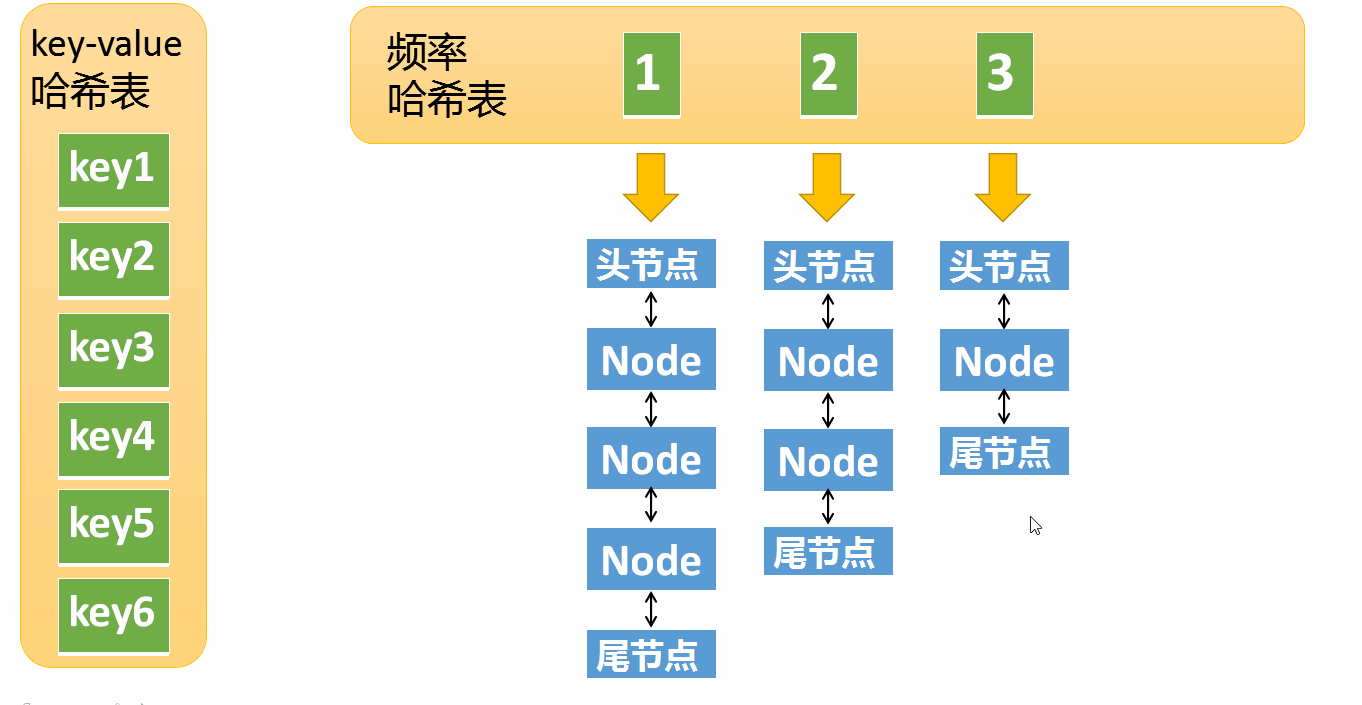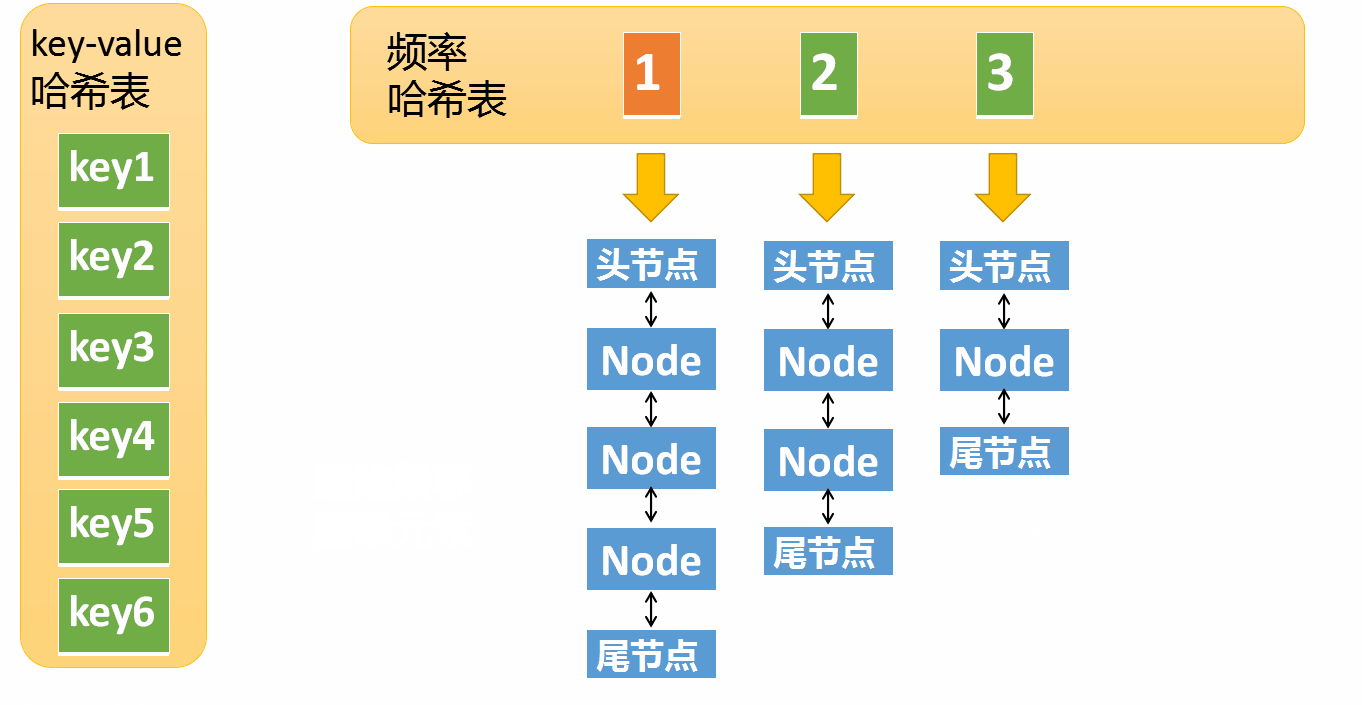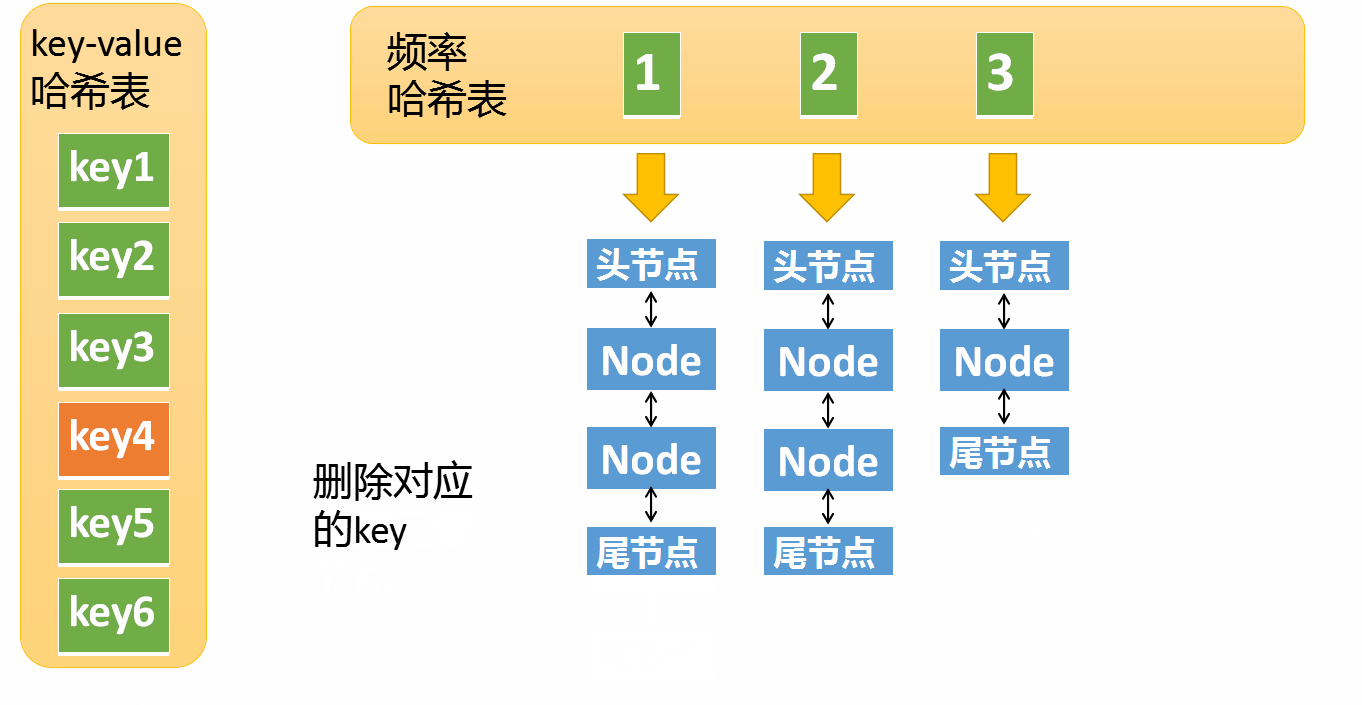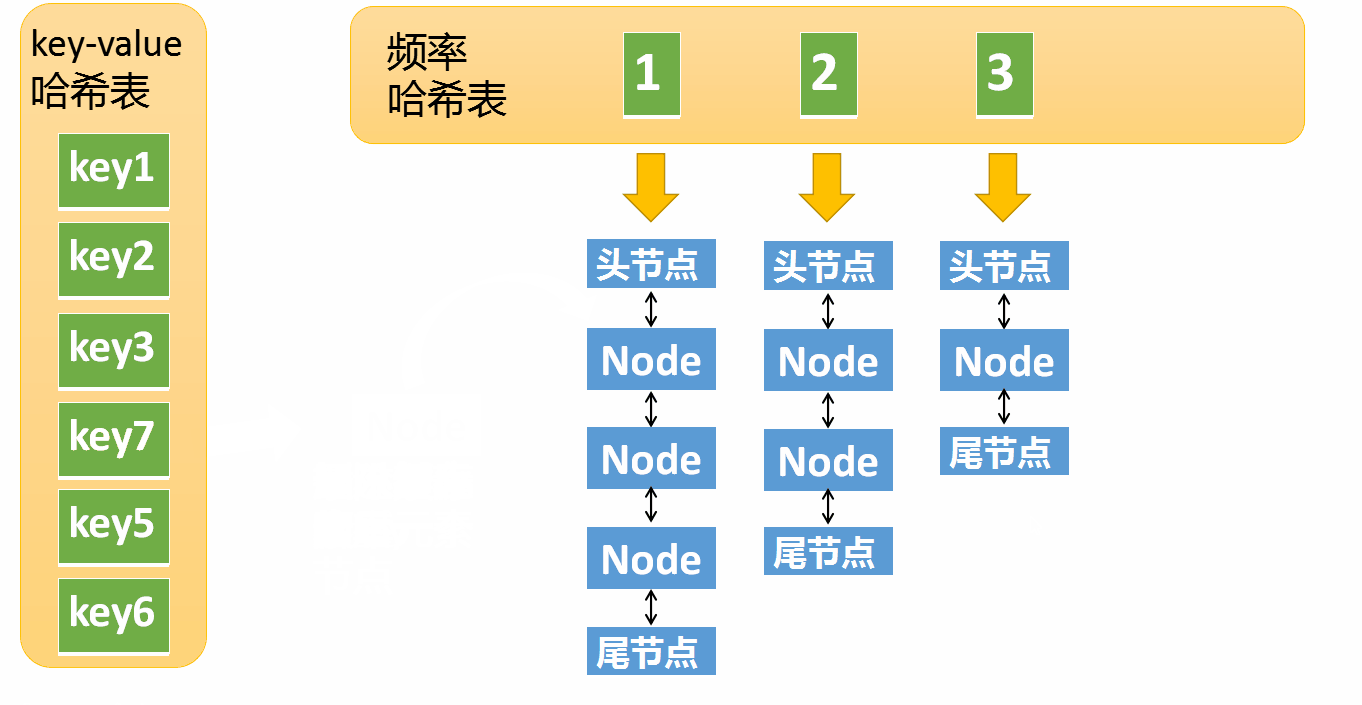
LRU The realization of is a Hashtable + One Double linked list
and LFU It's much more complicated , need Two hash tables + N A double linked list
- first freq_table( Word frequency bucket ):
- With frequency freq Index , Every word frequency has a bucket
- Inside the bucket is a two-way linked list , Node object Node There are three pieces of information in :key、value、 Word frequency freq
- When there is no data in the bucket , The corresponding word frequency bucket needs to be deleted

- the second key_table:
- Take the node key value key Index , Each index stores Corresponding Nodes in the freq_table The memory address in the linked list

- Take the node key value key Index , Each index stores Corresponding Nodes in the freq_table The memory address in the linked list
Specific operation
(1)get operation
- If key Returns if it does not exist -1
- If key There is , Returns the corresponding value, meanwhile :
- Remove the element from the access frequency i Remove from the linked list of , Put the frequency as i+1 In the linked list
- If the frequency i The linked list of is empty , Remove the linked list from the frequency hash table
The first one is very simple, needless to say , Let's look at the implementation of the second point 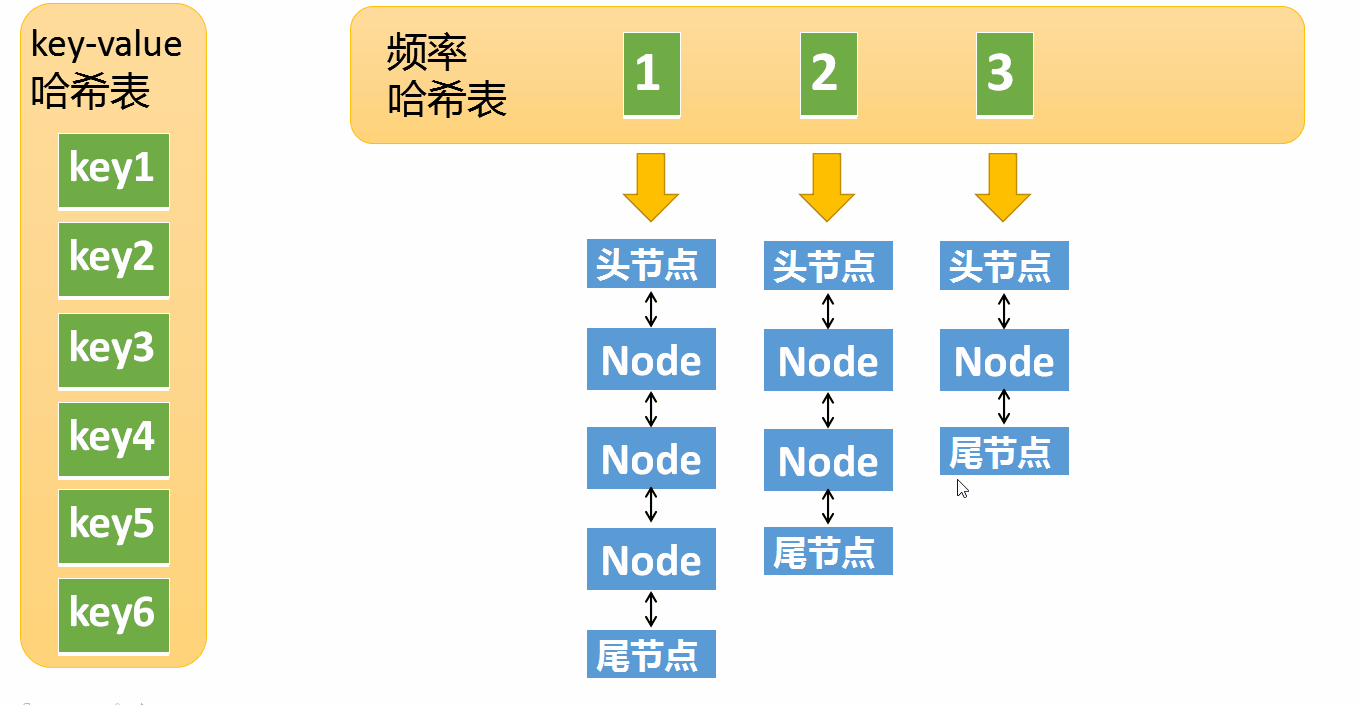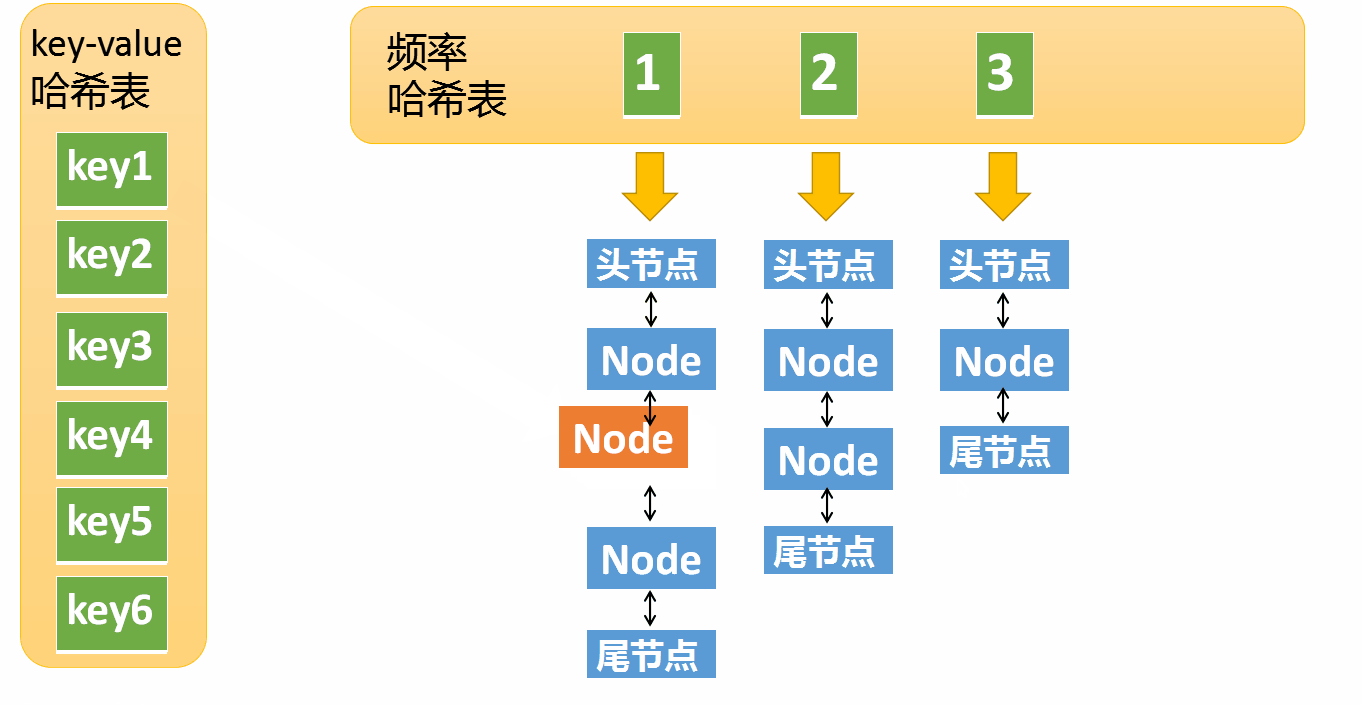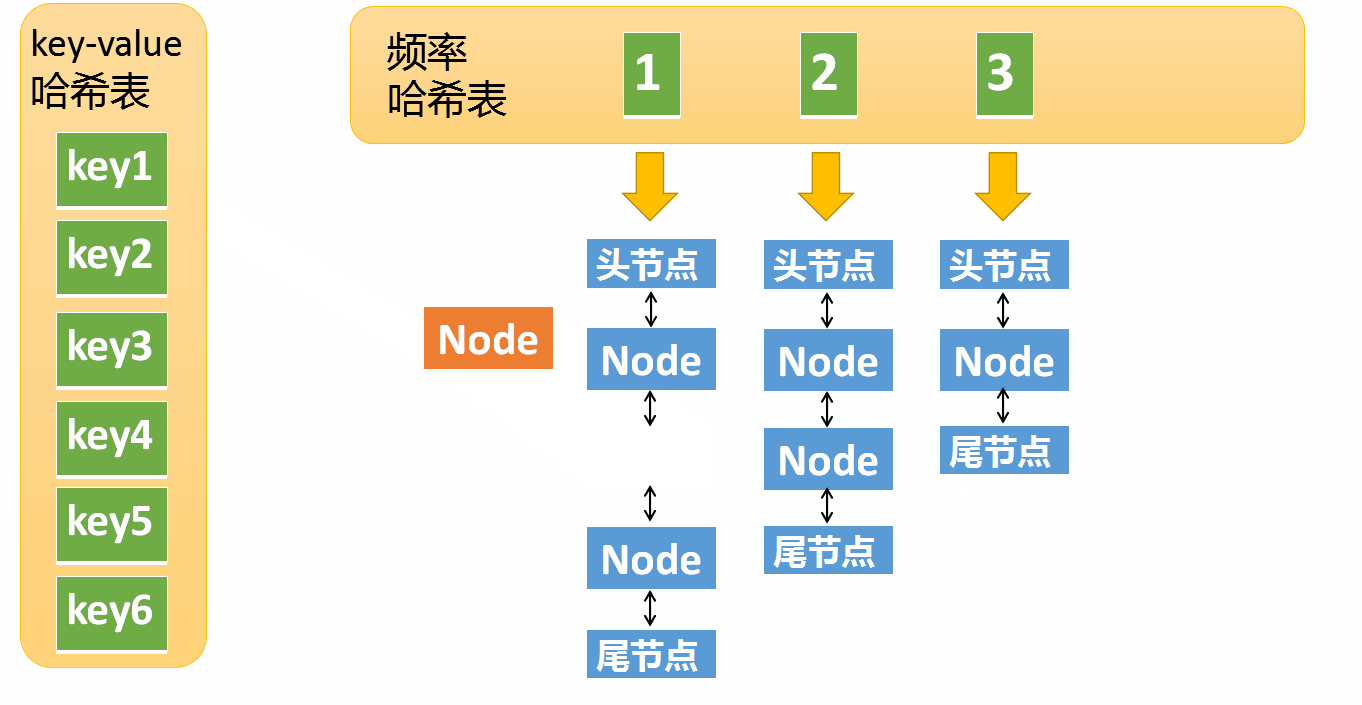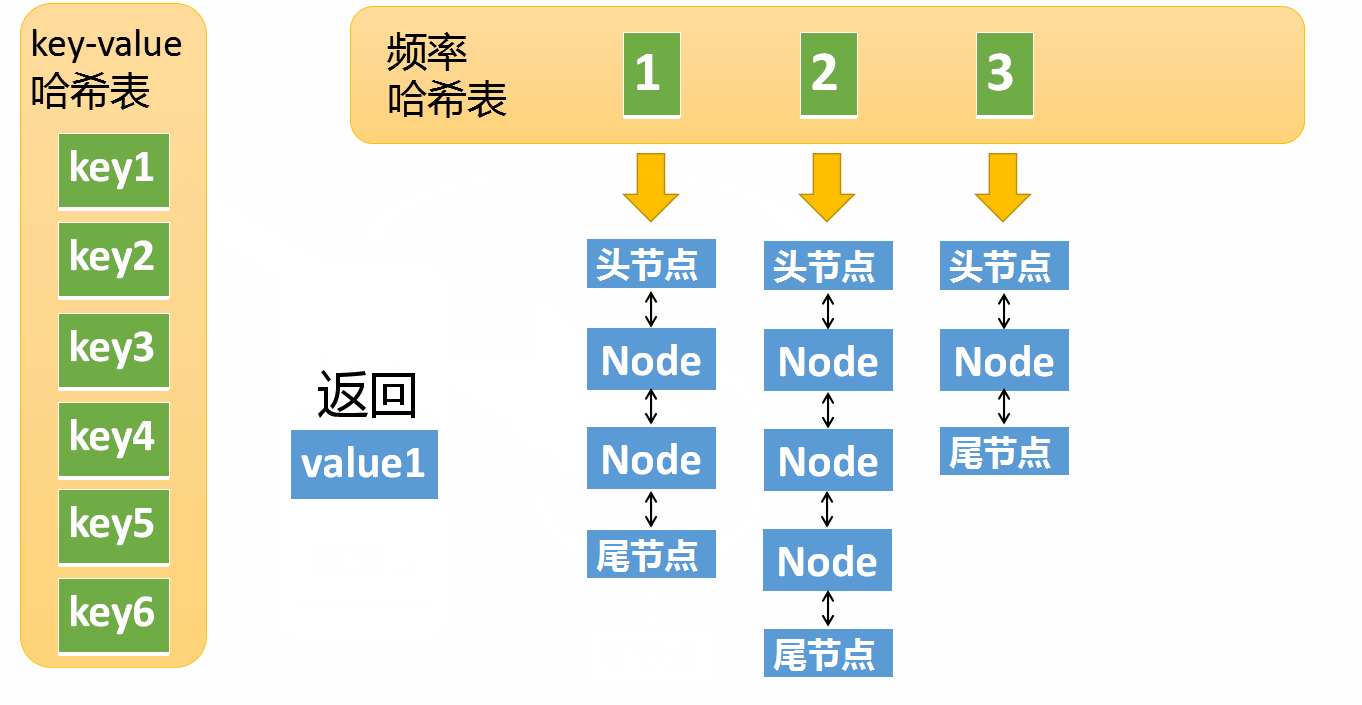
Suppose that the frequency of access to an element is 3, Now I've been interviewed again , Then you need to move this element to frequency 4 In the linked list . If this element is removed , frequency 3 The linked list is empty ( Only the head node and the tail node are left ) You need to delete this list , And delete the corresponding frequency ( Delete key=3)
put The operation is much more complicated , It includes the following situations
If key Already exist , Modify corresponding value, And will access frequency +1
- Remove the element from the access frequency i Remove from the linked list of , Put it on the frequency i+1 In the linked list
- If the frequency i The linked list of is empty , Remove the linked list from the frequency hash table
If key non-existent
- according to key Create a new node , The access frequency of the new node is 1, If there is no corresponding linked list in the frequency hash table, you need to create
- Then check the maximum capacity of the cache , Cache exceeds maximum capacity , Then delete the element with the lowest access frequency
How to find the element with the lowest frequency ? We maintain a minFreq The variable of , Used to record LFU The least frequent element in the cache , When the cache is full , Can quickly locate to the minimum frequent list , In order to achieve O(1) Time complexity deleting an element .
The specific way is :
- to update / When searching , Put the element frequency +1, Then if minFreq Not in the frequency hash table , Indicates that there are no elements in the frequency hash table , that minFreq need +1, otherwise minFreq unchanged .
- When inserting , This simple , Because the frequency of new elements is 1, So just put minFreq Change it to 1 that will do .
// Cached node information
struct Node {
int key, val, freq;
Node(int _key,int _val,int _freq): key(_key), val(_val), freq(_freq){
}
};
class LFUCache {
int minfreq, capacity;
unordered_map<int, list<Node>::iterator> key_table;
unordered_map<int, list<Node>> freq_table;
public:
LFUCache(int _capacity) {
minfreq = 0;
capacity = _capacity;
key_table.clear();
freq_table.clear();
}
int get(int key) {
if (capacity == 0) return -1;
auto it = key_table.find(key);
if (it == key_table.end()) return -1;
list<Node>::iterator node = it -> second;
int val = node -> val, freq = node -> freq;
freq_table[freq].erase(node);
// If the current list is empty , We need to remove... From the hash table , And updated minFreq
if (freq_table[freq].size() == 0) {
freq_table.erase(freq);
if (minfreq == freq) minfreq += 1;
}
// Insert into freq + 1 in
freq_table[freq + 1].push_front(Node(key, val, freq + 1));
key_table[key] = freq_table[freq + 1].begin();
return val;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
if (capacity == 0) return;
auto it = key_table.find(key);
if (it == key_table.end()) {
// The cache is full , You need to delete
if (key_table.size() == capacity) {
// adopt minFreq Get freq_table[minFreq] The end node of the linked list
auto it2 = freq_table[minfreq].back();
key_table.erase(it2.key);
freq_table[minfreq].pop_back();
if (freq_table[minfreq].size() == 0) {
freq_table.erase(minfreq);
}
}
freq_table[1].push_front(Node(key, value, 1));
key_table[key] = freq_table[1].begin();
minfreq = 1;
} else {
// And get The operation is basically the same , In addition to the need to update the cached values
list<Node>::iterator node = it -> second;
int freq = node -> freq;
freq_table[freq].erase(node);
if (freq_table[freq].size() == 0) {
freq_table.erase(freq);
if (minfreq == freq) minfreq += 1;
}
freq_table[freq + 1].push_front(Node(key, value, freq + 1));
key_table[key] = freq_table[freq + 1].begin();
}
}
};
边栏推荐
- 整流桥厂家ASEMI有哪些型号,整流桥厂家的电镀工艺怎么样?
- XML to VOC, VOC to coco, coco to Yolo, coco partition, coco check, Yolo check, coco visualization
- 网上炒股开户真的安全吗?
- 1055 The World‘s Richest
- RoleApp聚焦Web3,用“数据可持有”的钥匙开启Web3的大门
- 1054 The Dominant Color
- Apache Doris系列之:深入认识实时分析型数据库Apache Doris
- 学生思维VS职场思维
- Mysql死锁、锁超时、慢sql总结
- Deep decryption of go language context
猜你喜欢

EasyDSS使用mysql数据库,无法启动该如何解决?
![[Bi design teaching] how to run the program in SD card by single chip microcomputer](/img/22/d61d0d7aad347a13ca47a4779df362.png)
[Bi design teaching] how to run the program in SD card by single chip microcomputer
Unity 3D人物的粒子消散

Arthas小白入门

脱离炒作,数字藏品才能走得更远

基于STM32HAL库ADS1256调试笔记

西门子S7 模拟器使用教程

The training accuracy is comparable to alphafold2, and the speed is doubled. The helixfold training and reasoning code of the propeller is fully open source

华为无线设备配置不同业务VLAN的AP间非快速漫游

【Go语言】(一)环境搭建与了解VScode工具
随机推荐
1800万引进23名菲律宾博士引热议,学校老师回应:权宜之计
D static import object
【Swoole系列2.5】异步任务
如何做好测试用例的设计 软件测试零基础必看
Flink 的sink表插入到mysql表后,时间减少了8小时,谁知道 这是什么问题?
2022年下半年系统集成项目管理工程师认证招生简章
Cloud computing design and planning security control measures
13. 谈谈 Redis 的过期策略
Debezium系列之:show slave status查看主从延迟可能存在的不同情形
散户炒股选哪个证券公司手续费低,手机上开户安全吗
Matrikon OPC simulator tutorial
2022年下半年(软考高级)信息系统项目管理师认证招生简章
mysql约束与聚合查询
UNIPRO multi terminal deployment to meet customers' diversified needs
Deep understanding of TCP protocol
深入理解TCP协议
mysql事务
FileUploadBase$SizeLimitExceededException
Compréhension approfondie du protocole TCP
分糖果 华为od js