当前位置:网站首页>Dynamic memory management
Dynamic memory management
2022-07-20 21:50:00 【Swordsman】
Dynamic memory management
If the memory space is simply divided , It is divided into 3 Districts : The stack area , Heap area , Static zone
The stack area is mainly for storage : local variable , The formal parameter of the function , The return value of the function .
The stacking area is mainly for storage :malloc calloc realloc free Dynamic development of memory space .
The static area is mainly used to store : from static Decorated static variables , Including local variables and global variables .
Memory development mode
- Open up space in the stack area :
int i = 0;// Open a piece on the stack with a size of 4byte Space
float f = 0.0f;// Open a piece on the stack with a size of 4byte Space
double d = 0.0;// Open a piece on the stack with a size of 8byte Space
int arr[10] = {
0 };// Open a continuous piece on the stack with a size of 40byte Space
The size of the above development space is fixed , After development, it cannot be modified .
- Open up space in the stack area :
Now , It involves dynamic memory functions malloc calloc realloc free!
malloc
void* malloc(size_t size);
malloc The function is used to apply for a piece of space from memory , If the application is successful , Then return the starting address of the space ; Application failed , Return null pointer NULL.
A few notes :
- If the application is successful , The block space is not initialized .
- If
sizeyes 0, The standard does not define this behavior , The result depends on different compilers . void*Pointer of type cannot be dereferenced directly , You have to convert it into a specific type of pointer .
free
void free(void* ptr);
free Function is used to release the memory space opened by dynamic memory function , Because only open up , Don't release , Memory leaks .
A few notes :
ptrThe pointer can only point to spacemalloc calloc reallocFunction development .- If
ptryesNULL, befreeFunctions do nothing . - You cannot use a space opened up by a dynamic memory function multiple times
freeRelease .
calloc
void* calloc(size_t num, size_t size);
Follow malloc Function similar to ,calloc Function is also used to open up memory space , Not too malloc The difference is ,calloc Function is used to open num Size is size Continuous space .
It should be noted that :
callocIt also returns generic pointersvoid*, It cannot be dereferenced directly .callocFunction successfully opened up space , The starting address of the space is returned ; If the development fails, the null pointer is returnedNULL.callocWhen opening up space , By the way, initialize every byte of the space to 0.
realloc
void* realloc(void* ptr, size_t size);
realloc It is a function used to adjust the size of space opened up by dynamic memory functions .
What should be noted is :
ptrIt refers to the starting address of the space opened up by the dynamic memory function ; After adjustment , The size of the new memory space issize.- If the space adjustment is successful , Return the address of the adjustment space ; If you fail , Return null pointer
NULL. - If given
sizeSize is 0, Then the function followsmallocequally , Do nothing . reallocThe returned address may be the original address , It may also be the new address after adjustment .
realloc Two ways of opening up :
Use of dynamic memory functions
calloc and free
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main()
{
int* ptr = (int*)malloc(40);// Dynamic development 40 Bytes of space , And assign the address of the starting position to the integer pointer ptr
// Because the development may succeed , It's also possible to fail , Therefore, it is in use ptr When the pointer , You need to first determine whether the pointer is empty
if (ptr == NULL)
{
printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));// Print error messages
return 1;
}
//...
// Use of dynamic memory space
// Dynamic memory space release
free(ptr);// Releasing just frees the space pointed to by the pointer , however ptr Or point to the original space , To ensure safety , Need to put ptr Set as NULL
ptr = NULL;
return 0;
}
malloc and free
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main()
{
int* ptr = malloc(sizeof(int), 10);// Dynamic development 10 An integer space
// Determine the return value
if (ptr == NULL)
{
printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));
return 1;
}
//...
// The relevant operation
// Memory free
free(ptr);
ptr = NULL;
return 0;
}
realloc and free
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main()
{
int* ptr = (int*)malloc(40);
if (ptr == NULL)
{
printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));
return 1;
}
int* p = (int*)free(ptr, 80);
// Judge whether the space is successfully opened
if (p != NULL)
{
ptr = p;
}
//...
// Memory free
free(ptr);
ptr = NULL;
return 0;
}
Errors related to dynamic memory development
- Yes
NULLTo dereference .
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int* p = malloc(10 * sizeof(int));
*p = 20;
free(p);
p = NULL:
return 0;
}
In this code , Use malloc Dynamic development 10 An integer space , The development may fail , Return null pointer , If a pointer does not have an explicit point, it cannot be dereferenced directly !
- Operation goes beyond the space opened up dynamically .
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main()
{
int* ptr = (int*)malloc(10 * sizeof(int));
if (ptr == NULL)
{
printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));
return 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i++)
{
ptr[i] = i;
//p[i] <--> *(p + i)
}
// Memory release
free(ptr);
ptr = NULL;
return 0;
}
- Free non dynamically opened memory
#include <stdio.h>
#inclue <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a = 0;
int* ptr = &a;
//...
free(ptr);
ptr = NULL;
return 0;
}
- Release a part of dynamic memory
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main()
{
int* ptr = (int*)malloc(10 * sizeof(int));
if (ptr == NULL)
{
printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));
return 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
ptr++;
}
//ptr After the cycle, it no longer points to the starting position of dynamic opening memory .
free(ptr);
ptr = NULL;
return 0;
}
- Multiple releases of the same dynamically opened memory
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main()
{
int* ptr = (int*)malloc(10 * sizeof(int));
if (ptr == NULL)
{
printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));
return 1;
}
//...
free(ptr);
ptr = NULL;
//...
free(ptr);
ptr = NULL;
return 0;
}
- Forget to free dynamically opened memory ( Cause memory leaks )
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main()
{
int* ptr = (int*)malloc(10 * sizeof(int));
if (ptr == NULL)
{
printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));
return 1;
}
//... The relevant operation
//... No memory release
return 0;
}
- Continue to use after dynamic memory is released
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main()
{
int* ptr = (int*)malloc(10 * sizeof(int));
if (ptr == NULL)
{
printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));
return 1;
}
//... The relevant operation
// Memory free
free(ptr);
//ptr = NULL;
*ptr = 10;
return 0;
}
Flexible array
There are several points that must be made clear :
- Flexible arrays can only appear in structures .
- The flexible array member must be the last member in the structure , in other words , There are at least two members in the structure .
- Use
sizeofCalculate the size of the structure , Flexible array members are not included . - Arrays containing flexible array members should use
mallocFunction to allocate memory , The size should be larger than the size of the structure itself .
give an example
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
typedef struct S
{
char c;
int i;
int arr[0];
}type_s;
int main()
{
type_s* p = (type_s*)malloc(sizeof(type_s) + 100 * sizeof(int));
if (p == NULL)
{
printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));
return 1;
}
p->c = 'w';
p->i = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
p->arr[i] = i;
}
// Dynamic memory release
free(p);
p = NULL;
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

开启创客教育课程建设的实体空间

Data Governance Research Report - data element equity allocation path (2022), 50 Pages pdf

docker安装MySQL5.7

微服务测试
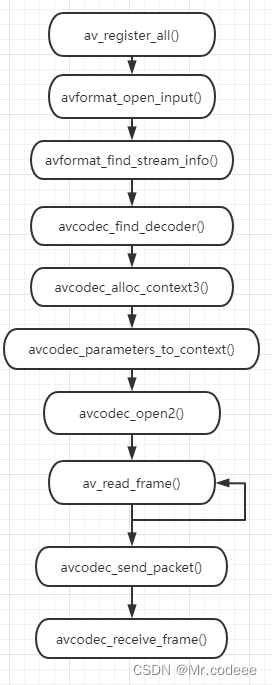
Ffmpeg video decoding

请问Redis 如何实现库存扣减操作和防止被超卖?

Qt的命令行解析

PMP每日一练 | 考试不迷路-7.19
Cannot make QOpenGLContext current in a different thread : PyQt多线程崩溃的解决方法
Dest0g3 520迎新赛-web-funny_upload
随机推荐
July 18, 2022, village of p6722 "mcoi-01" in Luogu
东莞证券买股票开户安全吗?
2022年全国最新消防设施操作员(初级消防设施操作员)模拟题及答案
docker安装MySQL5.7
2022年湖南工学院ACM集训第四次周测题解
Arrays and pointers
English sentence pattern reference exclusive Edition - object clause
适应大众化教育的创客理念设计
mongo 索引备份
面试大厂Android开发的准备
CSAPP:cap2
使用Redis + lua脚本实现分布式限流
Gson study notes
Skywalking full link monitoring cluster and dynamic deployment
2022河南萌新联赛第(二)场:河南理工大学 C - 斩龙
CSAPP:cap2
在信息技术下的创客教育新型研究
y71.第四章 Prometheus大厂监控体系及实战 -- prometheus server安装(二)
VS2017 30天试用结束后无法使用,登录界面卡主问题
Dest0g3 520迎新赛-web-funny_upload