当前位置:网站首页>Fast-lio2 code analysis (I)
Fast-lio2 code analysis (I)
2022-07-20 06:22:00 【Hermit_ Rabbit】
0. brief introduction
Now more and more lidar methods have sprung up , Recently FAST-LIO The series represented by is gradually accepted by the public . and FAST-LIO2 Our work is more and more well known and studied by the public . Recently, the author is also studying FAST-LIO2 Knowledge about , Here will be introduced in the form of a long article FAST-LIO2.0 Learning experience of . This paper will combine the form of code with the paper , Intuitively analyze the core algorithm part of the paper . At the same time, it is also used as one's own learning notes for later generations to learn .
1. Laser radar
about FAST-LIO2 Code for , The main data is through preprocess And IMU_Processing Get the corresponding sensor data , And call in the main program ESF And IKD-Tree Complete the optimization . First, let's take a look at the lidar part .
1.1 preprocess.h
First, a series of enum Information about , adopt enum Choose different lidar types , Feature point features, etc , And pass orgtype Store some other attributes of some LIDAR Points .
// Enumeration type : Indicates the type of radar supported
enum LID_TYPE
{
AVIA = 1,
VELO16,
OUST64
}; //{1, 2, 3}
// Enumeration type : Indicates the type of feature point
enum Feature
{
Nor, // Normal point
Poss_Plane, // Possible plane points
Real_Plane, // Determined plane point
Edge_Jump, // There are crossing edges
Edge_Plane, // The plane point on the edge
Wire, // Line segment This may be an invalid point ? That is, small segments in space ?
ZeroPoint // Invalid point Not used in the program
};
// Enumeration type : Location identification
enum Surround
{
Prev, // Previous
Next // After a
};
// Enumeration type : Indicates the type of crossing edge
enum E_jump
{
Nr_nor, // normal
Nr_zero, // 0
Nr_180, // 180
Nr_inf, // infinity The jump is far away ?
Nr_blind // In the blind spot ?
};
// orgtype class : Some other properties used to store LIDAR Points
struct orgtype
{
double range; // Point cloud in xy The distance between the plane and the radar center
double dista; // The distance between the current point and the next point
// Suppose the radar origin is O The previous point is M The current point is A The latter point is N
double angle[2]; // This is the horn OAM And angle OAN Of cos value
double intersect; // This is the horn MAN Of cos value
E_jump edj[2]; // The type of front and back points
Feature ftype; // Point type
// Constructors
orgtype()
{
range = 0;
edj[Prev] = Nr_nor;
edj[Next] = Nr_nor;
ftype = Nor; // The default is normal
intersect = 2;
}
};
among LID_TYPE These are related to the following data structures . adopt enum Choose different lidar data , To set different data structures .
// velodyne data structure
namespace velodyne_ros
{
struct EIGEN_ALIGN16 Point
{
PCL_ADD_POINT4D; // 4D Point coordinate type
float intensity; // Strength
float time; // Time
uint16_t ring; // The number of turns the point belongs to
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW // Memory alignment
};
} // namespace velodyne_ros
// register velodyne_ros Of Point type
POINT_CLOUD_REGISTER_POINT_STRUCT(velodyne_ros::Point,
(float, x, x)(float, y, y)(float, z, z)(float, intensity, intensity)(float, time, time)(uint16_t, ring, ring))
// ouster data structure
namespace ouster_ros
{
struct EIGEN_ALIGN16 Point
{
PCL_ADD_POINT4D; // 4D Point coordinate type
float intensity; // Strength
uint32_t t; // Time
uint16_t reflectivity; // Reflectivity
uint8_t ring; // The number of turns the point belongs to
uint16_t ambient; // Not used
uint32_t range; // distance
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW // Memory alignment
};
} // namespace ouster_ros
// clang-format off
// register ouster Of Point type
POINT_CLOUD_REGISTER_POINT_STRUCT(ouster_ros::Point,
(float, x, x)
(float, y, y)
(float, z, z)
(float, intensity, intensity)
// use std::uint32_t to avoid conflicting with pcl::uint32_t
(std::uint32_t, t, t)
(std::uint16_t, reflectivity, reflectivity)
(std::uint8_t, ring, ring)
(std::uint16_t, ambient, ambient)
(std::uint32_t, range, range)
)
Then these are Preprocess Body function of , Its main function is to preprocess LIDAR point cloud data .
// Preproscess class : It is used for preprocessing LIDAR point cloud data
class Preprocess
{
public:
// EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
Preprocess(); // Constructors
~Preprocess(); // Destructor
void process(const livox_ros_driver::CustomMsg::ConstPtr &msg, PointCloudXYZI::Ptr &pcl_out); // Yes Livox Customize Msg Format of lidar data processing
void process(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2::ConstPtr &msg, PointCloudXYZI::Ptr &pcl_out); // Yes ros Of Msg Format of lidar data processing
void set(bool feat_en, int lid_type, double bld, int pfilt_num);
// sensor_msgs::PointCloud2::ConstPtr pointcloud;
PointCloudXYZI pl_full, pl_corn, pl_surf; // All points 、 Edge point 、 Plane point
PointCloudXYZI pl_buff[128]; //maximum 128 line lidar
vector<orgtype> typess[128]; //maximum 128 line lidar
int lidar_type, point_filter_num, N_SCANS, SCAN_RATE; // Radar type 、 Sampling interval 、 Number of scan lines 、 Scanning frequency
double blind; // Minimum distance threshold ( Blind area )
bool feature_enabled, given_offset_time; // Whether to extract features 、 Whether to perform time offset
ros::Publisher pub_full, pub_surf, pub_corn; // Release all points 、 Publish plane points 、 Publish edge points
private:
void avia_handler(const livox_ros_driver::CustomMsg::ConstPtr &msg); // Used to deal with Livox Lidar data processing
void oust64_handler(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2::ConstPtr &msg); // Used to deal with ouster Lidar data processing
void velodyne_handler(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2::ConstPtr &msg); // Used to deal with velodyne Lidar data processing
void give_feature(PointCloudXYZI &pl, vector<orgtype> &types);
void pub_func(PointCloudXYZI &pl, const ros::Time &ct);
int plane_judge(const PointCloudXYZI &pl, vector<orgtype> &types, uint i, uint &i_nex, Eigen::Vector3d &curr_direct);
bool small_plane(const PointCloudXYZI &pl, vector<orgtype> &types, uint i_cur, uint &i_nex, Eigen::Vector3d &curr_direct); // Not used
bool edge_jump_judge(const PointCloudXYZI &pl, vector<orgtype> &types, uint i, Surround nor_dir);
int group_size;
double disA, disB, inf_bound;
double limit_maxmid, limit_midmin, limit_maxmin;
double p2l_ratio;
double jump_up_limit, jump_down_limit;
double cos160;
double edgea, edgeb;
double smallp_intersect, smallp_ratio;
double vx, vy, vz;
};
1.2 preprocess.cpp
Above is the header file , The detailed code is in preprocess.cpp in , Here we will introduce each function in detail , First, constructors and destructors , It mainly stores some radar parameters
Preprocess::Preprocess()
: feature_enabled(0), lidar_type(AVIA), blind(0.01), point_filter_num(1)
{
inf_bound = 10; // Set of efficient points , Greater than 10m Is a blind spot
N_SCANS = 6; // Number of lines of multi line lidar
group_size = 8; // 8 A group of points
disA = 0.01; // Distance threshold of point set , Judge whether it is a plane
disB = 0.1; // Distance threshold of point set , Judge whether it is a plane
p2l_ratio = 225; // Point to line distance threshold , It needs to be greater than this value to judge the composition surface
limit_maxmid = 6.25; // The range of distance change rate from the midpoint to the left
limit_midmin = 6.25; // The range of distance change rate from the midpoint to the right
limit_maxmin = 3.24; // Range of distance change rate from left to right
jump_up_limit = 170.0;
jump_down_limit = 8.0;
cos160 = 160.0;
edgea = 2; // If the distance between points is more than twice, it is considered as occlusion
edgeb = 0.1; // The distance between points exceeds 0.1m It is considered to be covered
smallp_intersect = 172.5;
smallp_ratio = 1.2; // If the angle of three points is greater than 172.5 degree , And the proportion is less than 1.2 times , It is considered as a plane
given_offset_time = false; // Whether to provide time offset
jump_up_limit = cos(jump_up_limit / 180 * M_PI); // The angle is greater than 170 Degree point skip , Think in
jump_down_limit = cos(jump_down_limit / 180 * M_PI); // The angle is less than 8 Degree point skip
cos160 = cos(cos160 / 180 * M_PI); // Included angle limit
smallp_intersect = cos(smallp_intersect / 180 * M_PI); // If the angle of three points is greater than 172.5 degree , And the proportion is less than 1.2 times , It is considered as a plane
}
The next function is set function , It can be here laserMapping.cpp By using , However, this function is not used .
void Preprocess::set(bool feat_en, int lid_type, double bld, int pfilt_num)
{
feature_enabled = feat_en; // Whether to extract feature points
lidar_type = lid_type; // Type of radar
blind = bld; // Minimum distance threshold , That is to filter out 0~blind Point cloud in range
point_filter_num = pfilt_num; // Sampling interval , That is, every point_filter_num Take a point 1 A little bit
}
Below Preprocess The preprocessing function mainly includes the processing of different lidar , Here it is laserMapping.cpp Called , So as to get the processed point cloud , And preliminarily completed the screening . The next two are similar, so I won't talk about them carefully
/** * @brief Livox LIDAR point cloud preprocessing function * * @param msg livox LIDAR point cloud data , The format is livox_ros_driver::CustomMsg * @param pcl_out Output the processed point cloud data , The format is pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZINormal> */
void Preprocess::process(const livox_ros_driver::CustomMsg::ConstPtr &msg, PointCloudXYZI::Ptr &pcl_out)
{
avia_handler(msg);
*pcl_out = pl_surf;
}
void Preprocess::process(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2::ConstPtr &msg, PointCloudXYZI::Ptr &pcl_out)
{
switch (lidar_type)
{
case OUST64:
oust64_handler(msg);
break;
case VELO16:
velodyne_handler(msg);
break;
default:
printf("Error LiDAR Type");
break;
}
*pcl_out = pl_surf;
}
The following is handle Function to preprocess the issued point cloud data . Here we show Livox Preprocessing of LIDAR point cloud data . The operation here is to get livox Raw data , Then it is spliced again through harness and reflectivity
void Preprocess::avia_handler(const livox_ros_driver::CustomMsg::ConstPtr &msg)
{
// Clear the previous point cloud cache
pl_surf.clear(); // Clear the previous plane point cloud cache
pl_corn.clear(); // Clear the previous corner cloud cache
pl_full.clear(); // Clear the previous full point cloud cache
double t1 = omp_get_wtime(); // I didn't use it later
int plsize = msg->point_num; // The total number of point clouds in a frame
// cout<<"plsie: "<<plsize<<endl;
pl_corn.reserve(plsize); // Allocate space
pl_surf.reserve(plsize); // Allocate space
pl_full.resize(plsize); // Allocate space
for (int i = 0; i < N_SCANS; i++)
{
pl_buff[i].clear();
pl_buff[i].reserve(plsize); // every last scan Number of saved point clouds
}
uint valid_num = 0; // Number of effective point clouds
// feature extraction (FastLIO2 Feature extraction is not performed by default )
if (feature_enabled)
{
// Process each point cloud separately
for (uint i = 1; i < plsize; i++)
{
// Only take the number of lines in 0~N_SCANS And the echo order is 0 perhaps 1 Point cloud of
if ((msg->points[i].line < N_SCANS) && ((msg->points[i].tag & 0x30) == 0x10 || (msg->points[i].tag & 0x30) == 0x00))
{
pl_full[i].x = msg->points[i].x; // Point cloud x Axis coordinates
pl_full[i].y = msg->points[i].y; // Point cloud y Axis coordinates
pl_full[i].z = msg->points[i].z; // Point cloud z Axis coordinates
pl_full[i].intensity = msg->points[i].reflectivity; // Point cloud intensity
pl_full[i].curvature = msg->points[i].offset_time / float(1000000); // Use curvature as the time of each laser point
bool is_new = false;
// Only if the distance between the current point and the previous point is large enough (>1e-7), To consider the current point as a useful point , Add to the corresponding line Of pl_buff In line
if ((abs(pl_full[i].x - pl_full[i - 1].x) > 1e-7) || (abs(pl_full[i].y - pl_full[i - 1].y) > 1e-7) || (abs(pl_full[i].z - pl_full[i - 1].z) > 1e-7))
{
pl_buff[msg->points[i].line].push_back(pl_full[i]); // Add the current point to the corresponding line Of pl_buff In line
}
}
}
static int count = 0;
static double time = 0.0;
count++;
double t0 = omp_get_wtime();
// For each line The lidar in is processed separately
for (int j = 0; j < N_SCANS; j++)
{
// If it's time to line The point cloud in is too small , Then proceed to the next line
if (pl_buff[j].size() <= 5)
continue;
pcl::PointCloud<PointType> &pl = pl_buff[j];
plsize = pl.size();
vector<orgtype> &types = typess[j];
types.clear();
types.resize(plsize);
plsize--;
for (uint i = 0; i < plsize; i++)
{
types[i].range = pl[i].x * pl[i].x + pl[i].y * pl[i].y; // Calculate the distance from each point to the robot itself
vx = pl[i].x - pl[i + 1].x;
vy = pl[i].y - pl[i + 1].y;
vz = pl[i].z - pl[i + 1].z;
types[i].dista = vx * vx + vy * vy + vz * vz; // Calculate the distance between two separation points
}
// because i The last point is not i+1 So I asked for one alone range, No, distance
types[plsize].range = pl[plsize].x * pl[plsize].x + pl[plsize].y * pl[plsize].y;
give_feature(pl, types); // Give features
// pl_surf += pl;
}
time += omp_get_wtime() - t0;
printf("Feature extraction time: %lf \n", time / count);
}
else
{
// Process each point cloud separately
for (uint i = 1; i < plsize; i++)
{
// Only take the number of lines in 0~N_SCANS And the echo order is 0 perhaps 1 Point cloud of
if ((msg->points[i].line < N_SCANS) && ((msg->points[i].tag & 0x30) == 0x10 || (msg->points[i].tag & 0x30) == 0x00))
{
valid_num++; // Number of effective point clouds
// Equal interval downsampling
if (valid_num % point_filter_num == 0)
{
pl_full[i].x = msg->points[i].x; // Point cloud x Axis coordinates
pl_full[i].y = msg->points[i].y; // Point cloud y Axis coordinates
pl_full[i].z = msg->points[i].z; // Point cloud z Axis coordinates
pl_full[i].intensity = msg->points[i].reflectivity; // Point cloud intensity
pl_full[i].curvature = msg->points[i].offset_time / float(1000000); // use curvature as time of each laser points
// Only if the distance between the current point and the previous point is large enough (>1e-7), And outside the minimum distance threshold , To consider the current point as a useful point , Add to pl_surf In line
if ((abs(pl_full[i].x - pl_full[i - 1].x) > 1e-7) || (abs(pl_full[i].y - pl_full[i - 1].y) > 1e-7) || (abs(pl_full[i].z - pl_full[i - 1].z) > 1e-7) && (pl_full[i].x * pl_full[i].x + pl_full[i].y * pl_full[i].y > blind))
{
pl_surf.push_back(pl_full[i]);
}
}
}
}
}
}
In the program, we can see give_feature(pl, types); This function is mainly feature extraction , Now let's learn and understand this function , For each line Feature extraction from point cloud
void Preprocess::give_feature(pcl::PointCloud<PointType> &pl, vector<orgtype> &types)
{
int plsize = pl.size(); // Points of a single line
int plsize2;
if (plsize == 0)
{
printf("something wrong\n");
return;
}
uint head = 0;
// Not in a blind spot Start from the point where the line is not blind
while (types[head].range < blind)
{
head++;
}
// Surf
// group_size Default equal to 8
plsize2 = (plsize > group_size) ? (plsize - group_size) : 0; // Judge whether there is still... After the current point 8 A little bit If enough, it will gradually decrease
Eigen::Vector3d curr_direct(Eigen::Vector3d::Zero()); // The normal vector of the current plane
Eigen::Vector3d last_direct(Eigen::Vector3d::Zero()); // The normal vector of the previous plane
uint i_nex = 0, i2; // i2 Is the next point of the current point
uint last_i = 0; // last_i Saved index for the previous point
uint last_i_nex = 0; // last_i_nex Index of the next point of the previous point
int last_state = 0; // by 1 Represents that the last state is plane Otherwise 0
// Judge the pastry
int plane_type;
// Get 8 Points are used to judge the plane
for (uint i = head; i < plsize2; i++)
{
if (types[i].range < blind) // Points within the blind area are not processed
continue;
{
continue;
}
i2 = i; // to update i2
plane_type = plane_judge(pl, types, i, i_nex, curr_direct); // Find the plane , And return the type 0 1 2
if (plane_type == 1) // return 1 Generally, the default is plane
{
// Set the determined plane points and possible plane points
for (uint j = i; j <= i_nex; j++)
{
if (j != i && j != i_nex)
{
// Set all points between the start point and the end point as the determined plane points
types[j].ftype = Real_Plane;
}
else
{
// Set the start and end points as possible plane points
types[j].ftype = Poss_Plane;
}
}
// if(last_state==1 && fabs(last_direct.sum())>0.5)
// In the beginning last_state=0 Just skip
// after last_state=1
// If the previous state is a plane, judge whether the current point is a point on the edge of two planes or a point on a relatively flat plane
if (last_state == 1 && last_direct.norm() > 0.1)
{
double mod = last_direct.transpose() * curr_direct;
if (mod > -0.707 && mod < 0.707)
{
// modify ftype, The angle between the normal vectors of two faces is 45 Degree and 135 Between degrees Think of it as a point on the edge of two planes
types[i].ftype = Edge_Plane;
}
else
{
// Otherwise, it is considered to be a real plane point
types[i].ftype = Real_Plane;
}
}
i = i_nex - 1;
last_state = 1;
}
else // if(plane_type == 2)
{
// plane_type=0 or 2 When
i = i_nex;
last_state = 0; // Set to not a plane point
}
last_i = i2; // to update last_i
last_i_nex = i_nex; // to update last_i_nex
last_direct = curr_direct; // to update last_direct
}
// Judge the edge point
plsize2 = plsize > 3 ? plsize - 3 : 0; // If the remaining points are less than 3 Then the edge point is not judged , Otherwise, calculate which points are edge points
for (uint i = head + 3; i < plsize2; i++)
{
// The point can't be in the blind area perhaps Points must belong to normal points and possible plane points
if (types[i].range < blind || types[i].ftype >= Real_Plane)
{
continue;
}
// The point should not be too close to the front and rear points
if (types[i - 1].dista < 1e-16 || types[i].dista < 1e-16)
{
continue;
}
Eigen::Vector3d vec_a(pl[i].x, pl[i].y, pl[i].z); // The vector composed of the current point
Eigen::Vector3d vecs[2];
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
int m = -1;
if (j == 1)
{
m = 1;
}
// If the current previous / The latter point is in the blind area (4m)
if (types[i + m].range < blind)
{
if (types[i].range > inf_bound) // If it is greater than 10m
{
types[i].edj[j] = Nr_inf; // Give this point Nr_inf( The jump is far away )
}
else
{
types[i].edj[j] = Nr_blind; // Give this point Nr_blind( In the blind spot )
}
continue;
}
vecs[j] = Eigen::Vector3d(pl[i + m].x, pl[i + m].y, pl[i + m].z);
vecs[j] = vecs[j] - vec_a; // front / The vector from the back point to the current point
// If the origin of the radar coordinate system is O The current point is A front / The latter point is M and N
// Next OA Point multiplication MA/(|OA|*|MA|)
// Get is cos horn OAM Size
types[i].intersect = vecs[Prev].dot(vecs[Next]) / vecs[Prev].norm() / vecs[Next].norm(); // horn MAN Of cos value
// The previous point is the normal point && The next point is on the laser line && The distance between the current point and the next point is greater than 0.0225m && The distance between the current point and the next point is greater than four times the distance between the current point and the previous point
// This kind of edge point is like 7 The edge of this glyph ?
if (types[i].angle[j] < jump_up_limit) // cos(170)
{
types[i].edj[j] = Nr_180; // M stay OA Extend the line
}
else if (types[i].angle[j] > jump_down_limit) // cos(8)
{
types[i].edj[j] = Nr_zero; // M stay OA On
}
}
types[i].intersect = vecs[Prev].dot(vecs[Next]) / vecs[Prev].norm() / vecs[Next].norm();
if (types[i].edj[Prev] == Nr_nor && types[i].edj[Next] == Nr_zero && types[i].dista > 0.0225 && types[i].dista > 4 * types[i - 1].dista)
{
if (types[i].intersect > cos160) // horn MAN To be less than 160 degree Otherwise it will be parallel to the laser
{
if (edge_jump_judge(pl, types, i, Prev))
{
types[i].ftype = Edge_Jump;
}
}
}
// Similar to the above
// The previous point is on the laser beam && The latter point is normal && The distance between the previous point and the current point is greater than 0.0225m && The distance between the previous point and the current point is greater than four times the distance between the current point and the next point
else if (types[i].edj[Prev] == Nr_zero && types[i].edj[Next] == Nr_nor && types[i - 1].dista > 0.0225 && types[i - 1].dista > 4 * types[i].dista)
{
if (types[i].intersect > cos160)
{
if (edge_jump_judge(pl, types, i, Next))
{
types[i].ftype = Edge_Jump;
}
}
}
// The front is normal && ( Distance from the current point to the center >10m And the back point is in the blind area )
else if (types[i].edj[Prev] == Nr_nor && types[i].edj[Next] == Nr_inf)
{
if (edge_jump_judge(pl, types, i, Prev))
{
types[i].ftype = Edge_Jump;
}
}
//( Distance from the current point to the center >10m And the front point is in the blind area ) && The back is normal
else if (types[i].edj[Prev] == Nr_inf && types[i].edj[Next] == Nr_nor)
{
if (edge_jump_judge(pl, types, i, Next))
{
types[i].ftype = Edge_Jump;
}
}
// Neither front nor back is normal
else if (types[i].edj[Prev] > Nr_nor && types[i].edj[Next] > Nr_nor)
{
if (types[i].ftype == Nor)
{
types[i].ftype = Wire; // It should not be used in the program As a small line segment or useless point in space
}
}
}
plsize2 = plsize - 1;
double ratio;
// Keep looking for flat points
for (uint i = head + 1; i < plsize2; i++)
{
// front 、 At present 、 The next three points need not be in the blind area
if (types[i].range < blind || types[i - 1].range < blind || types[i + 1].range < blind)
{
continue;
}
// Front and current The distance between the current and subsequent points cannot be too close
if (types[i - 1].dista < 1e-8 || types[i].dista < 1e-8)
{
continue;
}
// There are still some normal points left. Continue to find plane points
if (types[i].ftype == Nor)
{
// Find the ratio of point to point spacing Large spacing / Small spacing
if (types[i - 1].dista > types[i].dista)
{
ratio = types[i - 1].dista / types[i].dista;
}
else
{
ratio = types[i].dista / types[i - 1].dista;
}
// If the included angle is greater than 172.5 degree && Spacing scale <1.2
if (types[i].intersect < smallp_intersect && ratio < smallp_ratio)
{
// The front and back three points are considered as plane points
if (types[i - 1].ftype == Nor)
{
types[i - 1].ftype = Real_Plane;
}
if (types[i + 1].ftype == Nor)
{
types[i + 1].ftype = Real_Plane;
}
types[i].ftype = Real_Plane;
}
}
}
// Store plane points
int last_surface = -1;
for (uint j = head; j < plsize; j++)
{
// Possible plane points and determined plane points
if (types[j].ftype == Poss_Plane || types[j].ftype == Real_Plane)
{
if (last_surface == -1)
{
last_surface = j;
}
// Usually there are several pastries connected
// Only plane points on the sampling interval can be used ( Here is indifference filtering Starting from each new pastry, take one every few points )
if (j == uint(last_surface + point_filter_num - 1))
{
PointType ap;
ap.x = pl[j].x;
ap.y = pl[j].y;
ap.z = pl[j].z;
ap.intensity = pl[j].intensity;
ap.curvature = pl[j].curvature;
pl_surf.push_back(ap);
last_surface = -1;
}
}
else
{
// Jump to the point of the larger edge A point at the edge of a plane
if (types[j].ftype == Edge_Jump || types[j].ftype == Edge_Plane)
{
pl_corn.push_back(pl[j]);
}
// If the pasta point found last time is filtered out without difference , And now it's on the edge
if (last_surface != -1)
{
PointType ap;
// Take the center of gravity of all points from the last face point to the edge line this time and store it as a face point
for (uint k = last_surface; k < j; k++)
{
ap.x += pl[k].x;
ap.y += pl[k].y;
ap.z += pl[k].z;
ap.intensity += pl[k].intensity;
ap.curvature += pl[k].curvature;
}
ap.x /= (j - last_surface);
ap.y /= (j - last_surface);
ap.z /= (j - last_surface);
ap.intensity /= (j - last_surface);
ap.curvature /= (j - last_surface);
pl_surf.push_back(ap);
}
last_surface = -1;
}
}
}
stay give_feature There are functions for extracting surface features and angular features in the function , Let's analyze it in detail , Surface features are mainly based on the distance between points to synthesize a vector , And calculate the extraction of face features by product . Here, face feature extraction and edge feature extraction and LOAM Similar , Here is to use LOAM To show .
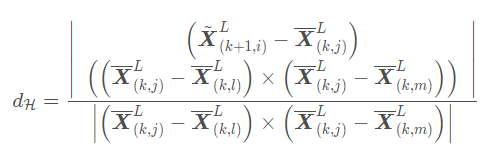
… Please refer to Ancient Moon House
边栏推荐
- EN 1504-2混凝土结构保护和修复产品—CE认证
- [surveying] leveling
- QQ群无法下载视频和图片解决方案
- 备战攻防演练,这里有一张腾讯安全重保布防图!
- Regular use of VMware virtual machine + snapshot
- Cordova fragment onactivityresult has no callback
- Ali test engineer's words will save you ten years of detours
- MySQL password modification error 1064 (42000):
- [Development Tutorial 4] crazy shell arm function mobile phone - development interface connection tutorial
- [jailhouse article] specific electronic platform to test the influence of hypervisors on the performance
猜你喜欢

Zabbix5.0配置企业微信告警

Selenium's pull-down + headless browser

深入理解ArrayList

刷题精选:力扣565.数组嵌套
![[jailhouse article] specific electronic platform to test the influence of hypervisors on the performance](/img/34/3a6ffcdf8e440916843950e1f463ac.png)
[jailhouse article] specific electronic platform to test the influence of hypervisors on the performance
C语言extern和static关键字详解

Financial banking software testing super large strategy, the most popular financial banking big secret cover questions

基于yarn1.x的monorepo实践分享
![[C exercise] arrow pattern](/img/a1/24af3bf47d2a44e022049320bf0558.png)
[C exercise] arrow pattern

【深度】新派LaaS协议Elephant:重振DeFi赛道发展的关键
随机推荐
Segment tree
7、【WebGIS实战】专题篇——API key
Cordova fragment onActivityResult没有回调
Sklearn通过precision_recall_curve获取F1最大值
7.18 simulation summary
Image zoom tool
【快速上手教程1】疯壳·开源编队无人机-开机测试
Window switching of selenium
线段树
Detailed explanation of extern and static keywords in C language
键入网址到网页显示,期间发生了什么?
基于ABP实现DDD--仓储实践
Zabbix5.0配置企业微信告警
LeetCode-394-字符串解码
MySQL修改密碼報錯 ERROR 1064 (42000):
FAST-LIO2代码解析(一)
DDD based on ABP -- warehousing practice
What are the obstacles that hinder the further development of NFT? Analyze from six aspects
Hello World 凑个数
EN 1504-2 concrete structure protection and repair products - CE certification